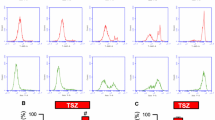
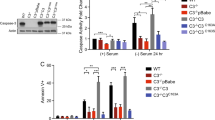
Abstract
MAGI-1, a member of the MAGUK family of proteins, is shown to be rapidly cleaved during Fas-induced apoptosis in mouse 3T3 A31 cells, and in UV irradiation- and staurosporine-induced apoptosis in HaCaT cells. This generates a 97 kDa N-terminal fragment that dissociates from the cell membrane; a process that is largely prevented in the presence of the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-fmk. In addition, we show that in vitro translated radiolabelled MAGI-1 is efficiently cleaved into 97 kDa and 68 kDa fragments by caspases-3 and -7 at physiological concentrations and mutating the MAGI-1 Asp761 to Ala completely abolished the caspase-induced cleavage. Moreover, in HaCaT cells overexpressing the MAGI-1 Asp761Ala mutant the disruption of cell-cell contacts was delayed during apoptosis, whereas other caspase-dependent processes such as nuclear condensation were not affected, suggesting that cell detachment is parallel to them. Thus, MAGI-1 cleavage appears to be an important step in the disassembly of cell-cell contacts during apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steller H (1995) Mechanism and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267:1445–1449
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456–1462
Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA (1997) Caspases: killer proteases. Trends Biochem Sci 22:299–306
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1997) Caspases: intracellular signaling by proteolysis. Cell 91:443–446
Brancolini C, Lazarevic D, Rodriguez J, Schneider C (1997) Dismantling cell-cell contacts during apoptosis is coupled to a caspase-dependent proteolytic cleavage of β-catenin. J Cell Biol 139:759–771
Brancolini C, Sgorbissa A, Schneider C (1998) Proteolytic processing of the adherens junctions components β-catenin and γ-catenin/plakoglobin during apoptosis. Cell Death Diff 5:1042–1050
Van de Craen M, Berx G, Van Den Brande I, Fiers W, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P (1999) Proteolytic cleavage of beta-catenin by caspases: an in vitro analysis. FEBS Lett 458:157–160
Cryns VL, Bergeron L, Zhu H, Li H, Yuan Y (1996) Specific cleavage of alpha-fodrin during Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is mediated by an interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme/ Ced 3 protease distinct from the poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase protease. J Biol Chem 271:31277–31282
Mashima T, Naito M, Noguchi K, Miller DK, Nicholson DW, Tsuruo T (1997) Actin cleavage by CPP-32/apopain during the development of apoptosis. Oncogene 14:1007–1012
Kothakota S, Azuma T, Reinhard C et al (1997) Caspase-3-generated fragment of gelsolin: effector of morphological change in apoptosis. Science 278:294–298
Steinhusen U, Weiske J, Badock V, Tauber R, Bommert K, Huber O (2001) Cleavage and shedding of E-cadherin after induction of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276:4972–4980
Levkau B, Herren B, Koyama H, Ross R, Raines EW (1998) Caspase-mediated cleavage of focal adhesion kinase pp125FAK and disassembly of focal adhesions in human endothelial cell apoptosis. J Exp Med 187:579–586
Weiske J, Schoneberg T, Schroder W, Hatzfeld M, Tauber R, Huber O (2001) The fate of desmosomal proteins in apoptotic cells. J Biol Chem 276:41175–41181
Bojarski C, Weiske J, Schoneberg T, Schroder W, Mankertz J, Schulzke JD, Florian P, Fromm M, Tauber R, Huber O (2004) The specific fates of tight junction proteins in apoptotic epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 117:2097–2107
Gregorc U, Ivanova S, Thomas M, Turk V, Banks L, Turk B (2005) hDLG/SAP97, a member of the MAGUK protein family, is a novel caspase target during cell-cell detachment in apoptosis. Biol Chem 386:705–710
Fanning AS, Anderson JM (1999) PDZ domains: fundamental building blocks in the organization of protein complexes at the plasma membrane. J Clin Invest 103:767–772
Garner CG, Nash J, Huganir RL (2000) PDZ domains in synapse assembly and signalling. Trends Cell Biol 10:274–280
Anderson JM (1996) Cell signalling: MAGUK magic. Curr Biol 6:382–384
Gomperts SN (1996) Clustering membrane proteins: it’s all coming together with the PSD-95/SAP90 protein family. Cell 84:659–662
Mitic LL, Anderson JM (1998) Molecular architecture of tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 60:121–142
Craven SE, Bredt DS (1998) PDZ proteins organize synaptic signaling pathways. Cell 93:495–498
Dobrosotskaya I, Guy RK, James GL (1997) MAGI-1, a membrane-associated guanylate kinase with a unique arrangement of protein-protein interaction domains. J Biol Chem 272:31589–31597
Wood JD, Yuan J, Margolis RL et al (1998) Atrophin-1, the DRPLA gene product, interacts with two families of WW domain-containing proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci 11:149–160
Laura RP, Ross S, Koeppen H, Lasky LA (2002) MAGI-1: a widely expressed, alternatively spliced tight junction protein. Exp Cell Res 275:155–170
Dobrosotskaya IY, James GL (2000) MAGI-1 interacts with beta-catenin and is associated with cell-cell adhesion structures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:903–909
Mino A, Ohtsuka T, Inoue E, Takai Y (2000) Membrane-associated guanylate kinase with inverted orientation (MAGI)-1/brain angiogenesis inhibitor 1-associated protein (BAP1) as a scaffolding molecule for Rap small G protein GDP/GTP exchange protein at tight junctions. Genes Cells 5:1009–1016
Patrie KM, Drescher AJ, Welihinda A, Mundel P, Margolis B (2002) Interaction of two actin-binding proteins, synaptopodin and alpha-actinin-4, with the tight junction protein MAGI-1. J Biol Chem 277:30183–30190
