Article Text
Abstract
Statins reduce cholesterol levels by inhibiting 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase and have an established role in the treatment of atherosclerotic disease. Recent research has identified anti-inflammatory properties of statins. Statins appear to reduce the stability of lipid raft formation with subsequent effects on immune activation and regulation, and also prevent the prenylation of signalling molecules with subsequent downregulation of gene expression. Both these effects result in reduced cytokine, chemokine, and adhesion molecule expression, with effects on cell apoptosis or proliferation. This review considers the evidence for the anti-inflammatory properties of statins in the lung, and how these effects are being applied to research into the role of statins as a novel treatment of respiratory diseases.
- CCL2, chemoattractant chemokine ligand 2
- COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CRP, C-reactive protein
- CTGF, connective tissue growth factor
- HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A
- IFN-γ, interferon γ
- ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- IL, interleukin
- IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- LFA-1, lymphocyte function associated antigen 1
- LPS, lipopolysaccharide
- MHC-II, major histocompatibility complex class II
- MMP, metalloprotease
- NF-κB, nuclear factor κB
- NK, natural killer
- TGF-β, transforming growth factor β
- TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor α
- asthma
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- statins
Statistics from Altmetric.com
- CCL2, chemoattractant chemokine ligand 2
- COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CRP, C-reactive protein
- CTGF, connective tissue growth factor
- HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A
- IFN-γ, interferon γ
- ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- IL, interleukin
- IPF, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- LFA-1, lymphocyte function associated antigen 1
- LPS, lipopolysaccharide
- MHC-II, major histocompatibility complex class II
- MMP, metalloprotease
- NF-κB, nuclear factor κB
- NK, natural killer
- TGF-β, transforming growth factor β
- TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor α
Statins are a class of cholesterol lowering drugs that decrease mortality from cardiovascular disease1–,3 and stroke.4,5 The beneficial effects of statins have been attributed to reduced cholesterol biosynthesis through competitive inhibition of the enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase (fig 1⇓). These studies also showed that treatment with statins provided greater protection than predicted from cholesterol reduction.6 Evidence has accumulated that statins lower C-reactive protein (CRP),7,8,9,10 a key indicator of inflammation, which itself is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular mortality and morbidity.11,12 This reduction in CRP is probably a consequence of the ability of statins to reduce the production of interleukin (IL)-6,13,14 the cytokine which activates the acute phase CRP response.15 Based on these observations, it has been proposed that the clinical effectiveness of statins might be due to a combination of functions including cholesterol reduction, anti-inflammatory, antithrombotic and immunomodulatory effects.
Cholesterol biosynthesis pathway showing potential effects of inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase by statins, causing a decrease in prenylation of signalling molecules as well as derivatives from mevalonate and cholesterol.
The purpose of this review is to outline the evidence for the anti-inflammatory properties of statins using observations from ex vivo and in vitro cell function, from experimental disease models, and clinical trials, and to suggest how these may be applicable to therapeutic advances for inflammatory lung disease.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Statins have several possible mechanisms of action that may be interrelated which result in the reduction of inflammation. These include (1) modulating the cholesterol content and thus reducing the stability of lipid raft formation and subsequent effects on the activation and regulation of immune cells, and (2) preventing the prenylation of signalling molecules and subsequent downregulation of gene expression, both resulting in reduced expression of cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules with effects on cell apoptosis or proliferation.
