Abstract
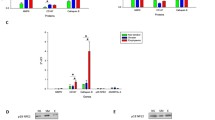
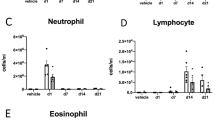
The environmental, genetic, and/or age-related changes in proteostasis induce inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. We quantified the correlation of protein expression of critical proteostasis mediators to severity of chronic lung disease using lung tissue samples from control and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) subjects (GOLD stage 0–IV) and cigarette smoke (CS)-induced murine model. The human bronchial epithelial cells, HEK-293, and Beas2B cells were used for in vitro experiments to verify the mechanisms. Our data verifies the correlation of higher expression of valosin-containing protein (VCP) retrograde translocation complex (VCP-Rma1-gp78) with severity of emphysema in COPD lung tissues and over-expression of inflammatory, ER stress and apoptotic mediators like NFκB, GADD-153/CHOP, and p-eIF2α. Moreover, subjects with severe emphysema had a higher accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins and deubiquitinating enzyme, UCHL-1, indicating towards the aggregation of misfolded or damaged proteins. The modulation of both protein degradation and synthesis rates by CS-extract substantiates the pathogenetic role of proteostasis-imbalance in emphysema and COPD. We identified that VCP also mediates proteasomal degradation of HDAC2 and Nrf2, as a potential mechanism for increased oxidative stress and corticosteroid resistance in COPD subjects with emphysema. Next, we confirmed that higher VCP expression associates with increased inflammation and apoptosis using in vitro and murine models. Our data clearly shows aberrant proteostasis in COPD subjects with severe emphysema. In addition, we evaluate therapeutic efficacy of salubrinal (ER stress inhibitor) to correct the proteostasis-imbalance based on its ability to control VCP expression and ubiquitin accumulation. Overall, our data demonstrate for the first time the critical role of proteostasis-imbalance in pathogenesis of severe emphysema.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahman I, Adcock IM (2006) Oxidative stress and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD. Eur Respir J 28(1):219–242
Moodie FM, Marwick JA, Anderson CS, Szulakowski P, Biswas SK, Bauter MR, Kilty I, Rahman I (2004) Oxidative stress and cigarette smoke alter chromatin remodeling but differentially regulate NF-kappaB activation and proinflammatory cytokine release in alveolar epithelial cells. FASEB J 18(15):1897–1899
Yang SR, Chida AS, Bauter MR, Shafiq N, Seweryniak K, Maggirwar SB, Kilty I, Rahman I (2006) Cigarette smoke induces proinflammatory cytokine release by activation of NF-kappaB and posttranslational modifications of histone deacetylase in macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291(1):L46–L57
Pryor WA, Stone K (1993) Oxidants in cigarette smoke. Radicals, hydrogen peroxide, peroxynitrate, and peroxynitrite. Ann NY Acad Sci 686:12–27, discussion 27–8
Yoshida T, Tuder RM (2007) Pathobiology of cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Physiol Rev 87(3):1047–1082
Eickmeier O, Huebner M, Herrmann E, Zissler U, Rosewich M (2010) Sputum biomarker profiles in cystic fibrosis (CF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and association between pulmonary function. Cytokine 50(2):152–157
Filosto S, Castillo S, Danielson A, Franzi L, Khan E, Kenyon N, Last J, Pinkerton K, Tuder R, Goldkorn T. (2011) Neutral sphingomyelinase 2: a novel target in cigarette smoke-induced apoptosis and lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol (in press)
Hetzer M, Meyer HH, Walther TC, Bilbao-Cortes D, Warren G, Mattaj IW (2001) Distinct AAA-ATPase p97 complexes function in discrete steps of nuclear assembly. Nat Cell Biol 3(12):1086–1091
Kondo H, Rabouille C, Newman R, Levine TP, Pappin D, Freemont P, Warren G (1997) p47 is a cofactor for p97-mediated membrane fusion. Nature 388(6637):75–78
Braun RJ, Zischka H (2008) Mechanisms of Cdc48/VCP-mediated cell death—from yeast apoptosis to human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783(7):1418–1435
Partridge JJ, Lopreiato JO Jr, Latterich M, Indig FE (2003) DNA damage modulates nucleolar interaction of the Werner protein with the AAA ATPase p97/VCP. Mol Biol Cell 14(10):4221–4229
