Article Text
Abstract
Background: Sleep disordered breathing (SDB) is common in neuromuscular diseases but its relationship to respiratory function is poorly defined. A study was undertaken to identify distinct patterns of SDB, to clarify the relationships between SDB and lung and respiratory muscle function, and to identify daytime predictors for SDB at its onset, for SDB with continuous hypercapnic hypoventilation, and for diurnal respiratory failure.
Methods: Upright and supine inspiratory vital capacity (IVC, % predicted), maximal inspiratory muscle pressure (Pimax), respiratory drive (P0.1), respiratory muscle effort (P0.1/Pimax), and arterial blood gas tensions were prospectively compared with polysomnography and capnometry (Ptcco2) in 42 patients with primary myopathies.
Results: IVC correlated with respiratory muscle function and gas exchange by day and night. SDB evolved in three distinct patterns from REM hypopnoeas, to REM hypopnoeas with REM hypoventilation, to REM/non-REM (continuous) hypoventilation, and preceded diurnal respiratory failure. SDB correlated with IVC and Pimax which yielded highly predictive thresholds for SDB onset (IVC <60%, Pimax <4.5 kPa), SDB with continuous hypoventilation (IVC <40%, Pimax <4.0 kPa), and SDB with diurnal respiratory failure (IVC <25%, Pimax <3.5 kPa).
Conclusion: Progressive ventilatory restriction in neuromuscular diseases correlates with respiratory muscle weakness and results in progressive SDB which, by pattern and severity, can be predicted from daytime lung and respiratory muscle function.
- primary myopathies
- neuromuscular disease
- sleep disordered breathing
- daytime predictors
- IVC, inspiratory vital capacity
- Pimax, maximal inspiratory muscle pressure
- P0.1Pimax, measure of respiratory muscle effort
- Paco2, arterial carbon dioxide tension
- Pao2, arterial oxygen tension
- Ptcco2, mean transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension
- Sao2
- mean nocturnal oxyhaemoglobin saturation
Statistics from Altmetric.com
- IVC, inspiratory vital capacity
- Pimax, maximal inspiratory muscle pressure
- P0.1Pimax, measure of respiratory muscle effort
- Paco2, arterial carbon dioxide tension
- Pao2, arterial oxygen tension
- Ptcco2, mean transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension
- Sao2
- mean nocturnal oxyhaemoglobin saturation
Sleep disordered breathing (SDB) is common in patients with neuromuscular diseases and respiratory muscle weakness. The primary mechanism involves reduction of alveolar ventilation (as normally occurs during sleep due to a fall in central respiratory drive), blunted arousal thresholds, and reduced respiratory muscle activity.1 Disproportionate loss of upper airway muscle tone and diaphragm weakness may add additional loads, particularly during REM sleep, the time of maximal muscle hypotonia.2,3 Imbalance between respiratory load, drive and muscular capacity predisposes to SDB with desaturations, hypopnoeas, obstructive and central apnoeas, and hypercapnic hypoventilation which occur preferentially in REM sleep.4
SDB is rarely apparent from daytime clinical assessment, but may develop early in the course of disease5 and progress as ventilatory restriction worsens.6,7 Hypercapnic hypoventilation is the most significant of the sleep induced breathing disorders, signalling a critical imbalance between ventilatory demand and capacity and a high risk of life threatening decompensations. Hypercapnic hypoventilation is a reflection of nocturnal respiratory failure which precedes and probably contributes to the development of daytime respiratory failure. Timely recognition requires a high index of suspicion and evaluation with polysomnography and nocturnal capnometry. Non-invasive ventilation provides effective treatment and may improve survival.8,9
Because polysomnography is time consuming, expensive and not universally available, daytime predictors of SDB have been sought; however, relationships between nocturnal respiratory variables and daytime lung function have been highly variable.4,5,8,10 Although forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) <40% was recently reported as a predictor of nocturnal hypoventilation, hypoventilation was defined as desaturations under 90% during more than 2% of total sleep time11 and is likely to have included transient episodes of limited relevance.
We have conducted a detailed study of daytime lung and respiratory muscle function and nocturnal respiration in a large group of patients with primary myopathies to test the hypothesis that SDB evolved in distinct patterns that were directly related to lung and respiratory muscle function. We were particularly interested to identify predictive thresholds for (1) SDB at its onset, (2) SDB involving hypercapnic hypoventilation during more than 50% of total sleep time, a degree of hypoventilation likely to require non-invasive ventilation, and (3) daytime respiratory failure.
