Abstract
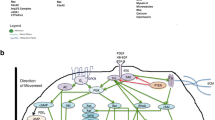
Inflammatory mediators play a critical role in the pathogenesis of chronic airway diseases and facilitate the recruitment, activation, and trafficking of inflammatory cells in the airways. Compelling evidence now shows that airway smooth muscle expresses adhesion molecules and secretes inflammatory mediators. Airway myocytes also express a repertoire of immunomodulatory proteins such as Toll-like receptors, chemokines, and cytokines. The underlying mechanisms by which these molecules modulate airway inflammation and the physiological consequences of these molecules are now being elucidated, suggesting that airway smooth muscle plays an important role in orchestrating and perpetuating airway inflammation, remodeling, and fibrosis in chronic airway diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Wegner CD, Gundel RH, Reilly P, et al.: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Science 1990, 247:456–459.
Lazaar AL, Albelda SM, Pilewski JM, et al.: T lymphocytes adhere to airway smooth muscle cells via integrins and CD44 and induce smooth muscle cell DNA synthesis. J Exp Med 1994, 180:807–816.
Ramos-Barbon D, Presley JF, Hamid QA, et al.: Antigen-specific CD4 + T cells drive airway smooth muscle remodeling in experimental asthma. J Clin Invest 2005, 115:1580–1589.
Beck-Schimmer B, Schimmer RC, Warner RL, et al.: Expression of lung vascular and airway ICAM-1 after exposure to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997, 17:344–352.
Panettieri RA, Jr., Lazaar AL, Puré E, et al.: Activation of cAMP-dependent pathways in human airway smooth muscle cells inhibits TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression and T lymphocyte adhesion. J Immunol 1995, 154:2358–2365.
Hughes JM, Arthur CA, Baracho S, et al.: Human eosinophil-airway smooth muscle cell interactions. Mediators Inflamm 2000, 9:93–99.
Lee CW, Lin WN, Lin CC, et al.: Transcriptional regulation of VCAM-1 expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human tracheal smooth muscle cells: involvement of MAPKs, NF-kappaB, p300, and histone acetylation. J Cell Physiol 2006, 207:174–186.
Braun-Fahrlander C, Riedler J, Herz U, et al.: Environmental exposure to endotoxin and its relation to asthma in school-age children. N Engl J Med 2002, 347:869–877.
Luo SF, Wang CC, Chiu CT, et al.: Lipopolysaccharide enhances bradykinin-induced signal transduction via activation of Ras/Raf/MEK/MAPK in canine tracheal smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 2000, 130:1799–1808.
Sukkar MB, Xie S, Khorasani NM, et al.: Toll-like receptor 2, 3, and 4 expression and function in human airway smooth muscle. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006, 118:641–648.
Morris GE, Whyte MK, Martin GF, et al.: Agonists of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 activate airway smooth muscle via mononuclear leukocytes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005, 171:814–822.
Bachar O, Adner M, Uddman R, et al.: Toll-like receptor stimulation induces airway hyper-responsiveness to brady-kinin, an effect mediated by JNK and NF-kappa B signaling pathways. Eur J Immunol 2004, 34:1196–1207.
Morris GE, Parker LC, Ward JR, et al.: Cooperative molecular and cellular networks regulate Toll-like receptor-dependent inflammatory responses. FASEB J 2006, 20:2153–2155.
Oliver BG, Johnston SL, Baraket M, et al.: Increased proinflammatory responses from asthmatic human airway smooth muscle cells in response to rhinovirus infection. Respir Res 2006, 7:71.
Gonzalo JA, Lloyd CM, Wen D, et al.: The coordinated action of CC chemokines in the lung orchestrates allergic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness. J Exp Med 1998, 188:157–167.
Wegmann M, Goggel R, Sel S, et al.: Effects of a low-molecular-weight CCR-3 antagonist on chronic experimental asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2007, 36:61–67.
Berkman N, Krishnan VL, Gilbey T, et al.: Expression of RANTES mRNA and protein in airways of patients with mild asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996, 154:1804–1811.
El-Shazly A, Berger P, Girodet PO, et al.: Fraktalkine produced by airway smooth muscle cells contributes to mast cell recruitment in asthma. J Immunol 2006, 176:1860–1868.
Sousa AR, Lane SJ, Nakhosteen JA, et al.: Increased expression of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in bronchial tissue from asthmatic subjects. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1994, 10:142–147.
Brightling CE, Ammit AJ, Kaur D, et al.: The CXCL10/CXCR3 axis mediates human lung mast cell migration to asthmatic airway smooth muscle. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005, 171:1103–1108.
Li D, Wang D, Griffiths-Johnson DA, et al.: Eotaxin protein and gene expression in guinea-pig lungs: constitutive expression and upregulation after allergen challenge. Eur Respir J 1997, 10:1946–1954.
Lazaar AL, Panettieri RA Jr: Airway smooth muscle as a regulator of immune responses and bronchomotor tone. Clin Chest Med 2006, 27:53–69.
Molet S, Hamid Q, Davoine F, et al.: IL-17 is increased in asthmatic airways and induces human bronchial fibroblasts to produce cytokines. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001, 108:430–438.
Wuyts WA, Vanaudenaerde BM, Dupont LJ, et al.: Interleukin-17-induced interleukin-8 release in human airway smooth muscle cells: role for mitogen-activated kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005, 24:875–881.
Rahman MS, Yamasaki A, Yang J, et al.: IL-17A induces eotaxin-1/CC chemokine ligand 11 expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: role of MAPK (Erk1/2, JNK, and p38) pathways. J Immunol 2006, 177:4064–4071.