Meyer HH, Shorter JG, Seemann J, Pappin D, Warren G (2000) A complex of mammalian ufd1 and npl4 links the AAA-ATPase, p97, to ubiquitin and nuclear transport pathways. EMBO J 19(10):2181–2192
Vij N (2008) AAA ATPase p97/VCP: cellular functions, disease and therapeutic potential. J Cell Mol Med 12(6A):2511–2518
Bodas M, Min T, Vij N. (2010) Early-age-related changes in proteostasis augment immunopathogenesis of sepsis and acute lung injury. PLoS One 5(11):e15480
Meusser B, Hirsch C, Jarosch E, Sommer T (2005) ERAD: the long road to destruction. Nat Cell Biol 7(8):766–772
Koegl M, Hoppe T, Schlenker S, Ulrich HD, Mayer TU, Jentsch S (1999) A novel ubiquitination factor, E4, is involved in multiubiquitin chain assembly. Cell 96(5):635–644
Ishigaki S, Hishikawa N, Niwa J, Iemura S, Natsume T, Hori S, Kakizuka A, Tanaka K, Sobue G (2004) Physical and functional interaction between Dorfin and Valosin-containing protein that are colocalized in ubiquitylated inclusions in neurodegenerative disorders. J Biol Chem 279(49):51376–51385
Zhong X, Shen Y, Ballar P, Apostolou A, Agami R, Fang S (2004) AAA ATPase p97/valosin-containing protein interacts with gp78, a ubiquitin ligase for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. J Biol Chem 279(44):45676–45684
Vij N, Fang S, Zeitlin PL (2006) Selective inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation rescues {Delta}F508-cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator and suppresses interleukin-8 levels: therapeutic implications. J Biol Chem 281(25):17369–17378
Morito D, Hirao K, Oda Y, Hosokawa N, Tokunaga F, Cyr DM, Tanaka K, Iwai K, Nagata AK (2008) Gp78 cooperates with RMA1 in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of CFTR{Delta}F508. Mol Biol Cell 19(4):1328–1336
Younger JM, Chen L, Ren HY, Rosser MF, Turnbull EL, Fan CY, Patterson C, Cyr DM (2006) Sequential quality-control checkpoints triage misfolded cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Cell 126(3):571–582
Vij N, Amoako MO, Mazur S, Zeitlin PL (2008) CHOP transcription factor mediates IL-8 signaling in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38(2):176–184
Malhotra D, Thimmulappa R, Navas-Acien A, Sandford A, Elliott M, Singh A, Chen L, Zhuang X, Hogg J, Pare P, Tuder RM, Biswal S (2008) Decline in NRF2-regulated antioxidants in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease lungs due to loss of its positive regulator, DJ-1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178(6):592–604
Malhotra D, Thimmulappa R, Vij N, Navas-Acien A, Sussan T, Merali S, Zhang L, Kelsen SG, Myers A, Wise R, Tuder R, Biswal S (2009) Heightened endoplasmic reticulum stress in the lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the role of Nrf2-regulated proteasomal activity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 180(12):1196–1207
Adenuga D, Yao H, March TH, Seagrave J, Rahman I (2009) Histone deacetylase 2 is phosphorylated, ubiquitinated, and degraded by cigarette smoke. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 40(4):464–473
Rabe KFHS, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ (2007) Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176(6):527–528
Vij N, Roberts L, Joyce S, Chakravarti S (2005) Lumican regulates corneal inflammatory responses by modulating Fas-Fas ligand signaling. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46(1):88–95
Bodas M, Min T, Mazur S, Vij N (2011) Critical modifier role of membrane-cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-dependent ceramide signaling in lung injury and emphysema. J Immunol 186(1):602–613
Kardosh AGE, Pyrko P, Uddin J, Hofman FM, Chen TC, Louie SG, Petasis NA, Schonthal AH (2008) Aggravated endoplasmic reticulum stress as a basis for enhanced glioblastoma cell killing by bortezomib in combination with celecoxib or its non-coxib analogue, 2, 5-dimethylcelecoxib. Cancer Res 68:843–851
Tagawa YHN, Kasai A, Hayakawa K, Okamura M, Yao J, Kitamura M (2008) Induction of apoptosis by cigarette smoke via ROS dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-homologous protein (CHOP). Free Radic Biol Med 45:50–59
Wang Z, Figueiredo-Pereira ME (2005) Inhibition of sequestosome 1/p62 up-regulation prevents aggregation of ubiquitinated proteins induced by prostaglandin J2 without reducing its neurotoxicity. Mol Cell Neurosci 29(2):222–231
