Article Text
Abstract
Background The natural history and time course of the onset of exacerbation events of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is incompletely understood.
Methods A prospective cohort of 212 patients with COPD was monitored using daily symptom diaries for a median of 2.8 years to characterise the time course of COPD exacerbation onset. Decision rules based on weighted self-reported symptoms were used to define opening and closing of exacerbation events. Event time intervals were analysed and logistic regression was used to determine the effects of patient covariates on exacerbation events.
Results Patients recorded 4439 episodes of worsening respiratory symptoms from baseline; 2444 (55%) events resolved spontaneously and 1995 (45%) resulted in a COPD exacerbation. In 1115 of the 1995 COPD exacerbations (56%) the onset was sudden and the exacerbation threshold was crossed on the same day symptoms began. In contrast, 44% of exacerbations were characterised by gradual onset of symptoms (median duration from symptom onset to exacerbation 4 days). Patients who experienced sudden onset exacerbations had greater mean daily symptom scores (7.86 vs 6.55 points, p<0.001), greater peak symptom scores (10.7 vs 10.2 points, p=0.003), earlier peak symptoms (4.5 vs 8.0 days, p<0.001) and shorter median recovery times back to baseline health status (11 vs 13 days, p<0.001). Multivariable analysis showed that gradual onset exacerbations were statistically associated with a longer duration of exacerbation recovery (OR 1.28, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.54, p=0.010).
Conclusions COPD exacerbations exhibit two distinct patterns—sudden and gradual onset. Sudden onset exacerbations are associated with increased respiratory symptoms but shorter exacerbation recovery times.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- diary data
- event history analysis
- exacerbation
- health process
- logistic regression
- medication
- score function
- symptoms
- COPD epidemiology
- COPD exacerbations
- COPD pharmacology
- cystic fibrosis
- COPD epidemiology
- COPD pathology
- lung physiology
- bronchiectasis
- COPD mechanisms
Statistics from Altmetric.com
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- diary data
- event history analysis
- exacerbation
- health process
- logistic regression
- medication
- score function
- symptoms
- COPD epidemiology
- COPD exacerbations
- COPD pharmacology
- cystic fibrosis
- COPD epidemiology
- COPD pathology
- lung physiology
- bronchiectasis
- COPD mechanisms
Key messages
What is the key question?
The natural history and time course of the onset of COPD exacerbation events is incompletely understood. Daily symptom diaries were used to study these events.
What is the bottom line?
Patients with COPD report many episodes of worsening of respiratory symptoms from baseline; the majority of these events resolve spontaneously without resulting in a COPD exacerbation. Two distinct types of COPD exacerbation were identified—sudden and gradual onset. Sudden exacerbations were associated with increased respiratory symptoms but shorter recovery times back to baseline health.
Why read on?
To determine how the pattern of onset of COPD exacerbation may impact on the subsequent clinical course of the patient.
Introduction
Individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are at risk for acute respiratory exacerbations. Acute exacerbations of COPD are characterised clinically by symptoms of worsening dyspnoea, cough, sputum production and sputum purulence, as well as by worsening of airflow obstruction.1 Exacerbations may be associated with acute viral or bacterial airway infections, or may occur independently of infection.2 3 Recent data from a longitudinal study of a large COPD cohort have revealed that exacerbations become more frequent as the severity of COPD progresses, and that a subgroup of patients may be prone to frequent exacerbations.4
Statistical modelling of the time course of COPD and patterns of exacerbations has received limited study,5 and the natural history and time course of exacerbation events is incompletely understood. Previous data have suggested that the median duration of recovery time following an acute exacerbation was 6–7 days for lung function and symptom scores, respectively.6 However, studies to date have not examined the onset of exacerbations or the nature of the prodrome phase which precedes exacerbations. This prodrome phase is of great interest, as knowledge of exacerbation onset can help physicians to time early therapeutic interventions appropriately.7
Our study used a longitudinal data set of daily symptom diary scores collected from patients with COPD. The objectives of the study were to characterise the time course of onset of COPD exacerbations and to attempt to distinguish unique patterns of COPD exacerbations based on the duration of symptom onset. A second objective was to determine whether differences in the pattern of exacerbation onset were associated with differences in clinical outcomes.
