Abstract
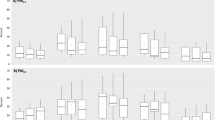
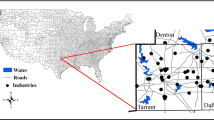
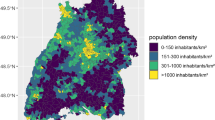
Air quality has emerged as a key determinant of important health outcomes in children and adults. This study aims to identify factors that influence local, within-community air quality, and to build a model for traffic-related air pollution (TRP).We utilized concentrations of NO2, NO, and total oxides of nitrogen (NOx), which were measured at 942 locations in 12 southern California communities. For each location, population density, elevation, land-use, and several indicators of traffic were calculated. A spatial random effects model was used to study the relationship of these predictors to each TRP.Variation in TRP was strongly correlated with traffic on nearby freeways and other major roads, and also with population density and elevation. After accounting for traffic, categories of land-use were not associated with the pollutants. Traffic had a larger relative impact in small urban (low regional pollution) communities than in large urban (high regional pollution) communities. For example, our best fitting model explained 70% of the variation in NOx in large urban areas and 76% in small urban areas. Compared with living at least 1,500 m from a freeway, living within 250 m of a freeway was associated with up to a 41% increase in TRP in a large urban area, and up to a 75% increase in small urban areas.Thus, traffic strongly affects local air quality in large and small urban areas, which has implications for exposure assessment and estimation of health risks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen R.W., Amram O., Wheeler A.J., and Brauer M. The transferability of NO and NO2 land use regression models between cities and pollutants. Atmos Environ 2011: 45 (2): 369–378.
Beckerman B., Jerrett M., Brook J.R., Verma D.K., Arain M.A., and Finkelstein M.M. Correlation of nitrogen dioxide with other traffic pollutants near a major expressway. Atmos Environ 2008: 42: 275–290.
Benson P. CALINE4--A Dispersion Model for Predicting Air Pollutant Concentrations Near Roadways, Report No. FHWA/CA/TL-84/15, California Department of Transportation, Sacramento, CA, 1989.
Brauer M., Hoek G., Van Vliet P., Meliefste K., Fischer P.H., and Wijga A., et al. Air pollution from traffic and the development of respiratory infections and asthmatic and allergic symptoms in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002: 166 (8): 1092–1098.
Briggs D., de Hoogh C., Gulliver J., Elliotta P., Kingham S., and Smallboned K. A regression-based method for mapping traffic-related air pollution: application and testing in four contrasting urban environments. Sci Total Environ 2000: 253 (1-3): 151–167.
Brunekreef B., Janssen N., de Hartog J., Harssema H., Knape M., and van Vliet P. Air pollution from truck traffic and lung function in children living near motorways. Am J Epidemiol 1997: 8: 298–303.
California Air Resources Board. User's Guide to EMFAC2007, Version 2.30. Calculating Emission Inventories For Vehicles In California. CARB, Sacramento, CA, 2007.
Caltrans, 2008. Caltrans 2007 California Motor Vehicle Stock, Travel and Fuel Forecast. California Department of Transportation, Sacramento, CA, May 2008.
Chinkin L.R., Main H.H., and Roberts P.T. Weekday/weekend Ozone Observations In The South Coast Air Basin Volume III: Analysis Of Summer 2000 Field Measurements And Supporting Data Final report STI-999670-2124-FR Sonoma Technology, Inc., Petaluma, CA, 2002.
Cyrys J., Hochadel M., Gehring U., Hoek G., Diegmann V., and Brunekreef B. . et al. GIS-based estimation of exposure to particulate matter and NO2 in an urban area: stochastic versus dispersion modeling. Environ Health Perspect 2005: 113 (8): 987–992.
Delfino R.J. Epidemiologic evidence for asthma and exposure to air toxics: linkages between occupational, indoor, and community air pollution research. Environ Health Perspect 2002: 110 (Suppl 4): 573–589.
Dijkema M.B.A., Gehring U., van Strien R.T., van der Zee S.C., Fischer P., and Hoek G., et al. A comparison of different approaches to estimate small scale spatial variation in outdoor NO2 concentrations. Environ Health Perspect 2010: 119 (5): 670–675.
