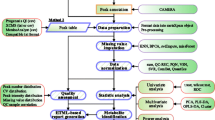
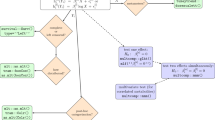
Many metabolomics, and other high-content or high-throughput, experiments are set up such that the primary aim is the discovery of biomarker metabolites that can discriminate, with a certain level of certainty, between nominally matched ‘case’ and ‘control’ samples. However, it is unfortunately very easy to find markers that are apparently persuasive but that are in fact entirely spurious, and there are well-known examples in the proteomics literature. The main types of danger are not entirely independent of each other, but include bias, inadequate sample size (especially relative to the number of metabolite variables and to the required statistical power to prove that a biomarker is discriminant), excessive false discovery rate due to multiple hypothesis testing, inappropriate choice of particular numerical methods, and overfitting (generally caused by the failure to perform adequate validation and cross-validation). Many studies fail to take these into account, and thereby fail to discover anything of true significance (despite their claims). We summarise these problems, and provide pointers to a substantial existing literature that should assist in the improved design and evaluation of metabolomics experiments, thereby allowing robust scientific conclusions to be drawn from the available data. We provide a list of some of the simpler checks that might improve one’s confidence that a candidate biomarker is not simply a statistical artefact, and suggest a series of preferred tests and visualisation tools that can assist readers and authors in assessing papers. These tools can be applied to individual metabolites by using multiple univariate tests performed in parallel across all metabolite peaks. They may also be applied to the validation of multivariate models. We stress in particular that classical p-values such as “p < 0.05”, that are often used in biomedicine, are far too optimistic when multiple tests are done simultaneously (as in metabolomics). Ultimately it is desirable that all data and metadata are available electronically, as this allows the entire community to assess conclusions drawn from them. These analyses apply to all high-dimensional ‘omics’ datasets.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaans P., Zantinge D. (1996) Data Mining. Addison-Wesley, Harlow, Essex
Alsberg B.K., Kell D.B., Goodacre R. (1998) Variable selection in discriminant partial least-squares analysis. Anal. Chem. 70: 4126–4133
Alsberg B.K., Woodward A.M., Winson M.K., Rowland J., Kell D.B. (1997) Wavelet denoising of infrared spectra. Analyst 122: 645–652
Altman D.G. (2001) Systematic reviews of evaluations of prognostic variables. BMJ 323: 224–228
Altman D.G., Deeks J.J. (2002) Meta-analysis, Simpson’s paradox, and the number needed to treat. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2: 3
Anthony M., Biggs N. (1992) Computational Learning Theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Baggerly K.A., Morris J.S., Coombes K.R. (2004) Reproducibility of SELDI-TOF protein patterns in serum: comparing datasets from different experiments. Bioinformatics 20: 777–785
Baker S.G. (2003) The central role of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves in evaluating tests for the early detection of cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 95: 511–515
Baldi P., Long A.D. (2001) A Bayesian framework for the analysis of microarray expression data: regularized t-test and statistical inferences of gene changes. Bioinformatics 17: 509–519
Barrow J.D., Silk J. (1995) The Left Hand of Creation: The Origin and Evolution of The Expanding Universe. Penguin, London
Bellman R. (1961) Adaptive Control Processes: A Guided Tour. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate – a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B Met. 57: 289–300
Bennett K., Demiriz A. (1998) Semi-supervised support vector machines. Adv. Neural Inf. Proc. Syst. 12: 368–374
Bernardo J.M., Smith A.F.M. (2000) Bayesian Theory. Wiley, Chichester
Berry D.A. (1996) Statistics: A Bayesian Perspective. Duxbury Press, Belmont
Berry M.J.A., Linoff G.S. (2000) Mastering the Art of Data Mining. Wiley, New York
Bezdek J.C. and Pal, S.K. (Eds) (1992). Fuzzy Models for Pattern recognition: Methods That Search for Structures In Data. IEEE Press., New York
Bland J.M., Altman D.G. (1995) Multiple significance tests: the Bonferroni method. BMJ 310: 170
Bland M. (2000) An Introduction to Medical Statistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Box G.E.P., Hunter W.G., Hunter J.S. (1978) Statistics for Experimenters. Wiley, New York
Bradford Hill A., Hill I.D. (1991) Bradford Hill’s Principles of medical statistics 12. Edward Arnold, London
