Abstract
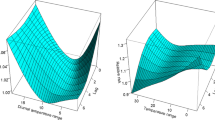
The objective of this study was to assess the relationship between diurnal temperature range (DTR) and emergency room (ER) admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in an ER in Taichung City, Taiwan. The design was a longitudinal study in which DTR was related to COPD admissions to the ER of the city’s largest hospital. Daily ER admissions for COPD and ambient temperature were collected from 1 January 2001 to 31 December 2002. There was a significant negative association between the average daily temperature and ER admissions for COPD (r = −0.95). However, a significant positive association between DTR and COPD admissions was found (r = 0.90). Using the Poisson regression model after adjusting for the effects of air pollutants and the day of the week, COPD admissions to the ER increased by 14% when DTR was over 9.6°C. COPD patients must be made aware of the increased risk posed by large DTR. Hospitals and ERs should take into account the increased demand of specific facilities during periods of large temperature variations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allegra JR, Cochrane DG, Allegra EM, Cable G (2002) Calendar patterns in the occurrence of cardiac arrest. Am J Emerg Med 20:513–517. doi:10.1053/ajem.2002.34799
Blanc PD, Eisner MD, Trupin L, Yelin EH, Katz PP, Balmes JR (2004) The association between occupational factors and adverse health outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Occup Environ Med 61:661–667. doi:10.1136/oem.2003.010058
Buff DD, Bavli SZ, Bloch MH, Serebryansky BM, Aman CS (1995) Circadian patterns of emergency asthma presentations: implications for staffing and treatment. Respir Care 40:624–630
Chen Y, Yang Q, Krewski D, Shi Y, Burnett RT, McGrail K (2004) Influence of relatively low level of particulate air pollution on hospitalization for COPD in elderly people. Inhal Toxicol 16:21–25. doi:10.1080/08958370490258129
Crowcroft NS, Cutts F, Zambon MC (1999) Respiratory syncytial virus: an underestimated cause of respiratory infection, with prospects for a vaccine. Commun Dis Public Health 2:234–241
Donaldson GC, Seemungal T, Jeffries DJ, Wedzicha JA (1999) Effect of temperature on lung function and symptoms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Respir Dis 13:844–849. doi:10.1034/j.1399–3003.1999.13d25.x
Duncan CJ, Duncan SR, Scott S (1997) The dynamics of measles epidemics. Theor Popul Biol 52:155–163. doi:10.1006/tpbi.1997.1326
Eccles R (2002) An explanation for the seasonality of acute upper respiratory tract viral infections. Acta Otolaryngol 122:183–191. doi:10.1080/00016480252814207
Eurowinter Group (1997) Cold exposure and winter mortality from ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, respiratory disease and all causes in warm and cold regions of Europe. Lancet 349:1341–1346. doi:10.1016/S0140–6736(96)12338–2
Gallerani M, Portaluppi F, Maida G, Chieregato A, Calzolari F, Trapella G et al (1996) Circadian and circannual rhythmicity in the occurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 27:1793–1797
Gordon CJ (2003) Role of environmental stress in the physiological response to chemical toxicants. Environ Res 92:1–7. doi:10.1016/S0013–9351(02)00008–7
Handley BA, Webster AJ (1995) Some factors affecting the airborne survival of bacteria outdoors. J Appl Bacteriol 79:368–378
Harre ESM, Price PD, Ayrey RB, Toop LJ, Martine IR, Town GI (1997) Respiratory effects of air pollution in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a three-month prospective study. Throax 52:1040–1044
Ho WC, Hartley WR, Myers L, Lin MH, Lin YS, Lien CH et al (2007) Air pollution, weather, and associated risk factors related to asthma prevalence and attack rate. Environ Res 104:402–409. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2007.01.007
Holmes S (1997) Mumps. In: Evans AS, Kaslow RA (eds) Viral infections of humans. Epidemiology and control. Plenum, New York, pp 531–550
Keating WR, Donaldson GC (1995) Cardiovascular mortality in winter. Arctic Med Res 54:16–18
Keating WR, Donaldson GC (2001) Mortality related to cold and air pollution in London after allowance for effects of associated weather patterns. Environ Res 86:209–216. doi:10.1006/enrs.2001.4255
Koskela HO, Koskela AK, Tukiainen HO (1996) Bronchoconstriction due to cold weather in COPD. The roles of direct airway effects and cutaneous reflex mechanisms. Chest 110:632–636. doi:10.1378/chest.110.3.632
Lee IM, Tsai SS, Chang CC, Ho CK, Yang CY (2007) Air pollution and hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a tropical city: Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Inhal Toxicol 19:393–398. doi:10.1080/08958370601174818
Liang KY, Zeger SL (1986) Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika 73:13–22. doi:10.1093/biomet/73.1.13
Liang W-M, Liu W-P, Chou S-Y, Kuo H-W (2008) Ambient temperature and emergency room admissions for acute coronary syndrome in Taiwan. Int J Biometeorol 52:223–229. doi:10.1007/s00484-007-0116-5
Lieberman D, Lieberman D, Friger MD (1999) Seasonal variation in hospital admissions for community acquired pneumonia: a 5-year study. J Infect 39:134–140. doi:10.1016/S0163–4453(99)90005–1
Lintner TJ, Brame KA (1993) The effects of season, climate, and air conditioning on the prevalence of Dermatophagoides mite allergens in house hold dust. J Allergy Clin Immunol 91:862–867. doi:10.1016/0091–6749(93)90343-E
Mercer JB (2003) Cold—an underrated risk factor for health. Environ Res 92:8–13. doi:10.1016/S0013–9351(02)00009–9
Peckova M, Fahrenbruch CE, Cobb LA, Hallstrom AP (1999) Weekly and seasonal variation in the incidence of cardiac arrests. Am Heart J 137:512–515
Pope CA III, Kanner RE (1993) Acute effects of PM10 pollution on pulmonary function of smokers with mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 147:1336–1340
Stensballe LG, Devasundaram JK, Simoes EA (2003) Respiratory syncytial virus epidemics: the ups and downs of a seasonal virus. Pediatr Infect Dis J 22(2):S21–S32. doi:10.1097/00006454–200302001–00004
Stout R, Crawford V (1991) Seasonal variations in fibrinogen concentrations among elderly people. Lancet 338:9–13. doi:10.1016/0140–6736(91)90004–9
Subiza J, Masiello JM, Subiza JL, Jerez M, Hinojosa M, Subiza E (1992) Prediction of annual variations in atmospheric concentrations of grass pollen: a method based on meteorological factors and grain crop estimates. Clin Exp Allergy 22:540–546. doi:10.1111/j.1365–2222.1992.tb00163.x
Woodhouse PR, Khaw KT, Plummer M, Foley A, Meade TW (1994) Seasonal variations of plasma fibrinogen and factor VII activity in the elderly: winter infections and death from cardiovascular disease. Lancet 343:345–349. doi:10.1016/S0140–6736(94)92689–1
Yang CY, Chen CJ (2007) Air pollution and hospital admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in a subtropical city: Taipei, Taiwan. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A 70:1214–1219. doi:10.1080/15287390701380880
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, WM., Liu, WP. & Kuo, HW. Diurnal temperature range and emergency room admissions for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Taiwan. Int J Biometeorol 53, 17–23 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-008-0187-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-008-0187-y