Methods
Study design and patients
This analysis used daily symptom diary data collected from a prospective longitudinal cohort of patients with COPD followed for a minimum of 2 years. The patients were recruited from outpatient clinics of the London Chest and Royal Free Hospitals, London. All patients had a diagnosis of COPD with a forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) <70% predicted for age, height, and sex; ratio of FEV1 to forced vital capacity (FVC) <70%; and minimal or no β2 agonist reversibility (<15% and/or <200 ml). Patients with significant respiratory diseases other than COPD (such as pulmonary fibrosis, asthma or bronchiectasis) were not recruited. Information on baseline body mass index (BMI), comorbidities, smoking status and sputum production was collected on all patients. Daily measures of symptoms, medication use, hospitalisations and clinic visits were recorded. All patients recorded daily, on diary cards, any increase in respiratory symptoms above those experienced at baseline. Symptoms were classified as major (dyspnoea, sputum purulence and sputum volume) or minor (nasal discharge/congestion, wheeze, sore throat and cough). Symptoms were also classified as those associated with viral exacerbations (nasal discharge/congestion or sore throat) and those associated with bacterial exacerbations (sputum purulence). Only increases in respiratory symptoms above baseline were recorded; patients with chronic stable respiratory symptoms were instructed not to note these on their diary cards. A sample copy of the daily symptom score diary card used in this study is shown in the online supplement.
Definition of opening, exacerbation and closing events
We used the daily symptom score obtained from the patient symptom diaries to determine the occurrence of the opening and closing of an exacerbation interval and the exacerbation event itself.
The daily symptom score is a simple weighted sum of symptoms. In accordance with previous definitions used by the London COPD Cohort, dyspnoea, sputum purulence and sputum volume were defined as major symptoms and nasal discharge/congestion, wheeze, sore throat and cough were defined as minor symptoms.6 8 Our calculation of the symptom score weighted each major symptom as 5 points and each minor symptom as 1 point (maximum daily symptom score=19 points). The peak daily symptom score occurred on the first day the symptom score achieved its maximum value during the exacerbation period.
A symptom score of 0 implies that patients are at their usual baseline state with respect to respiratory symptoms. An opening was defined as the first day of a positive symptom score indicating worsening of respiratory symptoms from baseline (ie, a symptom score ≥1 point) which followed 5 days in which symptom scores were equal to 0. An exacerbation was defined as the first of two or more consecutive days on which the patient recorded two or more new or worsening symptoms, at least one of which was a major symptom (ie, a daily symptom score of ≥6 points for two consecutive days). This definition is identical to the definition used in previous studies by the London Group.6 9 In accordance with previous definitions, a closing was defined as the first of 5 days with symptom scores equal to 0 that followed a day with a positive symptom score.9 An opening event could thus be followed by either an exacerbation event or by a closing event in a situation where respiratory symptoms commenced but resolved back to baseline levels without an intervening exacerbation. For convenience, we abbreviate opening as O, exacerbation as E and closing as C.
Time intervals between events
The duration of the exacerbation onset was calculated as the number of days between an opening event and the first day of the exacerbation event (the OE interval). The duration of exacerbation recovery (the EC interval) was defined as the number of days from the first day the exacerbation threshold was crossed until the first of 5 consecutive days in which symptoms had returned to usual baseline levels, which marked the closing event. The time to peak symptoms was calculated from the day the exacerbation threshold was crossed until the first day of maximum symptoms. Figure 1 shows the events and intervals.