Breiman L. (1966) The heuristics of instability in model selection. Ann. Statist. 24: 2350–2381
Breiman L. (2001) Statistical modeling: The two cultures. Stat. Sci. 16: 199–215
Brenner H., Gefeller O. (1997) Variation of sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios and predictive values with disease prevalence. Stat. Med. 16: 981–91
Brent R. (1999) Functional genomics: learning to think about gene expression data. Curr. Biol. 9: R338–R341
Brent R. (2000) Genomic biology. Cell 100: 169–183
Brent R., Lok L. (2005) A fishing buddy for hypothesis generators. Science 308: 504–506
Brereton R.G. (2003) Chemometrics: Data Analysis for the Laboratory and Chemical Plant. Wiley, New York
Broadhurst D., Goodacre R., Jones A., Rowland J.J. Kell D.B. (1997) Genetic algorithms as a method for variable selection in multiple linear regression and partial least squares regression, with applications to pyrolysis mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta. 348: 71–86
Brown M., Dunn W.B., Ellis D.I., Goodacre R., Handl J., Knowles J.D., O’Hagan S., Spasic I., Kell D.B. (2005) A metabolome pipeline: from concept to data to knowledge. Metabolomics 1: 35–46
Cabena P., Hadjinian P., Stadler R., Verhees J., Zanasi A. (1998) Discovering Data Mining: From Concept to Implementation. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Camacho D., de la Fuente A., Mendes P. (2005) The origins of correlations in metabolomics data. Metabolomics 1: 53–63
Cascante M., Boros L.G., Comin-Anduix B., de Atauri P., Centelles J.J., Lee P.W. (2002) Metabolic control analysis in drug discovery and disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 20: 243–249
Casella G., Berger R.L. (2002) Statistical Inference, 2. Duxbury, Pacific Grove, CA
Catchpole G.S., Beckmann M., Enot D.P., Mondhe M., Zywicki B., Taylor J., Hardy N., Smith A., King R.D., Kell D.B., Fiehn O., Draper J. (2005) Hierarchical metabolomics demonstrates substantial compositional similarity between genetically modified and conventional potato crops. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102: 14458–14462
Chatfield C. (1995) Model uncertainty, data mining and statistical inference. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 158: 419–466
Chen M., Hofestädt R. (2006) A medical bioinformatics approach for metabolic disorders: biomedical data prediction, modeling, and systematic analysis. J. Biomed. Inform. 39: 147–159
Chen V.C.P., Tsui K.L., Barton R.R., Meckesheimer M. (2006) A review on design, modeling and applications of computer experiments. IIE Trans. 38: 273–291
Cleveland W.S. (1993) Visualizing Data. Hobart Press, Summit, NJ
Cleveland W.S. (1994) The Elements of Graphing Data. Hobart Press, Summit, NJ
Coello Coello C.A., van Veldhuizen D.A., Lamont G.B. (2002) Evolutionary Algorithms for Solving Multi-Objective Problems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York
Conover W.J. (1980) Practical Nonparametric Statistics. Wiley, New York
Cook R.J., Farewell V.T. (1996) Multiplicity considerations in the design and analysis of clinical trials. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. A 159: 93–110
Cornfield J. (1966) Sequential trials, sequential analysis and likelihood rinciple. Am. Stat. 20: 18–23
Cornish-Bowden A., Cárdenas M.L. (2000) From genome to cellular phenotype-a role for metabolic flux analysis? Nat. Biotechnol. 18: 267–269
Crary S.B. (2002) Design of computer experiments for metamodel generation. Analog. Integr. Circ. Sig. Proc. 32: 7–16
Cui X., Churchill G.A. (2003) Statistical tests for differential expression in cDNA microarray experiments. Genome Biol. 4: 210
Dasgupta P., Chakrabarti P.P., DeSarkar S.C. (1999) Multiobjective Heuristic Search. Vieweg, Braunschweig
Deb K. (2001) Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms. Wiley, New York
Deming S.N., Morgan S.L. (1993) Experimental Design: A Chemometric Approach. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Demiriz A., Bennett K., Embrechts M.J. (1999) Semi-supervised clustering using genetic algorithms. In Dagli C.H., Buczak A.L., Ghosh J., Embrechts M.J., Ersoy O. (Eds.), Intelligent Engineering Systems Through Artificial Neural Networks. ASME Press, New York, pp. 809–814
di Bernardo D., Thompson M.J., Gardner T.S., Chobot S.E., Eastwood E.L., Wojtovich A.P., Elliott S.J., Schaus S.E., Collins J.J. (2005) Chemogenomic profiling on a genome-wide scale using reverse-engineered gene networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 23: 377–383
Diamandis E.P. (2004) Analysis of serum proteomic patterns for early cancer diagnosis: drawing attention to potential problems. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 96: 353–356
Duda R.O., Hart P.E., Stork D.E. (2001) Pattern Classification, 2. John Wiley, London