Zuyderduyn S, Ninaber DK, Hiemstra PS, et al.: The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 enhances IL-8 release by human airway smooth muscle cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006, 117:1328–1335.
Chan V, Burgess JK, Ratoff JC, et al.: Extracellular matrix regulates enhanced eotaxin expression in asthmatic airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006, 174:379–385.
Peng Q, Lai D, Nguyen TT, et al.: Multiple beta 1 integrins mediate enhancement of human airway smooth muscle cytokine secretion by fibronectin and type I collagen. J Immunol 2005, 174:2258–2264.
Imai T, Hieshima K, Haskell C, et al.: Identification and molecular characterization of fractalkine receptor CX3CR1, which mediates both leukocyte migration and adhesion. Cell 1997, 91:521–530.
Tliba O, Panettieri RA Jr, Tliba S, et al.: TNF-α differentially regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory genes in human airway smooth muscle cells by activation of IFN-β-dependent CD38 pathway. Mol Pharmacol 2004, 66:322–329.
Hardaker EL, Bacon AM, Carlson K, et al.: Regulation of TNF-α-and IFN-γ-induced CXCL10 expression: participation of the airway smooth muscle in the pulmonary inflammatory response in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. FASEB J 2004, 18:191–193.
Sukkar MB, Issa R, Xie S, et al.: Fractalkine/CX3CL1 production by human airway smooth muscle cells: induction by IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha and regulation by TGF-beta and corticosteroids. Am J Physiol (Lung Cell Mol Physiol) 2004, 287:L1230–L1240.
John M, Hirst SJ, Jose PJ, et al.: Human airway smooth muscle cells express and release RANTES in response to T helper 1 cytokines. Regulation by T helper 2 cytokines and corticosteroids. J Immunol 1997, 158:1841–1847.
Tliba O, Tliba S, Huang CD, et al.: TNFα modulates airway smooth muscle function via the autocrine action of IFNβ. J Biol Chem 2003, 278:50615–50623.
Keslacy S, Tliba O, Baidouri H, et al.: Inhibition of TNFα-inducible inflammatory genes by IFNγ is associated with altered NF-κB transactivation and enhanced HDAC activity. Mol Pharmacol 2007, 71:609–618.
Wen FQ, Liu X, Manda W, et al.: TH2 Cytokine-enhanced and TGF-β-enhanced vascular endothelial growth factor production by cultured human airway smooth muscle cells is attenuated by IFN-γ and corticosteroids. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003, 111:1307–1318.
Lajoie-Kadoch S, Joubert P, Letuve S, et al.: TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma inversely modulate expression of the IL-17E receptor in airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol (Lung Cell Mol Physiol) 2006, 290:L1238–L1246.
Pujols L, Mullol J, Torrego A, et al.: Glucocorticoid receptors in human airways. Allergy 2004, 59:1042–1052.
Ammit AJ, Lazaar AL, Irani C, et al.: Tumor necrosis factor-α-induced secretion of RANTES and interleukin-6 from human airway smooth muscle cells: modulation by glucocorticoids and β-agonists. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002, 26:465–474.
Amrani Y, Lazaar AL, Panettieri RA Jr: Up-regulation of ICAM-1 by cytokines in human tracheal smooth muscle cells involves an NF-κB—dependent signaling pathway that is only partially sensitive to dexamethasone. J Immunol 1999, 163:2128–2134.
Pang L, Knox AJ: Regulation of TNF-α-induced eotaxin release from cultured human airway smooth muscle cells by β2-agonists and corticosteroids. FASEB J 2001, 115:261–269.
Tliba O, Cidlowski JA, Amrani Y: CD38 expression is insensitive to steroid action in cells treated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma by a mechanism involving the up-regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor beta isoform. Mol Pharmacol 2006, 69:588–596.
Tran T, Fernandes DJ, Schuliga M, et al.: Stimulus-dependent glucocorticoid-resistance of GM-CSF production in human cultured airway smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 2005, 145:123–131.
Adcock IM, Gilbey T, Gelder CM, et al.: Glucocorticoid receptor localization in normal and asthmatic lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996, 154:771–782.
Roth M, Johnson PR, Borger P, et al.: Dysfunctional interaction of C/EBPalpha and the glucocorticoid receptor in asthmatic bronchial smooth-muscle cells. N Engl J Med 2004, 351:560–574.
Roth M, Johnson PR, Rudiger JJ, et al.: Interaction between glucocorticoids and beta2 agonists on bronchial airway smooth muscle cells through synchronised cellular signalling. Lancet 2002, 360:1293–1299.
Adcock IM, Ito K: Steroid resistance in asthma: a major problem requiring novel solutions or a non-issue? Curr Opin Pharmacol 2004, 4:257–262.
Miller M, Cho JY, McElwain K, et al.: Corticosteroids prevent myofibroblast accumulation and airway remodeling in mice. Am J Physiol (Lung Cell Mol Physiol) 2006, 290:L162–L169.
Bonacci JV, Schuliga M, Harris T, et al.: Collagen impairs glucocorticoid actions in airway smooth muscle through integrin signalling. Br J Pharmacol 2006, 149:365–373.
Oakley RH, Sar M, Cidlowski JA: The human glucocorticoid receptor beta isoform. Expression, biochemical properties, and putative function. J Biol Chem 1996, 271:9550–9559.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tliba, O., Panettieri, R.A. Regulation of inflammation by airway smooth muscle. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 8, 262–268 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-008-0043-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-008-0043-5