Time course and calculation of the onset and duration of exacerbation intervals: a sudden onset exacerbation is shown on the left and a gradual onset exacerbation is shown on the right. Note that for sudden onset exacerbations the OE interval is 0 days and for gradual onset exacerbations the OE interval is ≥1 day. The opening event was defined as the first day of a worsening of respiratory symptoms above usual baseline values (ie, a daily symptom score ≥1). An exacerbation was defined as the first of ≥2 consecutive days on which the patient recorded ≥2 new or worsening symptoms, at least one of which was a major symptom (ie, a daily symptom score of ≥6 points for 2 consecutive days). A closing (C) was defined as the first of 5 consecutive days in which symptoms had returned to their usual baseline levels. OE, number of days between an opening event and the first day of the exacerbation event.
Patients were not always able to maintain continuous diaries for the study period so some provision was required for missing daily records. There were 1290 gaps of one or two missing diary days in the complete dataset. For these short gaps we used an imputation rule; if a symptom was present on the day before and after the gap then its presence was imputed for the missing period, otherwise the symptom was considered to have been absent during the gap. Where a gap exceeded 2 days, the patient record was assumed to enter a new epoch and the preceding period of data was right censored.
Alternative sensitivity analysis
A few patients recorded daily worsening of a single minor symptom for relatively long periods (>20 consecutive days) in their patient symptom diaries. To adjust for this anomaly, we performed a sensitivity analysis in which we discounted a single minor symptom. In this alternative analysis, an exacerbation definition was modified to require at least one new major symptom and one new minor symptom over and above one minor symptom that may have been chronically reported (ie, a symptom score ≥7 points for 2 consecutive days constituted a COPD exacerbation in the sensitivity analysis).
Statistical analysis
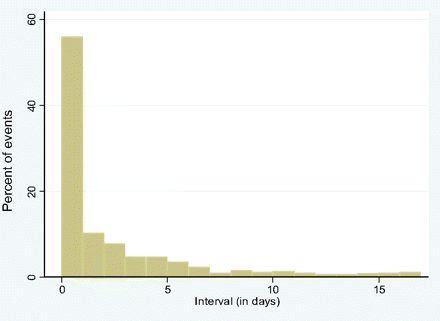
Intervals between events were highly skewed (figure 2) and not normally distributed, so medians and IQRs were used to describe their distributions. The median and the mode of the distribution of OE intervals was 0 days. Thus, exacerbations were grouped and analysed as either sudden onset exacerbations whereby the exacerbation threshold was crossed on the same day as symptoms began (ie, OE interval = 0 days) or gradual onset exacerbations (OE interval ≥1 day).
Histogram of OE intervals from the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease diary dataset. An OE interval of 0 days is the median and the mode for the distribution. The histogram indicates two apparent patterns of exacerbation, those with an OE of 0 days and all others. OE, number of days between an opening event and the first day of the exacerbation event.
Reported values of means and proportions are accompanied by 95% CIs. χ2 and exact tests for contingency tables and analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests for means were used to determine if symptoms and treatment differed depending on whether the OE interval was sudden or gradual. We employed a generalised estimating equation (GEE) logistic model with an exchangeable within-patient correlation structure to account for individual patients having multiple exacerbations. The GEE logistic regression model was used to analyse factors associated with sudden exacerbation onset. We included in the model all patient-related covariates that were judged a priori to be clinically important. Variables included were: presence of chronic sputum production, smoking status, age, sex, baseline FEV1 percentage predicted, history of cardiovascular disease and BMI (stratified as <20, 20–25, 25–30, ≥30 kg/m2, with 20–25 kg/m2 being the reference). The number of viral symptoms (0, 1 or 2) and bacterial symptoms (0 or 1) at exacerbation were also included. Finally, the season of the exacerbation was included (winter season was defined as November to the end of February, spring as March and April, summer as May to the end of August and autumn was the reference season defined as September and October). GEE logistic regression was also used to analyse whether exacerbation recovery time was prolonged or not, including the same patient-related covariates as well as an indicator variable for whether exacerbation onset was sudden or not. For the latter logistic regression, the EC interval was dichotomised according to whether it was longer than the median value (12 days). Logistic regression was used, rather than linear regression, because of the highly skewed distribution of EC intervals. Data were analysed using STATA V.10.0 (Stata Corporation). p Values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient characteristics
The baseline characteristics of the 212 patients are shown in table 1. The mean baseline FEV1 was 44.6% predicted (95% CI 42.4% to 46.8%). Patients in the cohort contributed data for a median of 2.8 years (IQR 2.0–4.7), and 890 patient-years of diary data were collected in total. The median exacerbation rate per patient per year was 2.33 (IQR 1.42–3.83, range 0–13).