Duesberg P., Stindl R., Hehlmann R. (2000) Explaining the high mutation rates of cancer cells to drug and multidrug resistance by chromosome reassortments that are catalyzed by aneuploidy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 14295–14300
Eades P. (1984) A heuristic for graph drawing. Congressus Numerantium 42: 149–160
Ebbels T.M.D., Buxton B.F., Jones D.T. (2006) springScape: visualisation of microarray and contextual bioinformatic data using spring embedding an ‘information landscape’. Bioinformatics 22, e99–e108
Edwards A.W.F. (1992) Likelihood. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Edwards D. (2000) Introduction to Graphical Modeling. 2nd ed. Springer, Berlin
Efron B., Gong G. (1983) A Leisurely Look at the Bootstrap, the Jackknife, and Cross-Validation. Am. Stat. 37: 36–48
Efron B., Tibshirani R. (2002) Empirical Bayes methods and false discovery rates for microarrays. Genet. Epidemiol. 23: 70–86
Efron B., Tibshirani R.J. (1993) Introduction to the Bootstrap. Chapman and Hall, London
Egan J.P. (1975) Signal Detection Theory and ROC Analysis. Academic Press, New York
Ein-Dor L., Zuk O., Domany E. (2006) Thousands of samples are needed to generate a robust gene list for predicting outcome in cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 103: 5923–5928
Eriksson L., Johansson E., Kettaneh-Wold N., Wold S. (2001) Multi- and Megavariate Data Analysis: Principles and Applications. Umetrics Academy, Umeå
Evans W.E., Johnson J.A. (2001) Pharmacogenomics: the inherited basis for interindividual differences in drug response. Annu. Rev. Genomics. Hum. Genet. 2: 9–39
Evans W.E., Relling M.V. (1999) Pharmacogenomics: translating functional genomics into rational therapeutics. Science 286: 487–491
Evans W.E., Relling M.V. (2004) Moving towards individualized medicine with pharmacogenomics. Nature 429: 464–468
Everitt B.S. (1993) Cluster Analysis. Edward Arnold, London
Farnum M.A., DesJarlais, R. and Agrafiotis, D.K. (2003). Molecular diversity in Gasteiger, J. (Ed.), Handbook of Cheminformatics: vol 4 From Data to Knowledge. Wiley/VCH, Weinheim, pp. 1640–1686
Fell D.A. (1996) Understanding the Control of Metabolism. Portland Press, London
Fielding A.H., Bell J.F. (1997) A review of methods for the assessment of prediction errors in conservation presence/absence models. Environ. Conserv. 24: 38–49
Fortner B. (1995) The Data Handbook. 2nd ed. Springer, New York
Frey H.C., Patil S.R. (2002) Identification and review of sensitivity analysis methods. Risk Anal. 22: 553–578
Friendly M. (2000) Visualising Categorical Data. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Fruchterman T.M.J., Reingold E.M. (1991) Graph Drawing by Force-Directed Placement. Software –practice & experience 21: 1129–1164
Gansner E.R., North S.C. (2000) An open graph visualization system and its applications to software engineering. Software: Practice and Experience 30: 1203–1233
Gardner M.J., Altman D.G. (1989) Statistics with Confidence: Confidence Intervals And Statistical Guidelines. BMJ, London
Gillet V.J., Khatib W., Willett P., Fleming P.J., Green D.V.S. (2002) Combinatorial library design using a multiobjective genetic algorithm. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 42: 375–385
Goble C.A., Stevens R., Ng G., Bechhofer S., Paton N.W., Baker P.G., Peim M., Brass A. (2001) Transparent access to multiple bioinformatics information sources. IBM. Syst. J. 40: 532–551
Goffeau A., Barrell B.G., Bussey H., Davis R.W., Dujon B., Feldmann H., Galibert F., Hoheisel J.D., Jacq C., Johnston M., Louis E.J., Mewes H.W., Murakami Y., Philippsen P., Tettelin H., Oliver S.G. (1996) Life With 6000 Genes. Science 274: 546–567
Golbraikh A., Tropsha A. (2002) Beware of q2!. J. Mol. Graph Model 20: 269–276
Golub T.R., Slonim D.K., Tamayo P., Huard C., Gaasenbeek M., Mesirov J.P., Coller H., Loh M.L., Downing J.R., Caligiuri M.A., Bloomfield C.D., Lander E.S. (1999) Molecular classification of cancer: Class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 286: 531–537
Goodacre R., Kell D.B. (2003) Evolutionary computation for the interpretation of metabolome data. In Harrigan G.G., Goodacre R. (Eds.), Metabolic Profiling: Its Role in Biomarker Discovery and Gene Function Analysis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp. 239–256
Goodacre R., Neal M.J., Kell D.B. (1996) Quantitative analysis of multivariate data using artificial neural networks: a tutorial review and applications to the deconvolution of pyrolysis mass spectra. Z. Bakteriol. 284: 516–539
Goodman S.N., Royall R. (1988) Evidence and scientific research. Am. J. Publ. Health 78: 1568–1574
Greenaway W., May J., Scaysbrook T., Whatley F.R. (1991) Identification by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of 150 compounds in propolis. Z. Naturforsch. C 46: 111–121
