Abstract
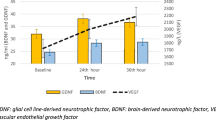
Rats were subjected to nonselective sleep disturbance for short periods under conditions designed to minimize the adverse influence of external stresses, such as environmental conditions and restricted movement, and both brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and its mRNA levels in the brain were then determined to investigate the influence of sleep disturbance itself on BDNF gene expression. Total sleep duration was partially but significantly reduced by disturbing the sleep/wake cycle for 1 and 2 h, gradually increased according to the time of disturbance, then returned to control levels at 6 h after the beginning of sleep disturbance. Under these conditions, the slight but significant elevation of corticotrophin-releasing factor (CRF) mRNA levels in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) was observed at an early stage of the sleep disturbance period. Sleep disturbance induced the elevation of both BDNF protein and its mRNA levels in the hippocampus but not in the cerebellum or the brainstem, and the elevated BDNF mRNA expression in the hippocampus returned toward basal levels during the sleep recovery period when the rebound of sleep duration was observed. These findings suggest the possibility that short-term disturbance of the sleep/wake cycle and, hence, the partial reduction of non-REM sleep duration, might exert a potential influence on neuronal and/or glial cells as an internal stressor, resulting in the elevation of BDNF gene expression in rat hippocampus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aliaga E., Arancibia S., Givalois L., and Tapia-Arancibia L. (2002) Osmotic stress increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA expression in the hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus with differential regulation of its transcripts. Relation to arginine-vasopressin content. Neuroscience 112, 841–850.
Barde Y. A. (1990) The nerve growth factor family. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 2, 237–248.
Bolton M. M., Pittman A. J., and Lo D. C. (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor differentially regulates excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in hippocampal cultures. J. Neurosci. 20, 3221–3232.
Bova R., Micheli M. R., Qualadrucci P., and Zucconi G. G. (1998) BDNF and trkB mRNAs oscillate in rat brain during the light-dark cycle. Mol. Brain Res. 57, 321–324.
Bradford M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Chao H. M., Sakai R. R., Ma L. Y., and McEwen B. S. (1998) Adrenal steroid regulation of neurotrophic factor expression in the rat hippocampus. Endocrinology 139, 3112–3118.
Chomczynski P. and Sacchi N. (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159.
Cirelli C. and Tononi G. (2000a) Differential expression of plasticity-related genes in waking and sleep and their regulation by the noradrenergic system. J. Neurosci. 20, 9187–9194.
Cirelli C. and Tononi G. (2000b) Gene expression in the brain across the sleep-waking cycle. Brain Res. 885, 303–321.
Givalois L., Marmigere F., Rage F., Arancibia S., and Tapia-Arancibia L. (2001) Immobilization stress rapidly and differentially modulates BDNF and TrkBmRNA expression in the pituitary gland of adult male rats. Neuroendocrinology 74, 148–159.
Graves L., Pack A. and Abel T. (2001) Sleep and memory: a molecular perspective. Trends Neurosci. 24, 237–243.
Hall J., Thomas K. L., and Everitt B. J. (2000) Rapid and selective induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during contextual learning. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 533–535.
Kang H. and Schuman E. M. (1995) Long-lasting neurotrophin-induced enhancement of synaptic transmission in the adult hippocampus. Science 267, 1658–1662.
Kesslak J. P., So V., Choi J., Cotman C. W., and Gomez-Pinilla F. (1998) Learning upregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger ribonucleic acid: a mechanism to facilitate encoding and circuit maintenance? Behav. Neurosci. 112, 1012–1019.
Klein R., Smeyne R. J., Wurst W., Long L. K., Auerbach B. A., Joyner A. L., and Barbacid M. (1993) Targeted disruption of the trkB neurotrophin receptor gene results in nervous system lesions and neonatal death. Cell 75, 113–122.
Kushikata T., Fang J., and Krueger J. M. (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances spontaneous sleep in rats and rabbits. Am. J. Physiol. 276, R1334-R1338.
Lessmann V., Gottmann K., and Heumann R. (1994) BDNF and NT-4/5 enhance glutamatergic synaptic transmission in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuroreport 6, 21–25.
Levine E. S., Dreyfus C. F., Black I. B., and Plummer M. R. (1995) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor rapidly enhances synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons via postsynaptic tyrosine kinase receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8074–8077.
Lindsay R. M., Thoenen H., and Barde Y. A. (1985) Placode and neural crest-derived sensory neurons are responsive at early developmental stages to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Dev. Biol. 112, 319–328.
Linnarsson S., Bjuörklund A. and Ernfors P. (1997) Learning deficit in BDNF mutant mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 9, 2581–2587.
Ma Y. L., Wang H. L., Wu H. C., Wei C. L., and Lee E. H. Y. (1998) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor antisense oligonucleotide impairs memory retention and inhibits long-term potentiation in rats. Neuroscience 82, 957–967.
