Abstract
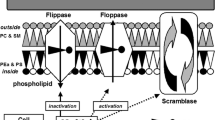
Microparticles are submicron vesicles shed from plasma membranes in response to cell activation, injury, and/or apoptosis. The measurement of the phospholipid content (mainly phosphatidylserine; PSer) of microparticles and the detection of proteins specific for the cells from which they are derived has allowed their quantification and characterization. Microparticles of various cellular origin (platelets, leukocytes, endothelial cells) are found in the plasma of healthy subjects, and their amount increases under pathological conditions. Endothelial microparticles (EMP) not only constitute an emerging marker of endothelial dysfunction, but are also considered to play a major biological role in inflammation, vascular injury, angiogenesis, and thrombosis. Although the mechanisms leading to their in vivo formation remain obscure, the release of EMP from cultured cells can be caused in vitro by a number of cytokines and apoptotic stimuli. Recent studies indicate that EMP are able to decrease nitric-oxide-dependent vasodilation, increase arterial stiffness, promote inflammation, and initiate thrombosis at their PSer-rich membrane, which highly co-expresses tissue factor. EMP are known to be elevated in acute coronary syndromes, in severe hypertension with end organ damage, and in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, all conditions associated with endothelial injury and pro-thrombotic state. The release of EMP has also been associated with endothelial dysfunction of patients with multiple sclerosis and lupus anticoagulant. More recent studies have focused on the role of low shear stress leading to endothelial cell apoptosis and subsequent EMP release in end-stage renal disease. Improved knowledge of EMP composition, their biological effects, and the mechanisms leading to their clearance will probably open new therapeutic approaches in the treatment of atherothrombosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid-Hussein MN, Meesters EW, Osmanovic N, Romijn FP, Nieewland R, Sturk A (2003) Antigenic characterization of endothelial cell-derived microparticles and their detection ex vivo. J Thromb Haemost 1:2434–2443
Amabile N, Guérin AP, Leroyer A, Mallat Z, Nguyen C, Boddaert J, London GM, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM (2005) Circulating endothelial microparticles are associated with vascular dysfunction in patients with end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3381–3388
Amabile N, Heiss C, Real WM, Minasi P, McGlothlin D, Rame EJ, Grossman W, DeMarco T, Yeghiazarians Y (2008) Circulating endothelial microparticle levels predict hemodynamic severity of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:1268–1275
Arteaga RB, Chirinos JA, Soriano AO, Jy W, Horstman L, Jimenez JJ, Mendez A, Ferreira A, deMarchena E, Ahn YS (2006) Endothelial microparticles and platelet and leukocyte activation in patients with the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol 98:70–74
Bakouloula B, Morel O, Faure A, Zobairi F, Jesel L, Trinh A, Zupan M, Canuet M, Grunebaum L, Brunette A, Desprez D, Chabot F, Weitzenblum E, Freyssinet JM, Chaouat A, Toti F (2008) Procoagulant membrane microparticles correlate with the severity of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:536–543
Berckmans RJ, Nieuwlands R, Boing AN, Romijn FP, Hack CE, Sturk A (2001) Cell-derived microparticles circulate in healthy humans and support low grade thrombin generation. Thromb Haemost 85:639–646
Bernal-Mizrachi L, Jy W, Jimenez JJ, Pastor J, Mauro LM, Horstman LL, deMarchena E, Ahn YS (2003) High levels of circulating endothelial microparticles in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Am Heart J 145:962–970
Bombeli T, Karsan A, Tait JF, Harlan JM (1997) Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells become procoagulant. Blood 89:2429–2442
Boulanger C, Scoazec A, Ebrahimian T, Henry P, Mathieu E, Tedgui A, Mallat Z (2001) Circulating microparticles from patients with myocardial infarction cause endothelial dysfunction. Circulation 104:2649–2652
Boulanger C, Amabile N, Tedgui A (2006) Circulating microparticles. A potential prognostic marker for atherosclerotic vascular disease. Hypertension 48:180–186
Boulanger C, Amabile N, Guérin AP, Pannier B, Leroyer AS, Nguyen C, Mallat Z, Tedgui A, London G (2007) In vivo shear stress determines circulating levels of endothelial microparticles in end-stage renal disease. Hypertension 49:1–7
Brogan PA, Shah V, Brachet C, Harnden A, Mant D, Klein N, Dillon MJ (2004) Endothelial and platelet microparticles in vasculitis of the young. Arthritis Rheum 50:927–936
Chamouard P, Desprez D, Hugel B, Kunzelmann C, Gidon-Jeangirard C, Lessard M, Baumann R, Freyssinet JM, Grunebaum L (2005) Circulating cell-derived microparticles in Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis Sci 50:574–580