Grimes D.S. (2006) Are statins analogues of vitamin D? Lancet 368: 83–6
Hand D., Mannila H., Smyth P. (2001) Principles of Data Mining. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Handl, J., Kell, D.B. and Knowles, J. (2006). Multiobjective optimization in bioinformatics and computational biology. IEEE Trans Comput Biol Bioinformatics (in the press)
Handl, J. and Knowles, J. (2004). Evolutionary Multiobjective Clustering. PPSN VIII, LNCS 3242, 1081–1091 (see http://dbk.ch.umist.ac.uk/Papers/HandlKnowlesPPSN-webversion.pdf)
Handl, J. and Knowles, J. (2006a) An evolutionary approach to multiobjective clustering. IEEE Trans Evol Comput (in press)
Handl, J. and Knowles, J. (2006b). Semi-supervised feature selection via multiobjective optimization. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN 2006). Proc WCCI 2006, IEEE Press, pp. 6351–6358
Handl J., Knowles J., Kell D.B. (2005) Computational cluster validation in post-genomic data analysis. Bioinformatics 21: 3201–3212
Hanley J.A., McNeil B.J. (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143: 29–36
Harrigan G.G., LaPlante R.H., Cosma G.N., Cockerell G., Goodacre R., Maddox J.F., Luyendyk J.P., Ganey P.E., Roth R.A. (2004) Application of high-throughput Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy in toxicology studies: contribution to a study on the development of an animal model for idiosyncratic toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 146: 197–205
Hastie T., Tibshirani R., Friedman J. (2001) The Elements Of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference and Prediction. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Heinrich R., Schuster S. (1996) The Regulation Of Cellular Systems. Chapman & Hall, New York
Hicks C.R., Turner K.V. Jr (1999) Fundamental Concepts in the Design of Experiments. 5th ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hollander M., Wolfe D.A. (1973) Nonparametric Statistical Methods. Wiley, New York
Horchner U., Kalivas J.H. (1995) Further investigation on a comparative study of simulated annealing and genetic algorithm for wavelength selection. Anal. Chim. Acta. 311: 1–13
Horning E.C., Horning M.G. (1971) Metabolic profiles: gas-phase methods for analysis of metabolites. Clin Chem 17: 802–809
Hubert L., Arabie P. (1985) Comparing partitions. J. Classif. 2: 193–218
Hutchinson A. (1994) Algorithmic Learning. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Ioannidis J.P. (2005a) Contradicted and initially stronger effects in highly cited clinical research. JAMA 294: 218–228
Ioannidis J.P. (2005b) Why most published research findings are false. PLoS Med. 2, e124
Ioannidis J.P., Ntzani E.E., Trikalinos T.A., Contopoulos-Ioannidis D.G. (2001) Replication validity of genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 29: 306–309
Ioannidis J.P., Trikalinos T.A. (2005) Early extreme contradictory estimates may appear in published research: the Proteus phenomenon in molecular genetics research and randomized trials. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 58: 543–549
Ioannidis J.P., Trikalinos T.A., Ntzani E.E., Contopoulos-Ioannidis D.G. (2003) Genetic associations in large versus small studies: an empirical assessment. Lancet 361: 567–571
Jarvis R.M., Goodacre R. (2005) Genetic algorithm optimization for pre-processing and variable selection of spectroscopic data. Bioinformatics 21: 860–868
Jellum E., Bjornson I., Nesbakken R., Johansson E., Wold S. (1981) Classification of human cancer cells by means of capillary gas chromatography and pattern recognition analysis. J. Chromatogr. 217: 231–237
Jensen F.V. (2001) Bayesian Networks and Decision Graphs. Springer, Berlin
Jolliffe I.T. (1986) Principal Component Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York
Judson R. (1997) Genetic algorithms and their use in chemistry. Rev. Comput. Chem. 10: 1–73
Jung S.H. (2005) Sample size for FDR-control in microarray data analysis. Bioinformatics 21: 3097–104
Kamada T., Kawai S. (1989) An algorithm for drawing general undirected graphs. Inf .Proc. Lett. 31: 7–15
Kannel W.B. (1995) Range of serum cholesterol values in the population developing coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 76: 69C–77C
Kell D.B. (2002a) Genotype:phenotype mapping: genes as computer programs. Trends. Genet. 18: 555–559
Kell D.B. (2002b) Metabolomics and machine learning: explanatory analysis of complex metabolome data using genetic programming to produce simple, robust rules. Mol. Biol. Rep. 29: 237–41
Kell D.B. (2004) Metabolomics and systems biology: making sense of the soup. Curr. Op. Microbiol. 7: 296–307
Kell D.B. (2006) Metabolomics, modelling and machine learning in systems biology: towards an understanding of the languages of cells . The 2005 Theodor Bücher lecture. FEBS J. 273: 873–894