METHODS
Subjects
Forty two patients (17 women) of mean (SD) age 28.7 (15.8) years (range 14–63) and body mass index (BMI) 18.7 (5.4) kg/m2 with primary myopathies were studied: 10 Duchenne muscular dystrophy, 10 congenital muscular dystrophy, seven limb girdle dystrophy, 12 acid maltase deficiency, one nemaline myopathy, one myotonic dystrophy, and one non-classified myopathy. A neurologist had assessed all patients and the diagnosis had been confirmed by histology and, where possible, by cell molecular biology. Twenty three patients were ambulatory, 19 were wheelchair bound. Thirteen patients (10 Duchenne muscular dystrophy, three congenital muscular dystrophy) had severe kyphoscoliosis, seven had had stabilisation surgery. No patient was using ventilatory support.
Lung function
Inspiratory vital capacity (IVC), forced expiratory volumes (FVC, FEV1), and flow-volume loops were measured with a hand held spirometer (Spiromed 180, Fukuda Sangyo, Pulmonary Products, Tokyo) calibrated before each use. Measurements were obtained in the sitting and supine positions if tolerated. The best of three consistent efforts (<5% variability) was used. Patients with obstructive ventilatory defect (FEV1/FVC <75%) were excluded. IVC, which correlates closely with FVC (R=0.98, p<0.0001), was selected as the reference measure for ventilatory capacity as it more directly reflects diaphragm function and is less affected by isolated expiratory muscle weaknesses. IVC% was used synonymously with IVC% predicted. Predicted values for adolescents were derived from the data of Zapletal et al12 and for adults from the data of the European Community of Steel and Coal.13 Supine measurements were used for comparative analysis with nocturnal respiratory variables. Arterial blood gas tensions were determined from radial artery or arterialised ear lobe blood in an automated blood gas analyser (AVL 500, AVL LIST GmbH Medizintechnik, Graz, Austria).
Maximal inspiratory muscle pressure (Pimax, best of three efforts) and mouth occlusion pressure at 0.1 s of tidal breathing (P0.1, mean of 8–10 consistent measurements) were determined using a computerised manometer allowing for online graphic display and quality control of pressure curves (ZAN Meβgeräte, Obertulba, Germany). Respiratory muscle effort was derived as P0.1/Pimax.7,14
Diaphragm weakness was defined as >20% postural fall in IVC combined with development of either dyspnoea, thoracoabdominal paradox, or accessory muscle activity.15
Polysomnography (PSG)
PSG was performed according to the standards of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine.16 No oxygen was supplemented. Electroencephalogram, electrooculogram, submental electromyogram and microphone, single lead electrocardiogram, oronasal flow and respiratory movement sensors (thermistor and piezoelectrical crystal; ProTech, Woodville, WA), oxyhaemoglobin saturation (INVIVO Pulse Oximeter 4500, INVIVO Research Inc, Orlando, FL, USA), and transcutaneous Pco2 (Ptcco2) (Radiometer, Copenhagen, Denmark) were recorded onto a computerised work station (Compumedics, Melbourne, Australia). Sleep stages and respiratory parameters were scored manually. Apnoeas were defined as >10 s cessation of airflow and respiratory effort (central) or >10 s cessation of airflow with persisting effort (obstructive). Hypopnoeas were defined as >10 s discernible reduction in airflow or thoracoabdominal effort accompanied by >3% oxyhaemoglobin desaturation or EEG arousal of >3 s. SDB was considered present if the respiratory disturbance index (RDI) was >5 events per hour of total sleep or 10 per hour of REM sleep. Hypoventilation was defined as Ptcco2 >6.67 kPa (50 mm Hg)7,17 for >50% of REM sleep alone (REM hypoventilation) or during both REM and >50% of non-REM sleep (continuous hypoventilation). Diurnal respiratory failure (dRF) was defined as daytime hypercapnia on arterial blood gas testing (Paco2 ≥6.0 kPa (45 mm Hg)) obtained before PSG, and nocturnal alveolar hypoventilation.