Other less well known anti-inflammatory properties of statins have been described, including antioxidant effects of some statins related to their ability to scavenge oxygen derived free radicals.16
Lipid rafts formation
Lipid rafts are small cell membrane structures or microdomains, rich in cholesterol and glycosphingolipid, which house intracellular enzymes, mainly kinases. These lipid rafts can be translocated by the actin cytoskeleton which controls their specific redistribution, clustering, and stabilisation within the cell membrane. When these rafts are assembled they form critical sites for processes such as cell movement, intracellular transport, or signal transduction. Lipid rafts act as platforms, bringing together molecules essential for the activation of immune cells, but also separating such molecules when the conditions for activation are not appropriate. Several strands of evidence suggest that the inhibition of cholesterol synthesis by statins disrupts these lipid rafts and thereby influences the function of lymphocytes.17 A central component of the interaction between lymphocytes and antigen presenting cells, which results in T cell activation, is interferon γ (IFN-γ) induced upregulation and assembly of the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II). Statins reduce IFN-γ production by Th1 cells18 and thus act as repressors of MHC-II mediated T cell activation.19,20
Prenylation and regulation of cytokine synthesis
Altered cytokine synthesis observed with statin therapy may be a consequence of altered lipid raft formation. However, there is an alternative or additional pathway of cytokine synthesis that may be affected by statins. The mevalonate synthetic pathway mediated by HMG-CoA reductase is crucial for the biosynthesis of isoprenoids (fig 1⇑), which are essential for normal cellular proliferation and activity. Farnesyl pyrophosphate is a later intermediate on this pathway and serves as a precursor for the synthesis of various isoprenoids—for example, geranylgeranyl or farnesyl groups—which prenylate proteins through covalent links. These can anchor these proteins to lipid rafts. Many prenylated proteins play important roles in the regulation of cell growth, cell secretion, and signal transduction. Thus, by inhibiting prenylation, statins affect many cell processes involved in inflammation.
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY EFFECTS OF STATINS ON NON-RESPIRATORY CELLS AND DISEASES
These two complementary mechanisms of prenylation and lipid raft stability allow statins to affect the function of many different cells and to attenuate inflammation in experimental models of disease.
Cell adhesion molecules
Statins interfere with cell binding by reducing leucocyte–endothelial cell adhesion.21,22 This occurs because statins attenuate the upregulation of P-selectin normally seen on activated endothelial cells,23 and they also interfere with monocyte24 and lymphocyte attachment to endothelium by suppressing intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and lymphocyte function associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) interactions.25 Statins have been shown to decrease the expression of the receptor for chemoattractant chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) expression on endothelial cells in rats26 and on monocytes from pigs,27 and thereby reduce monocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium.
Cytokine and mediator release
Statins alter protein expression, seen in altered cytokine release. In vitro experiments looking at spontaneous and lipopolysaccharide induced secretion of IL-6 and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α in human cell lines showed reduced output due to statins in both cases.13,28 Fluvastatin and simvastatin (but not pravastatin) reduce production of IL-6 and IL-1β in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.29 Atorvastatin has also been shown to inhibit production of TNF-α.30 Lovastatin induces Th2 production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10 in vitro.18 Increased prostacyclin31 and decreased endothelin32 production are seen in human endothelial cells after statin treatment.
Cellular apoptosis or proliferation
Statins increase apoptosis, as shown in human vascular endothelial cells33 and in plasma cell lines from patients with multiple myeloma.34 Proliferation of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes is inhibited by statins,35,36 and statins can alter the ratio of Th1 to Th2 lymphocytes; cerivastatin, simvastatin, lovastatin, and atorvastatin can promote Th2 polarisation through suppression of Th1 lymphocyte development and augmentation of Th2 lymphocyte development from naive CD4+ T cells when primed in vitro.37 Statins also reduce the proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts in rat and rabbit models.38
Antioxidant effects
Metabolites of atorvastatin have been shown to possess potent antioxidative properties,39,40 and to protect very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), low density lipoprotein (LDL), and high density lipoprotein (HDL) from oxidation.41 Simvastatin acts as an antioxidant in rat liver microsomes,42 vascular smooth muscle,43 and human lipoprotein particles,44 which may contribute to its anti-atherogenic effect.
Experimental models of disease
Statins have diverse effects on many chronic animal models of autoimmune disease. In models of systemic lupus erythematosus the administration of atorvastatin resulted in a significant reduction in serum IgG anti-dsDNA antibodies and decreased proteinuria, reduced glomerular immunoglobulin deposition, and glomerular injury. Disease improvement was paralleled by decreased expression of MHC-II on monocytes and B lymphocytes. T cell proliferation was impaired by atorvastatin in vitro and in vivo and a significant decrease in glomerular MHC-II expression was also observed.45 Cerivastatin and simvastatin have also been shown to inhibit the human neutrophil response to ANCA in vitro.46
In experiments with collagen induced arthritis in mice, simvastatin was given intraperitoneally either before (prophylactically) or after (therapeutically) induction of arthritis and a marked reduction in serum IL-6 and IFN-γ was seen, with a significant histological improvement.47
In a mouse model of autoimmune retinal disease, treatment with 20 mg/kg/day intraperitoneal lovastatin over 7 days suppressed clinical ocular pathology, retinal vascular leakage, and leucocytic infiltration into the retina.48 The effect was reversed by co-administration of mevalonolactone, the downstream product of HMG-CoA reductase.
