Summary
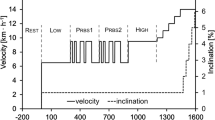
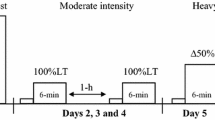
The effect of training on \(\dot V\operatorname{O} _2 \) max, endurance capacity (EC) and ventilation during maximal exercise (\(\dot V_E\) max) were studied in 17 normal subjects aged 21–51 years. At the beginning of the study 11 of the subjects (eight women and three men) were untrained (U) and six others (three women and three men) trained regularly (T). A maximal intensity exercise (on a cycle ergometer) which could be sustained for 45 min (MIE45) was performed three times per week for 6 weeks; the total mechanical work (TMW) corresponding to the MIE45 per session varied between 3.14 and 9.24 kJ·kg−1. Before training, \(\dot V\operatorname{O} _2 \)max (a), \(\dot V_E\) max (b), and TMW (c) were higher in T than in U subjects. Training increased these variables in most of the subjects; the increase being significantly higher (x ± SEM) in U (a=+29.9±3.8%; b=49.6±6.5%; c=47±6.9%) than in T subjects (a=6.6±3.8%; b=17.5±3.6%; c=19.1±2.8%). In all but three cases the % increase of TMW was higher than that of \(\dot V\operatorname{O} _2 \) max, suggesting a higher sensitivity of TMW in measuring EC. The significant increase in \(\dot V_E\) max, maximal voluntary ventilation, peak flows (inspiratory and expiratory) and static maximum pressures indicate that this training protocol improves in healthy subjects the performance of respiratory muscles as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aide-mémoire pour la pratique de l'examen de la fonction ventilatoire par la spirographie, 2ème ed, vol I/XI. Commission des Communautés Européennes, Luxembourg 1971
Atomi Y, Miyashita M (1980) Effect of training intensity in adult females on aerobic power, related to lean body mass. Eur J Appl Physiol 44: 109–116
Benzi G, Panceri P, De Bernardi M, Villa Arcelli E, D'Angelo L, Arrigoni E, Berte F (1975) Mitochondrial enzymatic adaptation of skeletal muscle to endurance training. J Appl Physiol 38: 565–569
Black LF, Hyatt RE (1969) Maximal respiratory pressures. Normal values and relationship to age and sex. Am Rev Respir Dis 99: 696–702
Costill DL, Fink WJ, Pollock ML (1976) Muscle fiber composition and enzyme activities of elite distance runners. Med Sci Sports 8: 96–100
Daniels JT, Yarbrough RA, Foster C (1978) Changes in \(\dot V\operatorname{O} _2 \) max and running performance with training. Eur J Appl Physiol 39: 249–254
Davies CTM, Knibbs AV (1971) The training stimulus: the effects of intensity, duration and frequency of effort on maximum aerobic power output. Int Z Angew Physiol 29: 299–305
Eddy DO, Sparxs XL, Adelizi DA (1977) The effects of continuous and interval training in women and men. Eur J Appl Physiol 37: 83–92
Fox EL, Bartels RL, Billings CE, Mathews DK, Bason R, Webb WM (1973) Intensity and distance of interval training programs and changes in aerobic power. Med Sci Sports 5: 18–22
Gimenez M, Salinas W, Servera E, Kuntz C (1981) \(\dot V\operatorname{O} _2 \) max during progressive and constant bicycle exercise in sedentary men and women. Eur J Appl Physiol 46: 237–248
Gimenez M, Servera E, Salinas W (1982) Square-Wave Endurance Exercise Test (SWEET) for training and assessment in trained and untrained subjects. I. Description and cardiorespiratory responses. Eur J Appl Physiol 49: 359–368
Gollnick PD, Armstrong RB, Saltin B, Saubert CW, Sembrowich WL, Shepherd RE (1973) Effect of training on enzyme activity and fiber composition of human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 34: 107–111
Henriksson J, Reitman JS (1977) Time course of changes in human skeletal muscle succinate dehydrogenase and cytochrome oxidase activities and maximal oxygen uptake with physical activity and inactivity. Acta Physiol Scand 99: 91–97
Hickson RC, Bomze HA, Holloszy JO (1977) Linear increase in aerobic power induced by a strenuous program of endurance exercise. J Appl Physiol 42: 372–376
Kasch FW, Wallace JP (1976) Physiological variables during ten years of endurance exercise. Med Sci Sports 8: 5–8
Kearney JT, Stull GA, Ewing Jr JL, Strein JW (1976) Cardiorespiratory responses of sedentary college women as a function of training intensity. J Appl Physiol 41: 822–825
Keens TG, Krastins IRB, Vannamaker EM, Levison H, Crozier DN, Bryan AC (1977) Ventilatory muscle endurance training in normal subjects and patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 116: 853–860
Knuttgen HL, Nordesjo LO, Ollander B, Saltin B (1973) Physical conditioning through interval training with young male adults. Med Sci Sports 5: 220–226
Leith DA, Bradley M (1976) Ventilatory muscle strength and endurance training. J Appl Physiol 41: 508–516
Martin BJ, Sparks KE, Zwillick CW, Weil JV (1979) Low exercise ventilation in endurance athletes. Med Sci Sports 11: 181–185
Mathews DX, Fox EL (1976) The physiological basis of physical education and athletics, vol 1. WB Saunders, London
Milic-Emili G, Petit JM, Deroanne R (1962) Mechanical work of breathing during exercise in trained and untrained subjects. J Appl Physiol 17: 43–49
Pollock ML, Cureton TK, Greninger L (1969) Effects of frequency of training on working capacity, cardiovascular function and body composition of adult men. Med Sci Sports 1: 70–74
Salinas W, Gimenez M (1981) Sujets sédentaires. EntraÎnement à l'exercice exhaustif en créneaux (45 min). Med Sport 55: 208–215
Saltin B, Blomquist G, Mitchell JH, Johnson RL, Wildenthal K, Chapman CB (1968) Response to exercise after bed rest and after training. Circulation 38 [Suppl 7]
Saltin B, Nazar K, Costill DL, Stein E, Jansson E, Essen B, Gollnick PD (1976) The nature of the training response: Peripheral and central adaptations to one-legged exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 96: 289–305
Shephard RJ (1968) Intensity, duration and frequency of exercise as determinants of the response to a training regime. Int Z Angew Physiol 26: 272–278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the European Economic Community (EEC) Luxembourg
Recipient of a CIES, was on leave from the Medical School of Concepcion, Chili
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gimenez, M., Cereceda, V., Teculescu, D. et al. Square-Wave Endurance Exercise Test (SWEET) for training and assessment in trained and untrained subjects. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 49, 379–387 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441299
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00441299