Baseline characteristics of the 212 patients at time of recruitment to the cohort
Distribution of opening, closing and exacerbation events
Patients recorded 4439 episodes of initial worsening of respiratory symptoms from baseline classified as opening events. Of these 4439 opening events, 2444 (55.1%, 95% CI 53.6% to 56.5%) resolved spontaneously and 1995 (44.9%, 95% CI 43.5% to 46.4%) resulted in a COPD exacerbation and were therefore classified as OE intervals. The median duration of OE and EC intervals were 0 days (IQR 0–3) and 12 days (IQR 6–26), respectively.
Sudden versus gradual onset of exacerbations
Two patterns of exacerbation onset were observed: sudden and gradual (figures 1 and 2). In 1115 of 1995 exacerbation events (55.9%, 95% CI 53.7% to 58.1%) the time course of exacerbation onset was sudden and the exacerbation threshold was crossed on the same day as symptoms began (ie, OE interval of 0 days) (figure 2). The other 44.1% of exacerbations (95% CI 41.9% to 46.3%) were characterised by gradual onset of symptoms, with a median duration from onset to exacerbation of 4 days (IQR 2–8) (figure 2).
Daily symptom scores were assessed from the diary data; the range of the daily symptom score was 0–19 points. Sudden onset exacerbations were associated with greater mean daily symptom scores over the course of the exacerbation period than gradual onset exacerbations (7.86 vs 6.55 points, p<0.001). Sudden onset exacerbations were also associated with greater peak symptom scores during the exacerbation (10.7 vs 10.2 points, p=0.003) and an earlier time to peak symptoms (4.5 vs 8.0 days, p<0.001).
Patients who experienced sudden exacerbations had shorter recovery times back to their baseline health (median EC interval = 11 days, IQR 6–22) compared with those who experienced gradual exacerbations (median EC interval = 13 days, IQR 7–29; p<0.001). Figure 3 shows histograms of the EC intervals stratified by whether the onset of symptoms was sudden or gradual. The distribution of EC intervals is left-shifted for exacerbations that follow sudden onset of symptoms.
Histograms of exacerbation recovery (EC) intervals grouped by whether the onset of symptoms was sudden (OE=0) or gradual (OE ≥1). OE, number of days between an opening event and the first day of the exacerbation event.
Risk factors for sudden onset exacerbations
Logistic regression was used to assess covariates that were potentially associated with a sudden onset of exacerbations (table 2). Viral symptoms (nasal discharge/congestion or sore throat) or bacterial symptoms (sputum purulence) were associated with sudden exacerbations. Sudden exacerbations were significantly less common during the spring months. Smokers tended to be somewhat more at risk for sudden exacerbations, although this association did not quite reach statistical significance (OR 1.37, 95% CI 0.99 to 1.91, p=0.060).
Logistic regression assessing potential risk factors for sudden onset exacerbations
Factors associated with longer exacerbation recovery times
Logistic regression was used to assess covariates that were potentially associated with a longer duration of recovery from exacerbation, defined as an EC interval of more than the median of 12 days (table 3). Prolonged exacerbation recovery times were associated with exacerbations that occurred during the winter months and with exacerbations that began with viral symptoms. A gradual onset of exacerbation was significantly associated with a longer recovery time (OR 1.28, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.54, p=0.010) in the multivariable analysis (table 3). Smoking status, age, baseline FEV1 percentage predicted and BMI were not statistically associated with recovery times.