Clinical studies
A double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial examined the efficacy of atorvastatin 40 mg daily for 6 months in rheumatoid arthritis. At the end of that period, patients who had received statin were found to have decreased plasma levels of lipids, fibrinogen and viscosity. The disease activity score improved significantly on atorvastatin treatment compared with placebo. CRP levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rate reduced by 50% and 28%, respectively, relative to placebo.49
Different statins may have different anti-inflammatory properties
It has recently become apparent that the different families of statins may have different biochemical functions. Kiener and colleagues50 showed that lipophilic statins such as atorvastatin and simvastatin have a much greater effect on inflammatory responses in human and mouse models than the hydrophilic pravastatin. Similarly, when looking at sensitisation of human smooth muscle cells to apoptotic agents, lovastatin and simvastatin had a powerful sensitising effect, atorvastatin had less of an effect, and pravastatin had no activity.51 There is also a dose-response effect—for example, cerivastatin is much more potent than fluvastatin in blocking NF-κB activation in human blood monocytes.52 Some statins have differing effects on protein expression—for example, in monocytes stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), pravastatin and fluvastatin may induce production of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-1853,54 whereas atorvastatin and simvastatin inhibit production of TNFα.13,14,30,55
It is therefore important to recognise that all statins may not have the same therapeutic potential. For example, a clinical study in 27 healthy volunteers found significant differences between the ex vivo immunological responses after atorvastatin and simvastatin treatment. Atorvastatin led to a significant downregulation in the expression of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DR and of the CD38 activation marker on peripheral T cells, whereas simvastatin upregulated both these molecules. In contrast, superantigen mediated T cell activation was inhibited by simvastatin and enhanced by atorvastatin.56
POTENTIAL THERAPEUTIC ROLE FOR STATINS IN RESPIRATORY DISEASE
The therapeutic effect of statins on cardiovascular and autoimmune disease seems to be broadly anti-inflammatory, which is also likely to apply to lung diseases in which there is an inflammatory component (fig 2⇓).
Potential anti-inflammatory effects of statins on different structural and inflammatory cells within the lungs.
Cellular inflammatory processes in the lung
There are several inflammatory processes in the lung that may be susceptible to the effects of statins.
Statins could affect the chemokine and adhesion molecule directed migration of inflammatory cells from blood into the airways.53,57–,59 Since both eosinophils and macrophages express the adhesion molecule LFA-1, this offers a potential target for modification of airway inflammation. Treatments other than statins targeted at reducing the expression of LFA-1 have been effective in decreasing airway eosinophilia in a mouse model of allergic asthma,60 and have reduced sputum eosinophilia after allergen challenge in asthmatic patients.61 Since statins can inhibit LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction, as seen in HIV,25 there is potential for statins to have an equivalent effect in asthma in which the pathophysiology is associated with eosinophil accumulation. Lovastatin has recently been shown to inhibit human alveolar epithelial production of IL-8,62 which might also contribute a beneficial effect of statins in the treatment of neutrophil associated inflammatory diseases of the lungs.
The observation that statins increase eosinophil apoptosis in humans63 suggests a further therapeutic role. The mechanism of this is probably due to the rapid reduction of cellular expression of CD40 after statin administration and this strongly inhibits eosinophil survival.64 Similarly, the neutrophilia associated with a mouse model of acute lung injury is markedly reduced with lovastatin treatment,65 and this modulation of neutrophil apoptosis may prove beneficial in other inflammatory lung diseases, such as smokers with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) where neutrophils are present and where corticosteroid treatment may be of limited benefit. In addition to induction of apoptosis, statins (in this case lovastatin) also enhance the clearance of apoptotic cells by human and mouse macrophages, a statin-specific effect reversible with mevalonate.66
Statins could affect the activation and proliferation of a variety of cells associated with lung inflammation. For example, statins suppress Th1 cell activation and IFN-γ production, as seen in a recent trial in rheumatoid arthritis49 and, by analogy, this treatment could decrease the IFN-γ dependent pathology of chronic asthma and pulmonary tuberculosis. Similarly, statins decrease natural killer (NK) cell activity in treated transplant patients,67 and this might be relevant to the pathogenesis of asthma in which NK cells may have a pathogenic role.68,69 The decrease in expression of MHC-II induced by statins has been observed on monocytes, macrophages, and on B lymphocytes in mice,45 which implies a widespread downregulatory effect on presentation and immune response to inhaled or lung associated antigens.