Kell D.B., Brown M., Davey H.M., Dunn W.B., Spasic I., Oliver S.G. (2005) Metabolic footprinting and Systems Biology: the medium is the message. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3: 557–565
Kell D.B., Darby R.M., Draper J. (2001) Genomic computing: explanatory analysis of plant expression profiling data using machine learning. Plant. Physiol. 126: 943–951
Kell D.B., King R.D. (2000) On the optimization of classes for the assignment of unidentified reading frames in functional genomics programmes: the need for machine learning. Trends Biotechnol. 18: 93–98
Kell D.B., Knowles J.D. (2006) The role of modeling in systems biology. In Szallasi Z., Stelling J., Periwal V. (Eds.), System Modeling in Cellular Biology: From Concepts to Nuts and Bolts. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp. 3–18
Kell D.B., Oliver S.G. (2004) Here is the evidence, now what is the hypothesis? The complementary roles of inductive and hypothesis-driven science in the post-genomic era. Bioessays 26: 99–105
Kell D.B., Sonnleitner B. (1995) GMP - Good Modelling Practice: an essential component of good manufacturing practice. Trends Biotechnol. 13: 481–492
Kell, D.B. and Welch, G.R. (1991). No turning back, Reductonism and Biological Complexity. Times Higher Educational Supplement 9th August, 15
Kell D.B., Westerhoff H.V. (1986) Metabolic control theory: its role in microbiology and biotechnology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 39: 305–320
Kemp, C., Griffiths, T., Stromsten, S. and Tenenbaum, J.B. (2003) Semi-supervised learning with trees. Adv. Neural Inf Proc Syst 16
Kenny, L.C., Dunn, W.B., Ellis, D.I., Myers, J., Baker, P.N., The GOPEC Consortium and Kell, D.B. (2005) Novel biomarkers for pre-eclampsia detected using metabolomics and machine learning. Metabolomics 1, 227–234 - online DOI: 10.1007/s11306–005–0003–1
Kim S.K., Lund J., Kiraly M., Duke K., Jiang M., Stuart J.M., Eizinger A., Wylie B.N., Davidson G.S. (2001) A gene expression map for Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 293: 2087–2092
Kirkwood B.R., Sterne J.A.C. (2003) Essential Medical Statistics. Blackwell, Oxford
Kirschenlohr H.L., Griffin J.L., Clarke S.C., Rhydwen R., Grace A.A., Schofield P.M., Brindle K.M., Metcalfe J.C. (2006) Proton NMR analysis of plasma is a weak predictor of coronary artery disease. Nat. Med. 12: 705–710
Knowles, J.D. and Hughes, E.J. (2005). Multiobjective optimization on a budget of 250 evaluations. Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization (EMO 2005), LNCS 3410, 176–190 http://dbk.ch.umist.ac.uk/knowles/pubs.html
Knowles, J.D., Watson, R.A. and Corne, D.W. (2001). Reducing local optima in single-objective problems by multi-objectivization in E. Zitzler et al., (ed.), Proc. 1st Int. Conf. on Evolutionary Multi-criterion Optimization (EMO’01), Springer, Berlin, pp. 269–283
Kohavi, R. (1995). A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 1137–1143
Kohonen T. (1989) Self-Organization and Associative Memory. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Kose F., Weckwerth W., Linke T., Fiehn O. (2001) Visualizing plant metabolomic correlation networks using clique-metabolite matrices. Bioinformatics 17: 1198–1208
Koza J.R. (1992) Genetic Programming: On The Programming of Computers by Means Of Natural Selection. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass
Koza J.R., Keane M.A., Streeter M.J., Mydlowec W., Yu J., Lanza G. (2003) Genetic Programming: Routine Human-Competitive Machine Intelligence. Kluwer, New York
Kruse R., Gebhardt J., Klawonn F. (1994) Foundations of Fuzzy Systems. John Wiley, Chichester
Kruskal, J.B. and Seery, J.B. (1980). Designing network diagrams. Proc. 1st General Conf. on Social Graphics, pp. 22–50
Krzanowski W.J. (1988) Principles of Multivariate Analysis: A User’s Perspective. Oxford Univeristy Press, Oxford
Langdon W.B. (1998) Genetic Programming And Data Structures: Genetic Programming + Data Structures = Automatic Programming!. Kluwer, Boston
Langley P., Simon H.A., Bradshaw G.L., Zytkow J.M. (1987) Scientific Discovery: Computational Exploration Of The Creative Processes. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Leon A.C. (2004) Multiplicity-adjusted sample size requirements: a strategy to maintain statistical power with Bonferroni adjustments. J. Clin. Psychiatry 65: 1511–1514
Li H.-X., Yen V.C. (1995) Fuzzy Sets And Fuzzy Decision-Making. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Li, T., Zhu, S., Li, Q., and Ogihara, M. (2003). Gene functional classification by semi-supervised learning from heterogeneous data. Proc ACM Symp. Appl. Computing. pp. 78–82
Liang Y., Kelemen A. (2006) Associating phenotypes with molecular events: recent statistical advances and challenges underpinning microarray experiments. Funct .Integr Genomics 6: 1–13