Carolan BJ, Heguy A, Harvey BG, Leopold PL, Ferris B, Crystal RG (2006) Up-regulation of expression of the ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 gene in human airway epithelium of cigarette smokers. Cancer Res 66(22):10729–10740
Yang H, Liu C, Zhong Y, Luo S, Monteiro MJ, Fang S. (2010) Huntingtin interacts with the cue domain of gp78 and inhibits gp78 binding to ubiquitin and p97/VCP. PLoS One 5(1):e8905
Jiang J, Ballinger CA, Wu Y, Dai Q, Cyr DM, Hohfeld J, Patterson C (2001) CHIP is a U-box-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase: identification of Hsc70 as a target for ubiquitylation. J Biol Chem 276(46):42938–42944
Rangasamy T, Guo J, Mitzner WA, Roman J, Singh A, Fryer AD, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW, Tuder RM, Georas SN, Biswal S (2005) Disruption of Nrf2 enhances susceptibility to severe airway inflammation and asthma in mice. J Exp Med 202(1):47–59
Goven D, Boutten A, Lecon-Malas V, Marchal-Somme J, Amara N, Crestani B, Fournier M, Leseche G, Soler P, Boczkowski J, Bonay M (2008) Altered Nrf2/Keap1-Bach1 equilibrium in pulmonary emphysema. Thorax 63(10):916–924
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Engel JD, Yamamoto M (1999) Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev 13(1):76–86
Barnes PJ (2009) Role of HDAC2 in the pathophysiology of COPD. Annu Rev Physiol 71:451–464
Ito KLS, Caramori G, Chung KF, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM (2001) Cigarette smoking reduces histone deacetylase 2 expression, enhances cytokine expression, and inhibits glucocorticoid actions in alveolar macrophages. FASEB J 15(6):1110–1112
Barnes PJ (2009) The cytokine network in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41(6):631–638
Kelsen SG, Duan X, Ji R, Perez O, Liu C, Merali S (2008) Cigarette smoke induces an unfolded protein response in the human lung: a proteomic approach. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38(5):541–550
Korfei M, Ruppert C, Mahavadi P, Henneke I, Markart P, Koch M, Lang G, Fink L, Bohle RM, Seeger W, Weaver TE, Guenther A (2008) Epithelial endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178(8):838–846
Vij N, Mazur S, Zeitlin PL (2006) VCP is involved in ERAD and aggresome formation of ∆F508-CFTR. Pediatr Pulmonol 41(29):209
Houghton AM, Mouded M, Shapiro SD (2008) Common origins of lung cancer and COPD. Nat Med 14(10):1023–1024
Rajendrasozhan S, Yang SR, Edirisinghe I, Yao H, Adenuga D, Rahman I (2008) Deacetylases and NF-kappaB in redox regulation of cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation: epigenetics in pathogenesis of COPD. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(4):799–811
Yao H, Yang SR, Kode A, Rajendrasozhan S, Caito S, Adenuga D, Henry R, Edirisinghe I, Rahman I (2007) Redox regulation of lung inflammation: role of NADPH oxidase and NF-kappaB signalling. Biochem Soc Trans 35(Pt 5):1151–1155
Rangasamy T, Cho CY, Thimmulappa RK, Zhen L, Srisuma SS, Kensler TW, Yamamoto M, Petrache I, Tuder RM, Biswal S (2004) Genetic ablation of Nrf2 enhances susceptibility to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. J Clin Invest 114(9):1248–1259
Rajendrasozhan S, Chung S, Sundar IK, Yao H, Rahman I (2010) Targeted disruption of NF-{kappa}B1 (p50) augments cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and emphysema in mice: a critical role of p50 in chromatin remodeling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 298(2):L197–L209
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K, Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D, Yuan J (2005) A selective inhibitor of eIF2alpha dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 307(5711):935–939
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Lung Tissue Research Consortium, NHLBI, NIH for human lung tissue samples and Johns Hopkins University histology core for H&E staining and processing of murine lung tissues. The study was supported by FAMRI and NIH (CTSA UL RR 025005 and RHL096931) grants to NV.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Taehong Min and Manish Bodas contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 4,071 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, T., Bodas, M., Mazur, S. et al. Critical role of proteostasis-imbalance in pathogenesis of COPD and severe emphysema. J Mol Med 89, 577–593 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0732-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0732-8