Statistical analysis
Analysis was performed with Statistica 6.0 software package (StatSoft Inc, Tulsa, OK, USA). Interrelationships between vital capacity, respiratory muscle function, polysomnographic parameters, and gas exchange were analysed using the Spearman’s rank test. Group comparisons were performed using the Mann-Whitney U test. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed with SDB as the dependent variable and IVC, Pimax, age, and BMI as the independent variables. Predictive values of IVC and Pimax were computed by applying bidimensional analysis at equal sensitivity to specificity ratio to the respective receiver operator curves (ROC). The dependent variable with the maximal area under the curve (AUC) was considered to be the strongest predictor. All results are presented as mean (SD) values. p values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Lung and respiratory muscle function
Upright IVC was normal in nine patients, 60–79% in five, 40–59% in seven, 20–39% in 14, and <20% in seven patients. Daytime hypercapnia was present in 12 patients (Paco2 8.3 (2.1) kPa, Pao2 8.3 (2.3) kPa, IVC 18.2 (2.1)%). Diaphragm weakness was found in 11 patients (26%) and occurred at any degree of ventilatory restriction. It resulted in a supine fall in IVC of 32.6 (10.8)% and a supine fall in Pimax of 18.2 (13.8)%. IVC correlated with Pimax (R=0.67, p<0.0001), P0.1/Pimax (R=–0.68, p<0.0001), daytime Pao2 (R=0.53, p<0.001), and Paco2 (R=–0.50, p=0.001; fig 1). The relationship was curvilinear with both Paco2 and P0.1/Pimax. Paco2 and P0.1/Pimax, however, did not interrelate (R=0.51, p<0.001).
Daytime respiratory function shown as relationships between IVC and (A) Pimax (R=0.67, p<0.0001), (B) P0.1/Pimax (R=–0.68, p<0.0001), (C) Paco2 (R=–0.50, p<0.001), and (D) Pao2 (R=0.53, p<0.001); n=42. IVC=inspiratory vital capacity; Pimax=maximal inspiratory muscle pressure; P0.1/Pimax=measure of respiratory muscle effort; Paco2=arterial carbon dioxide tension; Pao2=arterial oxygen tension.
Sleep disordered breathing
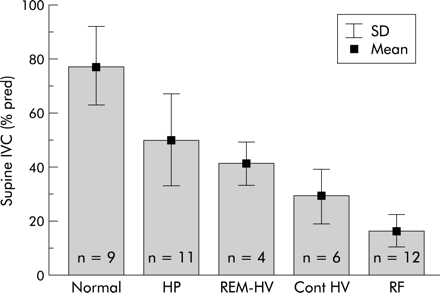
SDB was found in 33 patients. Obstructive apnoeas were found in only six patients, two with Duchenne muscular dystrophy, two with limb girdle dystrophy, and two with acid maltase deficiency. The predominant finding in all subjects were hypopnoeas which lacked terminating snorts and lost circumscription at lower grades of ventilatory restriction. SDB in all patients (n=33) evolved in three distinct patterns from REM sleep hypopnoeas in mild ventilatory restriction to REM sleep hypopnoeas with REM hypoventilation in moderate ventilatory restriction to sleep stage independent (continuous) hypoventilation with or without REM sleep hypopnoeas in severe restriction. The SDB pattern was closely correlated with IVC (R=0.88; fig 2), Pimax (R=0.65, p<0.0005), P0.1/Pimax (R=0.7, p<0.0005), and mean Ptcco2 (R=–0.83, p<0.0005). Hypoventilation (as % of total sleep time) occurred in 1.5 (3.2)% of those with REM hypopnoeas (mean Ptcco2 6.0 (0.3) kPa, maximal Ptcco2 6.4 (0.4) kPa), in 20.0 (21.2)% of those with REM hypopnoeas with REM hypoventilation (mean Ptcco2 6.2 (0.4) kPa, maximal Ptcco2 7.3 (0.8) kPa), and in 66.2 (36.1)% of those with continuous hypoventilation (mean Ptcco2 7.0 (0.4) kPa, maximal Ptcco2 7.9 0.9 kPa). IVC and Pimax also correlated with mean Sao2 and mean Ptcco2 (fig 3). Multiple regression analysis identified IVC (p<0.0001) and Pimax (p<0.001), but not age or BMI, as the strongest determinants of SDB.
Relationships between IVC and respiratory abnormality (R=0.88, p<0.0001). Normal=no sleep disordered breathing; HP=hypopnoeas in REM sleep; REM-HV=hypoventilation in REM sleep; REM/non-REM-HV=continuous hypoventilation in REM and non-REM sleep; RF=diurnal respiratory failure.
Nocturnal respiratory function expressed as relationships between (A) IVC and Sao2 (R=0.74, p<0.0001), (B) IVC and Ptcco2 (R=–0.8, p<0.0001), (C) Pimax and Sao2 (R=0.55, p<0.0005), and (D) Pimax and Ptcco2 (R=–0.56, p<0.0001). IVC=inspiratory vital capacity; Pimax=maximal inspiratory pressure; Sao2=mean nocturnal oxyhaemoglobin saturation; Ptcco2=mean transcutaneous carbon dioxide tension.