Linden A. (2006) Measuring diagnostic and predictive accuracy in disease management: an introduction to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 12: 132–139
Lucasius C.B., Beckers M.L.M., Kateman G. (1994) Genetic algorithms in wavelength selection – a comparative-study. Analytica Chimica Acta 286: 135–153
Lucasius C.B., Kateman G. (1994) Understanding and using genetic algorithms .2. Representation, configuration and hybridization. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 25: 99–145
Mackay D.J.C. (2003) Information Theory, Inference and Learning Algorithms. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Manly B.F.J. (1994) Multivariate Statistical Methods : A Primer. Chapman and Hall, London
Martens H., Næs T. (1989) Multivariate Calibration. John Wiley, Chichester
Metz C.E. (1978) Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin Nucl Med 8: 283–98
Michalewicz Z., Fogel D.B. (2000) How to Solve it: Modern Heuristics. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg
Michalski R.S., Bratko I., Kubat M. (Eds) (1998) Machine Learning and Data Mining. Methods and applications, Wiley, Chichester
Michie D., Spiegelhalter D.J., Taylor C.C. (eds) (1994) Machine Learning Neural and Statistical Classification. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Miller A.J. (1990) Subset Selection in Regression. Chapman and Hall, London
Mitchell T.M. (1997) Machine Learning. McGraw Hill, New York
Montgomery D.C. (2001) Design and Analysis of Experiments. 5th edition. Wiley, Chichester
Myers R.H., Montgomery D.C. (1995) Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization using Designed Experiments. Wiley, New York
Natarajan S., Glick H., Criqui M., Horowitz D., Lipsitz S.R., Kinosian B. (2003) Cholesterol measures to identify and treat individuals at risk for coronary heart disease. Am. J. Prev. Med. 25: 50–7
Needham C.J., Bradford J.R., Bulpitt A.J., Westhead D.R. (2006) Inference in Bayesian networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 24: 51–53
Ntzani E.E., Ioannidis J.P. (2003) Predictive ability of DNA microarrays for cancer outcomes and correlates: an empirical assessment. Lancet 362: 1439–44
O’Hagan S., Dunn W.B., Brown M., Knowles J.D., Kell D.B. (2005) Closed-loop, multiobjective optimisation of analytical instrumentation: gas-chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry of the metabolomes of human serum and of yeast fermentations. Anal. Chem. 77: 290–303
Oakley J.E., O’Hagan A. (2004) Probabilistic sensitivity analysis of complex models: a Bayesian approach. JR Stat. Soc. A 66: 751–769
Obuchowski N.A., Lieber M.L., Wians F.H. Jr. (2004) ROC curves in clinical chemistry: uses, misuses, and possible solutions. Clin. Chem. 50: 1118–25
Oinn T., Addis M., Ferris J., Marvin D., Senger M., Greenwood M., Carver T., Glover K., Pocock M.R., Wipat A., Li P. (2004) Taverna: a tool for the composition and enactment of bioinformatics workflows. Bioinformatics 20: 3045–3054
Oinn T., Li P., Kell D., Goble C., Goderis A., Greenwood M., Hull D., Stevens R., Turi D., Zhao J. (2006) Taverna/Mygrid: Aligning a Workflow System with the Life Sciences Community Workflows for eScience. Springer, Guildford, pp. 299–318
Oliver S.G., Winson M.K., Kell D.B., Baganz F. (1998) Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends Biotechnol. 16: 373–378
Pearl J. (1988) Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems: Networks of Plausible Inference. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco
Pearl J. (2000) Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Peleg M., Yeh I., Altman R.B. (2002) Modelling biological processes using workflow and Petri Net models. Bioinformatics 18: 825–37
Perneger T.V. (1998) What’s wrong with Bonferroni adjustments. BMJ 316: 1236–8
Petricoin E.F. III, Ardekani A.M., Hitt B.A., Levine P.J., Fusaro V.A., Steinberg S.M., Mills G.B., Simone C., Fishman D.A., Kohn E.C., Liotta L.A. (2002) Use of proteomic patterns in serum to identify ovarian cancer. Lancet 359: 572–577
Potter S.C., Clarke L., Curwen V., Keenan S., Mongin E., Searle S.M., Stabenau A., Storey R., Clamp M. (2004) The Ensembl analysis pipeline. Genome Res. 14: 934–941
Raamsdonk L.M., Teusink B., Broadhurst D., Zhang N., Hayes A., Walsh M., Berden J.A., Brindle K.M., Kell D.B., Rowland J.J., Westerhoff H.V., van Dam K., Oliver S.G. (2001) A functional genomics strategy that uses metabolome data to reveal the phenotype of silent mutations. Nat. Biotechnol. 19: 45–50
Ramoni M., Sabastini P. (1998) Theory and Practice of Bayesian Belief Networks. Edward Arnold, London
Ransohoff D.F. (2004) Rules of evidence for cancer molecular-marker discovery and validation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 4: 309–314