Chargaff E, West R (1946) The biological significance of the thromboplastic protein of blood. J Biol Chem 166:189–197
Chironi G, Simon A, Hugel B, Del-Pino M, Gariepy J, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A (2006) Circulating leukocyte-derived microparticles predict subclinical atherosclerosis burden in asymptomatic subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:2775–2780
Chironi G, Craiem D, Miranda-Lacet J, Levenson J, Simon A (2008) Impact of shear stimulus, risk factors burden and early atherosclerosis on the time-course of brachial artery flow-mediated vasodilation. J Hypertens 26:508–515
Combes V, Simon AC, Grau GE, Arnoux D, Camoin L, Sabatier F, Mutin M, Sanmarco M, Sampol J, Dignat-George F (1999) In vitro generation of endothelial microparticles and possible prothrombotic activity in patients with lupus anticoagulant. J Clin Invest 104:93–102
Diamant M, Nieuwland R, Pablo RF, Sturk A, Smit JWA, Radder JK (2002) Elevated numbers of tissue-factor exposing microparticles correlate with components of the metabolic syndrome in uncomplicated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 106:2442–2447
Diamant M, Tushuizen ME, Sturk A, Nieuwland R (2004) Cellular microparticles: new players in the field of vascular disease? Eur J Clin Invest 34:392–401
Dignat-George F, Camoin-Jau L, Sabatier F, Arnoux D, Anfosso F, Bardin N, Veit V, Combes V, Gentile S, Moal V, Sanmarco M, Sampol J (2004) Endothelial microparticles: a potential contribution to the thrombotic complications of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Thromb Haemost 91:667–673
Esposito K, Ciotola M, Schisano B, Gualdiero R, Sardelli L, Misso L, Giannetti G, Giugliano D (2006) Endothelial microparticles correlate with endothelial dysfunction in obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3676–3679
Esposito K, Ciotola M, Giugliano F, Schisano B, Improta L, Improta MR, Beneduce F, Rispoli M, De-Sio M, Giugliano D (2007) Endothelial microparticles correlate with erectile dysfunction in diabetic men. Int J Impot Res 19:161–166
Faure V, Dou L, Sabatier F, Cerini C, Sampol J, Berland Y, Brunet P, Dignat-George F (2006) Elevation of circulating endothelial microparticles in patients with chronic renal failure. J Thromb Haemost 4:566–573
Heiss C, Amabile N, Lee AC, Real WM, Schick SF, Lao D, Wong ML, Jahn S, Angeli FS, Minasi P, Springer ML, Hammond SK, Glantz SA, Grossman W, Balmes JR, Yeghiazarians Y (2008) Brief secondhand smoke exposure depresses endothelial progenitor cells activity and endothelial function: sustained vascular injury and blunted nitric oxide production. J Am Coll Cardiol 51:1760–1771
Hugel B, Martinez C, Kunzelmann C, Freyssinet JM (2005) Membrane microparticles: two sides of the coin. Physiology 20:22–27
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM, Horstman LL, Ahn ZS (2001) Elevated endothelial microparticles in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: findings from brain and renal microvascular cell culture and patients with active disease. Br J Haematol 112:81–90
Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Mauro LM, Soderland C, Horstman LL, Ahn YS (2003) Endothelial cells release phenotypically and quantitatively distinct microparticles in activation and apoptosis. Thromb Res 109:175–180
Jy W, Jimenez JJ, Mauro LM, Horstman LL, Cheng P, Ahn ER, Bidot CJ, Ahn YS (2005) Endothelial microparticles induce formation of platelet aggregates via a von Willebrand factor/ristocetin dependent pathway, rendering them resistant to dissociation. Thromb Haemost 3:1301–1308
Kahn I, Zucker-Franklin D, Karpatkin S (1975) Microthrombocytis and platelet fragmentation associated with idiopathic/autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol 31:449–460
Koga H, Sugiyama S, Kugiyama K, Watanabe K, Fukushima H, Tanaka T, Sakamoto T, Yoshimura M, Jinnouchi H, Ogawa H (2005) Elevated levels of VE-cadherin-positive endothelial microparticles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1622–1630
Lee YJ, Jy W, Horstman LL, Janania J, Reyes Y, Kelley RE, Ahn YS (1993) Elevated platelet microparticles in transient ischemic attacks, lacunar infarcts, and multi-infarct dementias. Thromb Res 72:295–304
Leroyer AS, Isobe H, Leseche G, Castier Y, Wassef M, Mallat Z, Binder BR, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM (2007) Cellular origins and thrombogenic activity of microparticles isolated from human atherosclerotic plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol 49:772–777
Leroyer AS, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM (2008) Role of microparticles in atherothrombosis. J Int Med 263:528–537
Mallat Z, Hugel B, Ohan J, Lesèche G, Freyssinet J, Tedgui A (1999) Shed membrane microparticles with procoagulant potential in human atherosclerotic plaques. A role for apoptosis in plaque thrombogenicity. Circulation 99:348–353