Maquet P. (2001) The role of sleep in learning and memory. Science 294, 1048–1052.
Mizuno M., Yamade K., Olariu A., Nawa H., and Nabeshima T. (2000) Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test in rats. J. Neurosci. 20, 7116–7121.
Morita K., Tsuruo Y., Ishimura Y., Her S., Bell R. A., and Wong D. L. (1999) Influence of serum-free culture conditions on steroid 5α-reductase mRNA expression in rat C6 glioma cells. Brain Res. 830, 179–182.
Mu J.-S., Li W.-P., Yao Z.-B., and Zhou X.-F. (1999) Deprivation of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor results in impairment of spatial learning and memory in adult rats. Brain Res. 835, 259–265.
Peyron C., Wurts S. W., Srere H. K., Heller H. C., Edgar D. M., and Kilduff T. S. (1998) mRNA levels of brain derived neurotrophic factor increases in several brain regions after sleep deprivation. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 24, 1430.
Schaaf M. J., de Jong J., de Kloet E. R., and Vreugdenhil E. (1998) Downregulation of BDNF mRNA and protein in the rat hippocampus by corticosterone. Brain Res. 813, 112–120.
Schaaf M. J., de Kloet E. R., and Vreugdenhil E. (2000a) Corticosterone effects on BDNF expression in the hippocampus. Implication for memory formation. Stress 3, 201–208.
Schaaf M. J., Duurland R., de Klot E. R., and Vreugdenhil E. (2000b) Circadian variation of BDNF mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus. Mol. Brain Res. 75, 342–344.
Schaaf M. J., Hoetelmans R. W. M., de Kloet E. R., and Vreugdenhil E. (1997) Corticosterone regulates expression of BDNF and trkB mRNA but not NT-3 and trkC mRNA in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 48, 334–341.
Sei H., Fujihara H., Ueta Y., Morita K., Kitahama K., and Morita Y. (2003) Single eight-hour shift of lightdark cycle increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels in the rat hippocampus. Life Sci. 73, 53–59.
Sei H., Saitoh D., Yamamoto K., Morita K., and Morita Y. (2000) Differential effect of short-term REM sleep deprivation on NGF and BDNF protein levels in the rat brain. Brain Res. 877, 387–390.
Siegel J. M. (2001) The REM sleep-memory consolidation hypothesis. Science 294, 1058–1063.
Smith M., Makino S., Kvetnansky R., and Post R. M. (1995a) Stress and glucocorticoids affect the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 mRNAs in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 15, 1768–1777.
Smith M. A., Makino S., Kim S. Y., and Kvetnansky R. (1995b) Stress increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger ribonucleic acid in the hypothalamus and pituitary. Endocrinology 136, 3743–3750.
Sobue G., Yamamoto M., Doyu M., Li M., Yasuda T., and Mitsuma T. (1998) Expression of mRNAs for neurotrophins (NGF, BDNF, and NT-3) and their receptors (p75NGFR, trk, trkB, and trkC) in human peripheral neuropathies. Neurochem. Res. 23, 821–829.
Stickgold R., Hobson J. A., Fosse R., and Fosse M. (2001) Sleep, learning, and dreams: off-line memory reprocessing. Science 294, 1052–1057.
Suchecki D., Lobo L. L., Hipólide D. C., and Tufik S. (1998) Increased ACTH and corticosterone secretion induced by different methods of paradoxical sleep deprivation. J. Sleep Res. 7, 276–281.
Taishi P., Sanchez C., Wang Y., Fang J., Harding J. W., and Krueger J. M. (2001) Conditions that affect sleep alter the expression of molecules associated with synaptic plasticity. Am. J. Physiol. 281, R839-R845.
Thoenen H. (1995) Neurotrophins and neuronal plasticity. Science 270, 593–598.
Tononi G. and Cirelli C. (2001) Modulation of brain gene expression during sleep and wakefulness. a review of recent findings. Neuropsychopharmacology 25, S28-S35.
Ueta Y., Levy A., Chowdrey H. S., and Lightman H. S. (1995) Hypothalamic nitric oxide synthase gene expression is regulated by thyroid hormones. Endocrinology 136, 4182–4187.
Ueyama T., Kawai Y., Nemoto K., Sekimoto M., Tone S., and Senba E. (1997) Immobilization stress reduced the expression of neurotrophins and their receptors in the rat brain. Neurosci. Res. 28, 103–110.
Vaidya V. A., Terwilliger R. M., and Duman R. S. (1999) Role of 5-HT2A receptors in the stress-induced down-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rat hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 262, 1–4.
Zhou J., Zhang F., and Zhang Y. (2000) Corticosterone inhibits generation of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slice: involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Brain Res. 885, 182–191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujihara, H., Sei, H., Morita, Y. et al. Short-term sleep disturbance enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in rat hippocampus by acting as internal stressor. J Mol Neurosci 21, 223–231 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:21:3:223
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:21:3:223