Ransohoff D.F. (2005) Bias as a threat to the validity of cancer molecular-marker research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5: 142–149
Ransohoff D.F., Feinstein A.R. (1978) Problems of spectrum and bias in evaluating the efficacy of diagnostic tests. N. Engl. J. Med. 299: 926–930
Rapp P.E. (1993) Chaos in the neurosciences: cautionary tales from the frontier. Biologist 40: 89–94
Raubertas R.F., Rodewald L.E., Humiston S.G., Szilagyi P.G. (1994) ROC curves for classification trees. Med. Decis. Making 14: 169–174
Reiner A., Yekutieli D., Benjamini Y. (2003) Identifying differentially expressed genes using false discovery rate controlling procedures. Bioinformatics 19: 368–375
Ressom H.W., Varghese R.S., Abdel-Hamid M., Eissa S.A., Saha D., Goldman L., Petricoin E.F., Conrads T.P., Veenstra T.D., Loffredo C.A., Goldman R. (2005) Analysis of mass spectral serum profiles for biomarker selection. Bioinformatics 21: 4039–4045
Rifai N., Gillette M.A., Carr S.A. (2006) Protein biomarker discovery and validation: the long and uncertain path to clinical utility. Nat. Biotechnol. 24: 971–983
Ringuest J.L. (1992) Multiobjective Optimization: Behavioral and Computational Considerations. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Romano P., Marra D., Milanesi L. (2005) Web services and workflow management for biological resources. BMC Bioinformatics 6(Suppl 4), S24
Rothman K.J., Greenland S. (1998) Modern Epidemiology. 2nd ed. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Rowland J.J. (2003) Model selection methodology in supervised learning with evolutionary computation. Biosystems 72: 187–196
Royall R. (1997) Statistical Evidence: A Likelihood Paradigm. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London
Rud O.P. (2001) Data Mining Cookbook. Wiley, New York
Sacks J., Welch W., Mitchell T., Wynn H. (1989) Design and analysis of computer experiments (with discussion). Statist Sci 4: 409–435
Saltelli A., Tarantola S., Campolongo F., Ratt M. (2004) Sensitivity Analysis in Practice: A Guide to Assessing Scientific Models. Wiley, New York
Sammon J.W. Jr. (1969) A nonlinear mapping for data structure analysis. IEEE Trans. Computers C-18: 401–409
Schena M. (Ed) (2000) Microarray Biochip Technology. Eaton Publishing, Natick, MA
Seasholtz M.B., Kowalski B. (1993) The parsimony principle applied to multivariate calibration. Anal. Chim. Acta 277: 165–177
Seber G.A.F., Wild C.J. (1989) Nonlinear Regression. Wiley, New York
Sehgal M.S., Gondal I., Dooley L.S. (2005) Collateral missing value imputation: a new robust missing value estimation algorithm for microarray data. Bioinformatics 21: 2417–2423
Shaffer R.E., Small G.W. (1997) Learning optimization from nature – genetic algorithms and simulated annealing. Anal. Chem. 69, A236–A242
Sharp S.J., Thompson S.G., Altman D.G. (1996) The relation between treatment benefit and underlying risk in meta-analysis. BMJ 313: 735–738
Shipley B. (2001) Cause and Correlation in Biology: A User’s Guide to Path Analysis, Structural Equations and Causal Inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sokal R.R., Rohlf F.J. (1995) Biometry. 3rd edition. Freeman, New York
Stephan C., Wesseling S., Schink T., Jung K. (2003) Comparison of eight computer programs for receiver-operating characteristic analysis. Clin. Chem. 49: 433–439
Steuer R. (2006) On the analysis and interpretation of correlations in metabolomic data. Brief Bioinform. 7: 151–158
Steuer R., Kurths J., Fiehn O., Weckwerth W. (2003) Observing and interpreting correlations in metabolomic networks. Bioinformatics 19: 1019–1026
Stevens R., McEntire R., Goble C., Greenwood M., Zhao J., Wipat A., Li P. (2004) myGrid and the drug discovery process. DDT Biosilico. 4: 140–148
Storey J.D. (2002) A direct approach to false discovery rates. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B 64: 479–498
Storey J.D., Tibshirani R. (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 9440–5
Tas A.C., van der Greef J. (1994) Mass spectrometric profiling and pattern recognition. Mass Spectrum Rev. 13: 155–181
Todd J.A. (2006) Statistical false positive or true disease pathway? Nat. Genet. 38: 731–733
Troyanskaya O., Cantor M., Sherlock G., Brown P., Hastie T., Tibshirani R., Botstein D., Altman R.B. (2001) Missing value estimation methods for DNA microarrays. Bioinformatics 17: 520–525
Tu Y., Stolovitzky G., Klein U. (2002) Quantitative noise analysis for gene expression microarray experiments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99: 14031–14036
Tufte E.R. (2001) The Visual Display of Quantitative Information. 2nd ed. Graphics Press, Cheshire, CT
Tukey J.W. (1977) Exploratory Data Analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Urbanczyk-Wochniak E., Luedemann A., Kopka J., Selbig J., Roessner-Tunali U., Willmitzer L., Fernie A.R. (2003) Parallel analysis of transcript and metabolic profiles: a new approach in systems biology. EMBO Rep 4: 989–993