Dockery D., Cunningham J., Damokosh A., Neas L., Spengler J., and Koutrakis P., et al. Health effects of acid aerosols on North American children: respiratory symptoms. Environ Health Perspect 1996: 104: 500–505.
Dockery D.W., Pope 3rd C.A., Xu X., Spengler J.D., Ware J.H., and Fay M.E., et al. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N Engl J Med 1993: 329 (24): 1753–1759.
Edwards J., Walters S., and Griffiths R.K. Hospital admissions for asthma in preschool children: relationship to major roads in Birmingham, United Kingdom. Arch Environ Health 1994: 49 (4): 223–227.
Gauderman W.J., Avol E., Gilliland F., Vora H., Thomas D., and Berhane K., et al. The effect of air pollution on lung development from 10 to 18 years of age. N Engl J Med 2004: 351 (11): 1057–1067.
Gauderman W.J., Avol E., Lurmann F., Kuenzli N., Gilliland F., and Peters J., et al. Childhood asthma and exposure to traffic and nitrogen dioxide. Epidemiology 2005: 16 (6): 737–743.
Gauderman W.J., Vora H., McConnell R., Berhane K., Gilliland F., and Thomas D., et al. Effect of exposure to traffic on lung development from 10 to 18 years of age: a cohort study. Lancet 2007: 369 (9561): 571–577.
Gilbert N.L., Woodhouse S., Stieb D.M., and Brook J.R. Ambient nitrogen dioxide and distance from a major highway. Sci Total Environ 2003: 312: 43–46.
Gotschi T., Sunyer J., Chinn S., de Marco R., Forsberg B., and Gauderman J.W., et al. Air pollution and lung function in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey. Int J Epidemiol 2008: 37 (6): 1349–1358.
Hart J.E., Yanosky J.D., Puett R.C., Ryan L., Dockery D.W., and Smith T.J., et al. Spatial modeling of PM10 and NO2 in the continental United States, 1985–2000. Environ Health Perspect 2009: 117: 1690–1696.
Health Effects Institute, Special Report. Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure, and Health Effects. HEI, Boston, MA, 2010.
Hirsch T., Weiland S.K., von Mutius E., Safeca A.F., Grafe H., and Csaplovics E., et al. Inner city air pollution and respiratory health and atopy in children. Eur Respir J 1999: 14 (3): 669–677.
Hoek G., Beelen R., de Hoogh K., Vienneau D., Gulliver J., and Fischer P., et al. A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos Environ 2008: 42: 7561–7578.
Kan H., Heiss G., Rose K.M., Whitsel E.A., Lurmann F., and London S.J. Prospective analysis of traffic exposure as a risk factor for incident coronary heart disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Environ Health Perspect 2008: 116: 1463–1468.
Kim J., Smorodinsky S., Lipsett M., Singer B.C., Hodgson A.T., and Ostro B. Traffic-related air pollution near busy roads: the East Bay Children's Respiratory Health Study. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2004: 170: 520–526.
Koutrakis P., Wolfson J.M., Bunyaviroch A., and Froehlich S.A. Passive Ozone Sampler Based On A Reaction with Nitrite. Health Effects Institute, Boston, MA, 1994, 19–47.
Marshall J., Nethery E., and Brauer M. Within-urban variability in ambient air pollution: comparison of estimation methods. Atmos Environ 2008: 42: 1359–1369.
McConnell R., Berhane K., Gilliland F., London S.J., Vora H., and Avol E., et al. Air pollution and bronchitic symptoms in Southern California children with asthma. Environ Health Perspect 1999: 107 (9): 757–760.
McConnell R., Berhane K., Gilliland F., Molitor J., Thomas D., and Lurmann F., et al. Prospective study of air pollution and bronchitic symptoms in children with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003: 168 (7): 790–797.
McConnell R., Berhane K., Lurmann F., Molitor J., Gauderman W., and Avol E., et al. Traffic and asthma prevalence in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002: 165: A492.