Logistic regression assessing potential risk factors for longer exacerbation recovery times
Exacerbation treatments
Table 4 shows the treatment prescribed for the exacerbation stratified by whether the exacerbation onset was sudden or gradual. Information on treatment prescribed was available for 1231 exacerbations (62%) in the dataset; 756 of 1231 exacerbations (61.4%) were treated with either an antibiotic or systemic corticosteroids, or both. As shown in table 4, patients who presented with sudden onset exacerbations tended to receive less treatment than those with gradual onset exacerbations, but the differences in treatment received were not statistically different; 59.1% of those with sudden onset exacerbations received steroids and/or antibiotics compared with 64.1% of those with gradual onset exacerbations (p=0.069).
Treatments prescribed for the exacerbation: sudden onset versus gradual onset
Sensitivity analysis
The sensitivity analysis modified the exacerbation definition to require a symptom score of ≥7 points for two consecutive days. This analysis again confirmed that patients who experienced sudden exacerbations had shorter recovery times back to their baseline health status (median 10 days, IQR 6–20) compared with those who experienced gradual onset exacerbations (median 13 days, IQR 7–27) (p<0.001). Similarly, the sensitivity analysis confirmed that gradual onset of exacerbation was significantly associated with a longer recovery time in the multivariable analysis (OR 1.46, 95% CI 1.17 to 1.81, p<0.001).
Discussion
Our study is one of the first qualitative and quantitative studies of COPD exacerbation symptoms. We used decision rules based on daily symptom diary scores to characterise the time course and the onset of COPD exacerbations. The onset, or prodrome, of COPD exacerbations is a subject that has received very little study to date. We found that patients with COPD commonly report many episodes of initial worsening of respiratory symptoms from baseline, and that the majority of these events resolve spontaneously without resulting in a COPD exacerbation. However, of the 1995 COPD exacerbations which did develop, more than 50% were characterised by an acute onset of symptoms whereby the exacerbation threshold was crossed on the same day that respiratory symptoms actually started.
The two types of exacerbation—sudden onset and gradual onset—were found to be predictive of subsequent clinical outcomes. Exacerbations which began suddenly were associated with higher mean daily symptom scores and an earlier time to peak symptoms once the exacerbation began. Sudden onset exacerbations were also associated with statistically higher peak symptom scores, although the differences in peak symptoms (10.7 vs 10.2 points) may not be clinically important.
Although sudden onset exacerbations were associated with more respiratory symptoms, they also were associated with shorter recovery times back to baseline health status. Multivariable analysis showed that the type of the exacerbation (sudden vs gradual onset) was closely associated with the duration of recovery from the exacerbation.
The difference in exacerbation recovery times associated with sudden and gradual onset exacerbations is statistically significant, and is probably clinically significant as well. Patients who experienced gradual onset exacerbations had longer exacerbation recovery times; the median exacerbation recovery interval was prolonged by 15% (13 vs 11 days) for those with gradual onset exacerbations. The longest recovery times (as measured by the third quartile) showed an even more pronounced difference of 32% (29 vs 22 days) for those with gradual onset exacerbations.
Treatment did not significantly differ between sudden and gradual onset exacerbations, although patients with sudden onset exacerbations tended to be somewhat less likely to be treated with antibiotics and/or steroids. It thus seems unlikely that the association between sudden onset exacerbations and shorter exacerbation recovery times is being confounded by more treatment being offered to the sudden exacerbation group.