Valiant L.G. (1984) A theory of the learnable. Comm ACM 27: 1134–1142
van ′t Veer L.J., Dai H., van de Vijver M.J., He Y.D., Hart A.A., Mao M., Peterse H.L., van der Kooy K., Marton M.J., Witteveen A.T., Schreiber G.J., Kerkhoven R.M., Roberts C., Linsley P.S., Bernards R., Friend S.H. (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415: 530–536
van de Vijver M.J., He Y.D., van ′t Veer L.J., Dai H., Hart A.A., Voskuil D.W., Schreiber G.J., Peterse J.L., Roberts C., Marton M.J., Parrish M., Atsma D., Witteveen A., Glas A., Delahaye L., van der Velde T., Bartelink H., Rodenhuis S., Rutgers E.T., Friend S.H., Bernards R. (2002) A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 347: 1999–2009
van Rijsbergen C. (1979) Information Retrieval. Butterworth, London
Van Veldhuizen D.A., Lamont G.B. (2000) Multiobjective evolutionary algorithms: analyzing the state-of-the-art. Evol Comput 8: 125–147
Vapnik V.N. (1998) Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley, New York
von Mering C., Krause R., Snel B., Cornell M., Oliver S.G., Fields S., Bork P. (2002) Comparative assessment of large-scale data sets of protein-protein interactions. Nature 417: 399–403
Wacholder S., Chanock S., Garcia-Closas M., El Ghormli L., Rothman N. (2004) Assessing the probability that a positive report is false: an approach for molecular epidemiology studies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 96: 434–442
Wang Y., Klijn J.G., Zhang Y., Sieuwerts A.M., Look M.P., Yang F., Talantov D., Timmermans M., Meijer-van Gelder M.E., Yu J., Jatkoe T., Berns E.M., Atkins D., Foekens J.A. (2005) Gene-expression profiles to predict distant metastasis of lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer. Lancet 365: 671–679
Weckwerth W., Morgenthal K. (2005) Metabolomics: from pattern recognition to biological interpretation. Drug Discov. Today 10: 1551–1558
Weiss S.H., Kulikowski C.A. (1991) Computer Systems that Learn: Classification and Prediction Methods from Statistics, Neural Networks, Machine Learning, and Expert Systems. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Mateo, CA
Weiss S.M., Indurkhya N. (1998) Predictive Data Mining. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco
Westerhoff H.V., Kell D.B. (1987) Matrix method for determining the steps most rate-limiting to metabolic fluxes in biotechnological processes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 30: 101–107
White H. (1992) Artificial Neural Networks: Approximation and Learning Theory. Blackwell, Oxford
White T.A., Kell D.B. (2004) Comparative genomic assessment of novel broad-spectrum targets for antibacterial drugs. Comp. Func. Genomics 5: 304–327
Wilkinson L. (1999) The Grammar of Graphics. Springer-Verlag, New York
Williamson P.R., Gamble C., Altman D.G., Hutton J.L. (2005) Outcome selection bias in meta-analysis. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 14: 515–524
Wold S., Trygg J., Berglund A., Antti H. (2001) Some recent developments in PLS modeling. Chemometr. Intell. Lab Syst. 58: 131–150
Woodward M. (2000) Epidemiology: Study Design and Data analysis. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London
Xie Y., Pan W., Khodursky A.B. (2005) A note on using permutation-based false discovery rate estimates to compare different analysis methods for microarray data. Bioinformatics 21: 4280–4288
Zadeh L.A. (1965) Fuzzy sets. Information and Control 8: 338–353
Zhang J.H., Chung T.D.Y., Oldenburg K.R. (1999) A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 4: 67–73
Zhou X., Wang X., Dougherty E.R. (2003) Missing-value estimation using linear and non-linear regression with Bayesian gene selection. Bioinformatics 19: 2302–2307
Zhou X.H., Obuchowski N.A., McClish D.K. (2002) Statistical Methods in Diagnostic Medicine. Wiley, New York
Zitzler E. (1999) Evolutionary Algorithms for Multiobjective Optimization: Methods And Applications. Shaker Verlag, Aachen
Zupan J., Gasteiger J. (1993) Neural Networks for Chemists. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Zweig M.H., Campbell G. (1993) Receiver-Operating Characteristic (ROC) plots - a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin. Chem. 39: 561–577
Acknowledgments
We thank the BBSRC, MRC and BHF for financial support and many colleagues for useful discussions and examples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broadhurst, D.I., Kell, D.B. Statistical strategies for avoiding false discoveries in metabolomics and related experiments. Metabolomics 2, 171–196 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-006-0037-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-006-0037-z