McConnell R., Berhane K., Yao L., Jerrett M., Lurmann F., and Gilliland F., et al. Traffic, susceptibility, and childhood asthma. Environ Health Perspect 2006: 114 (5): 766–772.
Nicolai T., Carr D., Weiland S.K., Duhme H., von Ehrenstein O., and Wagner C., et al. Urban traffic and pollutant exposure related to respiratory outcomes and atopy in a large sample of children. Eur Respir J 2003: 21 (6): 956–963.
Peters A. Air quality and cardiovascular health: smoke and pollution matter. Circulation 2009: 120 (11): 924–927.
Peters J.M., Avol E., Navidi W., London S.J., Gauderman W.J., and Lurmann F., et al. A study of twelve Southern California communities with differing levels and types of air pollution. I. Prevalence of respiratory morbidity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999: 159 (3): 760–767.
Poplawski K., Gould T., Setton E., Allen R., Su J., and Larson T., et al. Intercity transferability of land use regression models for estimating ambient concentrations of nitrogen dioxide. J Expos Sci Environ Epidemiol 2008: 19: 107–117.
Roorda-Knape M.C., Janssen N.A.H., de Hartog J.J., Van Vliet P.H.N., Harssema H., and Brunekreef B. Air pollution from traffic in city districtc near major motorways. Atmos Environ 1998: 32 (11): 1921–1930.
Skene K.J., Gent J.F., McKay L.A., Belanger K., Leaderer B.P., and Holford T.R. Modeling effects of traffic and landscape characteristics on ambient nitrogen dioxide levels in Connecticut. Atmos Environ 2010: 44 (39): 5156–5164.
US Environmental Protection Agency. Strengthened National Standards for Nitrogen Dioxide, http://www.epa.gov/airquality/nitrogenoxides/actions.html.USEPA, Research Triangle Park, NC, 2010.
Venn A., Lewis S., Cooper M., Hubbard R., Hill I., and Boddy R., et al. Local road traffic activity and the prevalence, severity, and persistence of wheeze in school children: combined cross sectional and longitudinal study. Occup Environ Med 2000: 57 (3): 152–158.
Venn A.J., Lewis S.A., Cooper M., Hubbard R., and Britton J. Living near a main road and the risk of wheezing illness in children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001: 164 (12): 2177–2180.
Vienneau D., de Hoogh K., Beelen R., Fischer P., Hoek G., and Briggs D. Comparison of land-use regression models between Great Britain and the Netherlands. Atmos Environ 2010: 44 (5): 688–696.
Waller L., and Gotway C. Applied Spatial Statistics for Public Health Data. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2004.
Wu J., Funk T., Lurmann F., and Winer A.M. Improving spatial accuracy of roadway networks and geocoded addresses. Trans GIS 2005: 9 (4): 585–601.
Zhou Y., and Levy J.I. Factors influencing the spatial extent of mobile source air pollution impacts: A meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2007: 7: 89.
Zhu Y., Hinds W.C., Kim S., and Sioutas C. Concentration and size distribution of ultrafine particles near a major highway. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 2002: 52 (9): 1032–1042.
Zhu Y., Kuhn T., Mayo P., and Hinds W.C. Comparison of daytime and nighttime concentration profiles and size distributions of ultrafine particles near a major highway. Environ Sci Technol 2006: 40: 2531–2536.
Zmirou D., Gauvin S., Pin I., Momas I., Sahraoui F., and Just J., et al. Traffic related air pollution and incidence of childhood asthma: results of the Vesta case-control study. J Epidemiol Community Health 2004: 58: 18–23.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by research NIEHS Grants P30ES007048, U01ES015090, and R01ES016813 and NHLBI Grants R01HL087680 and RC2HL101651.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franklin, M., Vora, H., Avol, E. et al. Predictors of intra-community variation in air quality. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 22, 135–147 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2011.45
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2011.45
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Preparation and performance of photocatalytic NO degradation superhydrophobic coatings for tunnel
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2022)
-
Childhood traffic-related air pollution and adverse changes in subclinical atherosclerosis measures from childhood to adulthood
Environmental Health (2021)