Predictors of SDB
Predictive thresholds of IVC (fig 4) and Pimax were computed for SDB onset, SDB with continuous hypoventilation, and diurnal respiratory failure. Sensitivities, specificities and AUC values are summarised in table 1.
Predictors of sleep disordered breathing (SDB) and diurnal respiratory failure
Predictive thresholds of IVC computed for (A) onset of sleep disordered breathing (SDB), (B) SDB with continuous hypercapnic hypoventilation (HV), and (C) diurnal respiratory failure (RF). Left panels show scatter plots, right panels the ROC plots. Dashed lines indicate optimal cut off points for predictive values.
DISCUSSION
This study of daytime and nocturnal respiratory function in primary myopathies has shown close relationships between lung function, respiratory muscle function, and SDB, and has identified highly predictive thresholds for SDB onset, SDB with hypercapnic hypoventilation, and daytime respiratory failure which, because it is invariably associated with nocturnal hypoventilation, was classified as diurnal respiratory failure.
We confirmed that vital capacity related directly to respiratory muscle strength, a finding previously reported in polymyositis18 and Duchenne muscular dystrophy19 but not noted in other studies of neuromuscular diseases.4,5 We have expanded the existing data by showing for the first time that P0.1 and P0.1/Pimax increased progressively with declining respiratory muscle strength, a finding likely to reflect the compensatory rise in respiratory drive and muscle effort in an attempt to maintain alveolar ventilation. The close relationship between vital capacity and respiratory muscle function underlines the role of respiratory muscle weakness in the development of restrictive ventilatory defect and implies that intrinsic lung disease was absent. Indeed, our patients had no evidence of parenchymal lung disease and gas exchange was maintained in the near normal range until IVC fell to <25%. Acute on chronic respiratory failure was the presenting feature in three patients with IVC <25% and accounts for the disproportionate degree of hypoxaemia and hypercapnia seen in this setting.
Assuming that the same pathophysiology was present during sleep, we hypothesised that SDB would primarily depend on respiratory muscle function and ventilatory restriction. Sleep, because of its detrimental effects on respiratory muscle activity, drive and load, represents a significant stress test to the respiratory system, particularly in the setting of decreased respiratory muscle capacity. The severity of SDB is therefore likely to provide a good index of functional respiratory muscle reserve. Indeed, we found a significant correlation between vital capacity, respiratory muscle function, and SDB severity graded empirically by hypopnoea pattern and degree of hypercapnia. As expected, SDB occurred predominantly in REM sleep, a period of relative muscle hypotonia or atonia. SDB differed from the central or obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndromes previously reported20–22 and the RDI did not correlate with IVC. Hypopnoeas predominated in early restrictive disease but, as restriction worsened, changed into poorly circumscribed and ever more prolonged hypoventilatory phases that did not enter the hypopnoea score. RDI was therefore increased in the early phase but was normal in advanced restrictive disease. Ptcco2, by definition, increased with SDB severity. It also, however, showed a progressive increase with declining lung and respiratory muscle function, indicating progressive respiratory muscle fatigue as a result of the widening gap between sleep imposed demands and respiratory muscle capacity.
We wanted to identify predictive thresholds for SDB at its onset, for SDB with continuous hypercapnic hypoventilation, and for diurnal respiratory failure as they represent turning points in the course of a patient with progressive myopathic disease. The predictors have important implications for the practical management of these patients whose respiratory limitations may escape attention because of desynchronous involvement of peripheral and respiratory muscle groups, minimal dyspnoea because of adaptation and a sedentary life style, and normal blood gases until very late in the course of the disease. With severe muscle weakness life threatening complications may be triggered by minor increases in respiratory demands, such as occur with fever, respiratory infection, or surgical interventions. It is paramount to identify the patients at risk. Sitting/supine bedside spirometric testing at 6–12 month intervals provides a low cost, reproducible, and easy to perform test that allows stratification of patients into distinct risk groups. Those with IVC >60% are unlikely to have SDB, indicating good respiratory reserve and minimal risk of respiratory complications. Those with IVC <60% are predisposed to SDB, indicating reduced respiratory reserve and the need for polysomnography for assessment. At IVC <40% continuous hypercapnic hypoventilation becomes the major concern and capnometry is warranted for proper evaluation. As continuous hypercapnic hypoventilation indicates barely compensated respiratory failure and a high risk of acute respiratory deterioration, non-invasive ventilation might be considered at this point.23
Acknowledgments
C Schwake was supported by an interdisciplinary research grant from the University of Essen, grant # 107505-0/IFORES.