Statins may also have a role in attenuating the tissue repair and remodelling consequences of chronic aberrant immune activation and inflammation. For example, statins inhibit the proliferation of human airway smooth muscle70 and lower the expression of the profibrogenic cytokine transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1.71 Statins also reduce the tissue damage and cellular changes associated with cigarette smoking. The mechanism of this appears to be related to the reduction by statins of the production of matrix metalloprotease (MMP)-9 and airway remodelling in smoking rats72 and rabbits,73 and in human macrophages74 and monocytes30 from smokers. Other MMPs may also be reduced.73,75–,77 By targeting this key aspect of remodelling, this indicates a potential therapeutic role for statins in fibrotic lung diseases.
Finally, it is worth bearing in mind the different pharmacological properties between statins. For example, lovastatin seems to increase lymphocyte secretion of IL-4 and IL-5 in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis18 and therefore this particular statin may be of limited use in asthma where these cytokines are directly implicated in the pathogenesis.
Statin treatment of human and experimental respiratory diseases
Asthma
Atopic asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways characterised by airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammatory infiltrates in the bronchial walls containing lymphocytes and eosinophils, and elevated serum IgE levels. Th2 lymphocytes are thought to play a key role in the initiation and perpetuation of this airway inflammation,78–,80 mediated by the functions of their signal cytokines such as IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6. There is now evidence that Th1 cells may also contribute to disease,81,82 and IFN-γ secretion may exacerbate airway inflammation in chronic asthma.83
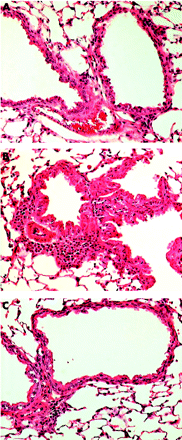
The potential benefits of statin therapy on inflammatory airway disease were demonstrated in a mouse model of allergic airways disease.84 In this model, airway eosinophilia was elicited using ovalbumin (OVA) as the allergen. Simvastatin given before each OVA challenge caused a reduction in inflammatory cell infiltrate and eosinophilia in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and a decrease in the OVA-specific production of IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-5 by thoracic node lymphocytes in vitro (fig 3⇓). The same anti-inflammatory effects of pravastatin have been reported in a similar experimental model of allergic airway inflammation.85 The anti-inflammatory properties of statins observed in animal models of allergic asthma84 and in smoking induced lung disease86 suggest that statin treatment could improve asthma control in smokers with asthma who are insensitive to treatment with corticosteroids.87
Histological evidence of decreased lung inflammation in mice treated with simvastatin. (A) Naive mouse given saline challenge. (B) Ovalbumin antigen challenged mouse showing peribronchial and perivascular inflammatory infiltrates with eosinophils and mucosal hyperplasia. (C) Ovalbumin challenged mouse treated with simvastatin showing a reduction in inflammatory infiltrates compared with (B). Stain: haematoxylin and eosin; magnification ×200. Reproduced with permission from McKay et al.84 © The American Association of Immunologists Inc, 2004.
COPD
In a rat model of smoking induced emphysema, Lee and co-workers72 found that simvastatin inhibited lung parenchymal destruction and peribronchial and perivascular inflammatory cell infiltration. Induction of MMP-9, a major inflammatory mediator, was reduced in the same model when the experiment was repeated using human lung microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. Pulmonary vascular remodelling was prevented and the decrease in endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression induced by smoking was inhibited.72 In a mouse model of emphysema, simvastatin reduced mRNA expression of IFN-γ, TNF-α and MMP-12 in the whole lung and reduced the numbers of neutrophils and lymphocytes and the concentration of TNF-α in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid,88 indicating reduced inflammation and remodelling.
