Summary
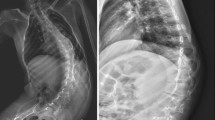
The notes and radiographs of 43 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy were reviewed. A significant inverse linear relationship between the severity of scoliosis and the percentage of predicted vital capacity and peak flow was found. The patients who stood had a significantly better lung function than patients who were confined to a wheelchair, and their scoliosis deteriorated significantly more slowly. Sixteen patients underwent surgical spinal stabilisation, 4 with Harrington instrumentation and 12 with segmental spinal instrumentation, at an average age of 12 years and 11 months. The average curve correction achieved was 40%. The decline in lung function seen pre-operatively was not only reversed, but a significant improvement was found at final follow-up.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aprin H, Bowen JR, MacEwen GD, Hall J (1982) Spine fusion in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 64:1179–1187
Benady SG (1978) Spinal muscular atrophy in childhood. A review of 50 cases. Dev Med Child Neurol 20:746–757
Brown JC, Zeller JL, Swank SM, Furumasa PT, Warath SL (1989) Surgical and functional results of spine fusion in spinal muscular atrophy. Spine 14:763–770
Brzustowicz LM, Lehner T, Castillo LH (1990) Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q 11.2–13.3. Nature 344:540–541
Cobb JR (1948) Outline for the study of scoliosis, instructional course lectures. Am Acad Orthop Surg 5:261–275
Dubowitz V (1974) Benign infantile spinal muscular atrophies. Dev Med Child Neurol 16:672–675
Dubowitz V (1978) Muscle disorders in childhood. Saunders, Philadelphia
Evans GA, Drennan JC, Russman BS (1981) Functional classification and orthopaedic management of spinal muscular atrophy. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 63:516–522
Furumasu J, Swank SM, Brown JC, Gilgoff I, Warath S, Zeller J (1989) Functional activities in spinal muscular atrophy patients after spinal fusion. Spine 14:771–775
Galasko CSB, Delaney C, Morris P (1992) Spinal stabilisation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 74: 210–214
Galasko CSB, Williamson JB, Delaney CM (1995) Lung function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Eur Spine J 4:263–267
Gilliam TC, Brzustowicz LM, Castilla LH (1990) Genetic homogeneity between acute and chronic forms of spinal muscular atrophy. Nature 345:823–825
Hardy JH, Curtis BH (1971) Neuromuscular scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 53:1021–1022
Hepper NGG, Black LF, Fowler WB (1965) The relationships of lung volume to height and arm span in normal subjects and in patients with spinal deformity. Am Rev Respir Dis 91:356–362
Kurz TL, Mubarak SJ, Schultz P, Park SM, Leach J (1983) Correlation of scoliosis and pulmonary function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Pediatr Orthop 3:347–353
Melki J, Abdelhak S, Sheth O (1990) Gene for chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophies maps to chromosome 5q. Nature 344:767–768
Merlini L, Granata C, Bonfiglioli S, Marini ML, Cervellati S, Savini R (1989) Scoliosis in spinal muscular atrophy: natural history and management. Dev Med Child Neurol 31:501–508
Morris P, Galasko CSB (1987) Anaesthesia for spinal stabilisation in children and adolescents with neuromuscular disease. In: Galasko CSB, Noble J (eds) Current trends in orthopaedic surgery. Manchester University Press, Manchester, pp 203–220
Namba T, Aberfield DC, Grob D (1970) Chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Sci 11:401–423
Noble-Jamieson CM, Heckmatt JZ, Dubowitz V, Silverman M (1986) Effects of posture and spinal bracing on respiratory function in neuromuscular disease. Arch Dis Child 61:178–181
Piasecki JO, Mahinpour S, Levine DB (1986) Long term follow-up of spinal fusion in spinal muscular atrophy. Clin Orthop 207:44–54
Riddick MF, Winter RB, Lutter LD (1982) Spinal deformities in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. A review of 36 patients. Spine 7:476–483
Rodillo E, Marini ML, Heckmatt JZ, Dubowitz V (1989) Scoliosis in spinal muscular atrophy: review of 63 cases. J Child Neurol 4:118–123
Schwentker EP, Gibson DA (1976) The orthopaedic aspects of spinal muscular atrophy. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 58:32–37
Vauzelle C, Stagnara P, Jouvinroux P (1973) Functional monitoring of the spinal cord during spinal surgery. Clin Orthop 93: 173
Williamson JB, Galasko CSB (1992) Spinal cord monitoring during operative correction of neuromuscular scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 74:870–873
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Paper read at the ESDS meeting, Birmingham, 1994, and selected for full publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, D., Galasko, C.S.B., Delaney, C. et al. Scoliosis and lung function in spinal muscular atrophy. Eur Spine J 4, 268–273 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301032
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301032