Abstract
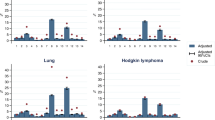
A population-based series of patients with cancer is likely to comprise more patients with serious co-morbidity than clinical trials because of restrictive eligibility criteria for the latter. Since co-morbidity may influence decision-making, we studied the age-specific prevalence of co-morbidity and its relationship to applied treatment. Data on all 194 patients with Hodgkin's disease (HD) and on 904 patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) diagnosed between 1993 and 1996 were derived from the Eindhoven Cancer Registry. In the age-group below 60 years, 87% of patients with HD and 80% with NHL did not have a co-morbid condition. The prevalence of serious co-morbidity was 56% for patients with Hodgkin's disease who were 60 years and over and 43% and 61% for non Hodgkin patients who were 60–69 years and 70 years and over, respectively. The most common co-morbid conditions were cardiovascular disease (18%), hypertension (13%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD; 13%), and diabetes mellitus (10%) for elderly Hodgkin's patients. For non-Hodgkin's patients of 60–69 years and 70 years and over, cardiovascular disease (15 and 22%, respectively), hypertension (14 and 14%, respectively), COPD (6 and 10% respectively), and diabetes mellitus (8 and 10%, respectively) were the most prevalent co-morbid conditions. The presence of co-morbidity was not related to stage or grade of disease at diagnosis. In the presence of co-morbidity, 50% less chemotherapy was administered to elderly patients with Hodgkin's disease and 10–15% less to elderly patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The presence of co-morbidity was associated with a decreased overall survival within the first 4 months after diagnosis in both Hodgkin's disease and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma for all age-groups. In conclusion, serious co-morbidity was found for more than half of all lymphoma patients who were 60 years and older. Elderly patients with serious co-morbidity received chemotherapy less often, which is likely to affect survival adversely, as was indicated by a decreased survival within the first 4 months after diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: August 31, 1998 / Accepted: February 23, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Spronsen, D., Janssen-Heijnen, M., Breed, W. et al. Prevalence of co-morbidity and its relationship to treatment among unselected patients with Hodgkin's disease and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, 1993–1996. Ann Hematol 78, 315–319 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770050521
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770050521