Pulmonary hypertension
Experiments with rat pulmonary arterial fibroblasts indicate that statins decrease the normal proliferation in response to hypoxia.89 Statins also induce apoptosis of pulmonary vascular cells, mediated by inhibiting the prenylation of the small GTP-binding proteins.90 This—in addition to an improvement in pulmonary artery pressure, ventricular and blood vessel remodelling, and polycythaemia seen in a rat model of pulmonary hypertension91—confers a significant survival advantage following treatment with simvastatin.72,92 An open label clinical case series of patients with pulmonary hypertension showed that simvastatin delays disease progression and may improve survival.93
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an aggressive interstitial lung disease commonly affecting adults from middle age onwards. The prognosis is invariably poor, with a median survival of 3–5 years from diagnosis and no currently available efficacious treatment. Features of the pathogenesis of IPF are cell proliferation, collagen deposition, angiogenesis, and fibroblast differentiation into the profibrogenic myofibroblast phenotype.94 This is mediated through connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), an autocrine growth factor which is induced by TGF-β1. Early experimental data suggest that simvastatin could modify critical determinants of the profibrogenic machinery responsible for the aggressive clinical profile of IPF, and could potentially prevent adverse lung parenchymal remodelling associated with persistent myofibroblast formation by inhibiting CTGF gene and protein expression and overriding the induction by TGF-β1.95 This hypothesis has recently been tested in a clinical trial of lovastatin and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in IPF, but preliminary data showed no improvement in survival.96
Acute lung injury
In a model of acute lung injury, mice treated with simvastatin showed decreased lung permeability and a significant reduction in NF-κB mediated gene transcription, suggesting a potential role for statins in the management of this disease.97 In this model the mice were exposed to aerosolised bacterial LPS followed by intratracheal keratinocyte derived chemokine, inducing an airspace neutrophil influx which was reduced by simvastatin. Reduced parenchymal myeloperoxidase and microvascular permeability, indicators of inflammation, were also seen with lovastatin, as well as reduced concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines in airway fluid and serum.97
Ex vivo studies of neutrophils isolated from lovastatin treated mice confirmed that the inhibitory effects were statin dependent, affecting Rac activation, actin polymerisation, chemotaxis and bacterial killing. This anti-inflammatory effect, which is beneficial to acute lung injury, may have detrimental effects on the normal antibacterial clearance mechanisms of the lung. For example, the innate pulmonary clearance of Klebsiella pneumoniae was inhibited by lovastatin and the blood dissemination of this organism was enhanced.97 In other words, lovastatin appears to decrease pulmonary inflammation but there may be an immunological cost in inhibiting host defence and promoting infection.65
Community acquired pneumonia
The concern for the possible adverse effect of statins in reducing resistance to lung infection was partly addressed in a retrospective cohort study of patients with community acquired pneumonia which showed that statins were associated with a 22% decrease in overall 30 day mortality (from 28% to 6%). This remained significant even after adjustment for potential confounders such as previous co-morbidity which would normally be expected to increase mortality.98 However, there is still a need to monitor prospectively the effects of statin treatment on the immune response.
Lung transplantation
The outcomes in lung transplantation were compared between 39 patients taking statins for hyperlipidaemia (mainly atorvastatin and pravastatin) and 161 untreated controls. Acute rejection was less frequent, bronchoalveolar lavage showed lower total cellularity as well as lower proportions of neutrophils and lymphocytes, and survival was 91% compared with 54% in controls.99 This raises intriguing possibilities of an immunosuppressive role for statins, which suggests we are only beginning to explore the many applications for these drugs.
CONCLUSIONS
New drugs for the treatment of respiratory diseases are needed. The anti-inflammatory properties of statins are numerous and complex and, although incompletely understood, there is tantalising evidence that they might prove to be of clinical benefit in the treatment of a range of inflammatory lung diseases. What is needed now is to extend the evidence of efficacy of statins in different inflammatory lung diseases, initially in the form of small scale proof-of-concept clinical trials. The choice of outcome measures used to assess efficacy will need to be carefully considered for each disease, since statins may influence biomarkers of inflammation to a greater extent than more conventional clinical end points. If the results of these clinical trials are encouraging, larger studies will be required to establish the effectiveness and adverse side effect profile of statin treatment in individual diseases.
REFERENCES
Footnotes
This study was funded by Asthma UK.
Competing interests: none declared