Our findings have important implications for the clinical care of COPD exacerbations. In a sudden onset exacerbation, a full-blown exacerbation follows almost immediately after the patient starts to develop worsening respiratory symptoms. Because more than half of exacerbations are of sudden onset, patients have little time in which to seek medical attention before crossing the exacerbation threshold. One implication is that COPD action plans, with provision of prespecified prescriptions for antibiotics and oral steroids, may be appropriate to ensure prompt and appropriate management of exacerbations.10 Previous studies suggest that prompt treatment of exacerbations is associated with better clinical outcomes.7 Other studies suggest that COPD self-management programmes which include action plans to ensure prompt treatment of COPD exacerbations can decrease emergency department visits for COPD by up to 40%.11 However, it should be stressed that action plans that contain only minimal or no patient self-management education have not been shown to reduce urgent healthcare utilisation for COPD.12
We believe that our methodology is robust and that our findings are generalisable because we used a validated symptomatic definition of exacerbations that has been used in many previous studies of COPD exacerbations by our group and by others.13 Moreover, we undertook a sensitivity analysis using a more stringent definition of acute exacerbations and obtained the same key results.
However, there are a few potential limitations of our study. Clearly our study depended on accurate and timely patient diary completion. Patients who enrolled in the study received training on how to fill out their diary cards, and diaries were reviewed periodically to ensure proper completion. However, patients were not always able to maintain continuous diaries for the study period, so imputation was required for short gaps in diary records and censoring was required for longer gaps.
Another limitation is that our study did not assess potential microbiological pathogens that may have been associated with individual exacerbations. It is tempting to speculate that sudden exacerbations may be those that are caused by infections (either viral or bacterial respiratory tract infections). Our analysis does suggest that opening events that began with viral-like symptoms (nasal discharge/congestion or sore throat) and events that began with bacterial symptoms (sputum purulence) were more likely to proceed to full-blown exacerbations, and these exacerbations were more likely to be of sudden onset. However, we do not have viral or bacterial cultures or PCR data available from respiratory secretions or upper airway secretions to confirm this.
Interestingly, as previously reported,14 viral symptoms at presentation were associated with a longer recovery time whereas bacterial symptoms were not. This may be because bacterial airway infections are readily treatable with antibiotics which may cut short the duration of symptoms, whereas specific therapies for viral infections are generally lacking, leaving viral exacerbations more likely to have longer natural histories until symptom resolution.
Certain patient characteristics, such as smoking, appeared to be associated with sudden onset of exacerbation, and this agrees with previous observations that smokers are more susceptible to viral infections.15 16 However, many patients had both types of exacerbation (sudden and protracted onset) during the study observation period. Thus, the varying pattern of exacerbation onset appears to be a feature of the COPD event stream for all patients and not a patient-dependent characteristic.
In summary, this is the first study to report that there are two patterns of COPD exacerbation onset and that the pattern of the prodrome phase prior to the exacerbation is predictive of the subsequent clinical course and recovery. The concept that recovery time from exacerbations can be predicted by the exacerbation prodrome is clinically important. Both the duration of onset of COPD exacerbations and the COPD recovery time may conceivably relate also to the aetiology of the actual exacerbation itself. Further research is required to correlate the microbiological aetiology and the time course of onset and recovery from COPD exacerbation events.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Manyun Liu for her extensive and expert help with data preparation, data analysis and computer programming. They are indebted to the entire research team of the London COPD Cohort for their diligence and care in creating and maintaining the diary data set and to the patients of the cohort who invested so much time and effort in maintaining their diary records so that other COPD patients could benefit from their experience with the disease.
References
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Data
This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
Files in this Data Supplement:
- Data Supplement - Manuscript file of format pdf
Footnotes
Funding The London COPD Cohort is funded by The Medical Research Council, UK. Financial help for this research was provided by a Development Research Award from the Department of Medicine of the University of Ottawa to SDA and GAW.
Competing interests None.
Patient consent Obtained.
Ethics approval Ethics approval was obtained from East London and the City and Royal Free Hospital research ethics committees. All patients provided written informed consent.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.