Hirabayashi S, Tajima M, Yao I, Nishimura W, Mori H, Hata Y (2003) JAM4, a junctional cell adhesion molecule interacting with a tight junction protein, MAGI-1. Mol Cell Biol 23:4267–4282
Glaunsinger BA, Lee SS, Thomas M, Banks L, Javier R (2000) Interactions of the PDZ-protein MAGI-1 with adenovirus E4-ORF1 and high-risk papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins. Oncogene 19:5270–5280
Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS (1997) Biochemical characteristics of caspases-3, -6, -7, and -8. J Biol Chem 272:25719–25723
Pace CN, Vajdos F, Fee L, Grimsley G, Gray T (1995) How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci 4:2411–2423
Gardiol D, Kühne C, Glaunsinger B, Lee SS, Javier R, Banks L (1999) Oncogenic human papillomavirus E6 proteins target the discs large tumour suppressor for proteasome-mediated degradation. Oncogene 18:5487–5496
Thiagarajan P, Tait JF (1990) Binding of annexin V/placental anticoagulant protein I to platelets. Evidence for phosphatidylserine exposure in the procoagulant response of activated platelets. J Biol Chem 265:17420–17423
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ et al (1995) Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med 182:1545–1556
Cirman T, Oresic K, Droga-Mazovec G, Turk V, Reed JC, Myers RM, Salvesen GS, Turk B (2004) Selective disruption of lysosomes in HeLa cells triggers apoptosis, mediated by cleavage of Bid by multiple papain-like lysosomal cathepsins. J Biol Chem 279:3578–3587
Gumbiner BM (1996) Cell adhesion: the molecular basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell 84:345–357
Balda MS, Matter K (1998) Tight junctions. J Cell Sci 111:541–547
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M (1999) Structural and signalling molecules come together at tight junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:628–633
Jezernik K, Sterle M, Batista U (1997) The distinct steps of cell detachment during development of mouse uroepithelial cells in the bladder. Cell Biol Int 21:1–6
Stevenson BR, Siliciano JD, Mooseker MS, Goodenough DA (1986) Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol 107:2401–2408
Jesaitis LA, Goodenough DA (1994) Molecular characterization and tissue distribution of ZO-2, a tight junction protein homologous to ZO-1 and Drosophila tumor suppressor gene dlg-A. J Cell Biol 124:949–961
Haskins J, Gu L, Wittchen ES, Hibbard J, Stevenson BR (1998) ZO-3, a novel member of the MAGUK protein family found at the tight junction, interacts with ZO-1 and occludin. J Cell Biol 141:199–208
Matsumine A, Ogai A, Senda T et al (1996) Binding of APC to the human homolog of the Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor protein. Science 272:1020–1023
Wu X, Hepner K, Castelino-Prabhu S et al (2000) Evidence for regulation of the PTEN tumor suppressor by a membrane-localized multi-PDZ domain containing scaffold protein MAGI-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4233–4238
Wu Y, Dowbenko D, Spencer S et al (2000) Interaction of the tumor suppressor PTEN/MMAC with a PDZ domain of MAGI3, a novel membrane-associated guanylate kinase. J Biol Chem 275:21477–21485
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM, Kaufmann SH (1999) Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 68:383–424
Nicholson DW (1999) Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Diff 6:1028–1042
Slee EA, Adrain C, Martin SJ (2001) Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276:7320–7326
Denault JB, Salvesen GS (2003) Human caspase-7 activity and regulation by its N-terminal peptide. J Biol Chem 278:34042–34050
Stennicke HR, Jürgensmeier JM, Shin H et al (1998) Pro-caspase-3 is a major physiologic target of caspase-8. J Biol Chem 273:27084–27090
Torres J, Rodriguez J, Myers MP et al (2003) Phosphorylation-regulated cleavage of the tumor suppressor PTEN by caspase-3: implications for the control of protein stability and PTEN-protein interactions. J Biol Chem 278:30652–30660
Adams CL, Chen Y-T, Smith SJ, Nelson WJ (1998) Mechanism of epithelial cell-cell adhesion and cell compaction revealed by high-resolution tracking of E-cadherin-green fluorescent protein. J Cell Biol 142:1105–1119
Vasioukhin V, Bauer C, Yin M, Fuchs E (2000) Directed actin polymerization is the driving force for epithelial cell-cell adhesion. Cell 100:209–219
Rajasekaran AK, Hojo M, Huima T, Rodriguez-Boulan E (1996) Catenins and zonula occludens-1 form a complex during early stages in the assembly of tight junctions. J Cell Biol 132:451–463
Reuver SM, Garner CG (1998) E-cadherin mediated cell adhesion recruits SAP97 into the cortical cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci 111:1071–1080
Fanning AS, Jameson B, Jesaitis LA, Anderson JM (1998) The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 273:29745–29753
Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Moroi S, Tsukita S (1997) Involvement of ZO-1 in cadherin-based cell adhesion through its direct binding to a-catenin and actin filaments. J Cell Biol 138:181–192
Itoh M, Morita K, Tsukita S (1999) Characterization of ZO-2 as a MAGUK family member associated with tight and adherens junctions with a binding affinity to occludin and a-catenin. J Biol Chem 274:5981–5986
Rosenblatt J, Raff MC, Cramer LP (2001) An epithelial cell destined for apoptosis signals its neighbors to extrude it by an actin- and myosin-dependent mechanism. Curr Biol 11:1847–1857
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregorc, U., Ivanova, S., Thomas, M. et al. Cleavage of MAGI-1, a tight junction PDZ protein, by caspases is an important step for cell-cell detachment in apoptosis. Apoptosis 12, 343–354 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0579-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-006-0579-6