Mallat Z, Benamer H, Hugel B, Benessiano J, Steg P, Freyssinet J, Tedgui A (2000) Elevated levels of shed membrane microparticles with procoagulant potential in the peripheral circulating blood of patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 101:841–843
Miguet L, Pacaud K, Felden C, Hugel B, Martinez MC, Freyssinet JM, Herbrecht R, Potier N, van Dorsselaer A, Mauvieux L (2006) Proteomic analysis of malignant lymphocyte membrane microparticles using double ionization coverage optimization. Proteomics 6:153–171
Minagar A, Jy W, Jimenez JJ, Sheremata WA, Mauro LM, Mao WW, Horstman LL, Ahn YS (2001) Elevated plasma endothelial microparticles in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 56:1319–1324
O’Brien J (1955) The platelet-like activity of serum. Br J Haematol 1:223–228
Perez-Casal M, Downe C, Fukudome K, Marx G, Toh CH (2005) Activated protein C induces the release of microparticle-associated endothelial protein C receptor. Blood 105:1515–1522
Piccin A, Murphy W, Smith O (2006) Circulating microparticles: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Blood Rev 21:157–171
Preston R, Jy W, Jimenez J, Mauro L, Horstman L, Valle M, Aime G, Ahn Y (2003) Effects of severe hypertension on endothelial and platelet microparticles. Hypertension 41:211–217
Rössig L, Haendeler J, Mallat Z, Hugel B, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A, Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM (2000) Congestive heart failure induces endothelial cell apoptosis: protective role of carvedilol. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:2081–2089
Rössig L, Hoffmann J, Hugel B, Mallat Z, Haase A, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A, Aicher A, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2001) Vitamin C inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis in congestive heart failure. Circulation 104:218–2187
Sabatier F, Darmon P, Hugel B, Combes V, Sanmarco M, Velut JG, Arnoux D, Charpiot P, Freyssinet JM, Olivier C, Sampol J, Dignat-George F (2002) Type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients display different patterns of cellular MP. Diabetes 5:2840–2845
Sapet C, Simoncini S, Loriod B, Puthier D, Sampol J, Nguyen C, Dignat-George F, Anfosso F (2006) Thrombin-induced endothelial microparticle generation: identification of a novel pathway involving ROCK-II activation by caspase-2. Blood 108:1868–1876
Shet AS, Aras O, Gupta K, Hass MJ, Rausch DJ, Saba N, Koopmeiners L, Key NS, Hebbel RP (2003) Sickle blood contains tissue factor-positive microparticles derived from endothelial cells and monocytes. Blood 102:2678–2683
Simak J, Holada K, Risitano AM, Zivny JH, Young NS, Vostal JG (2004) Elevatd circulating endothelial membrane microparticles in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Br J Haematol 125:804–813
Simon A, Chironi G, Levenson J (2006) Performance of subclinical arterial disease detection as a screening test for coronary heart disease. Hypertension 48:392–396
Simon A, Chironi G, Levenson J (2007) Comparative performance of subclinical atherosclerosis tests in predicting coronary heart disease in asymptomatic individuals. Eur Heart J 28:2967–2971
Soriano AO, Jy W, Chirinos JA, Valdivia MA, Velasquez HS, Jimenez JJ, Horstman LL, Kett DH, Schein RM, Ahn YS (2005) Levels of endothelial and platelet microparticles and their interactions with leukocytes negatively correlate with organ dysfunction and predict mortality in severe sepsis. Crit Care Med 33:2540–2546
VanWijk M, VanBavel E, Sturk A, Nieuwland R (2003) Microparticles in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc Res 59:277–287
Wang JM, Huang YJ, Wang Y, Xu MG, Wang LC, Wang SM, Tao J (2007a) Increased circulating CD31+/CD42- microparticles are associated with impaired systemic artery elasticity in healthy subjects. Am J Hypertens 20:965–966
Wang JM, Wang Y, Huang JY, Yang Z, Chen L, Wang LC (2007b) Reactive protein-induced endothelial microparticle generation in HUVECs is related to BH4-dependent NO formation. J Vasc Res 44:241–248
Warren B, Vales O (1972) The release of vesicles from platelets following adhesion to vessel walls in vitro. Br J Exp Pathol 53:206–215
Williams JB, Jauch EC, Lindsell CJ, Campos B (2007) Endothelial microparticle levels are similar in acute ischemic stroke and stroke mimics due to activation and not apoptosis/necrosis. Acad Emerg Med 14:685–690
Wolf P (1967) The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br J Haematol 13:269–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (Projet MIPRA-Met, ANR-05-PCOD-24–01).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chironi, G.N., Boulanger, C.M., Simon, A. et al. Endothelial microparticles in diseases. Cell Tissue Res 335, 143–151 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0710-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0710-9