Abstract
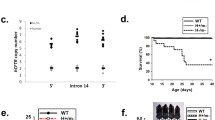
We have generated mice carrying the most common mutation in cystic fibrosis (CF), ΔF508, within the cystic fibrosis (Cftr) gene. Mutant animals show pathological and electrophysiological changes consistent with a CF phenotype. ΔF508−/− mice die from peritonitis and show deficiencies in cAMP–activated electrogenic Cl− transport. These mice produce ΔF508 transcripts and show the temperature–dependent trafficking defect first described for the human ΔF508 CFTR protein. A functional CFTR Cl− channel not demonstrated by null CF mice or present at 37 °C was detected following incubation of epithelial cells at 27 °C. Thus, these mice are an accurate ΔF508 model and will be valuable for testing drugs aimed at overcoming the ΔF508 trafficking defect.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jackson, A.D.M. The Natural History of Cystic Fibrosis ((Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1989).
Mearns, M.B. Cystic Fibrosis: The First 50 years. (John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1993).
Riordan, J.R. et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterisation of complementary DMA. Science 245, 1066–1072 (1989).
Kerem, B.-S. et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science 245, 1073–1080 (1989).
Anderson, M.P. et al. Demonstration that CFTR is a chloride channel by alteration of its anion selectivity. Science 253, 202–205 (1991).
Bear, C.E. et al. Purification and functional reconstitution of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Cell 68, 809–818 (1992).
Tsui, L.-C., Markiewicz, D., Zielenski, J., Corey, M. & Durie, P. Mutation analysis in cystic fibrosis. in Cystic Fibrosis: Current Topics Vol. 1, (eds Dodge, J.A., Brock, D.J.H., Widdicombe, J.H.) 27–44 (John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, 1993).
Snouwaert, J.N. et al. An animal model for cystic fibrosis made by gene targeting. Science 257, 1083–1088 (1992).
Clarke, L.L. et al. Defective epithelial chloride transport in a gene-targeted mouse model of cystic fibrosis. Science 257, 1125–1128 (1992).
Dorin, J.R. et al. Cystic fibrosis in the mouse by targeted insertional mutagenesis. Nature 359, 211–215 (1992).
Ratcliff, R. et al. Production of a severe cystic fibrosis mutation in mice by gene targeting. Nature Genet. 4, 35–41 (1993).
O'Neal, W.K. et al. A severe phenotype in mice with a duplication of exon 3 in the cystic fibrosis locus. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 1561–1569 (1993).
Gray, M.A., Winpenny, J.P., Porteous, D.J., Dorin, J.R. & Argent, B.E. CFTR and calcium-activated chloride currents in pancreatic duct cells of a transgenic CF mouse. Am. J. Physiol. 266, 213–221 (1994).
Grubb, B.R. et al. Inefficient gene transfer by adenovirus vector to cystic fibrosis airway epithelia of mice and humans. Nature 371, 802–806 (1994).
Alton, E.W. et al. Non-invasive liposome-mediated gene delivery can correct the ion transport defect in cystic fibrosis mutant mice. Nature Genet. 5, 135–142 (1993).
Hyde, S.C. et al. Correction of the ion transport defect in cystic fibrosis transgenic mice by gene therapy. Nature 362, 250–255 (1993).
Cheng, S.H. et al. Defective intracellular transport and processing of CFTR is the molecular basis of most cystic fibrosis. Cell 63, 827–834 (1990).
Denning, G.M. et al. Processing of mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is temperature-sensitive. Nature 358, 761–764 (1992).
Li, C. et al. The cystic fibrosis mutation (ΔF508) does not influence the chloride channel activity of CFTR. Nature Genet. 3, 311–316 (1993).
Lukacs, G.L. et al. The ΔF508 mutation decreases the stability of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in the plasma membrane. Determination of functional half-lives on transfected cells. J. biol. Chem. 268, 21592–21598 (1993).
Sherry, A.M., Cuppoletti, J. & Malinowska, D.H. Differential acidic pH sensitivity of ΔF508 CFTR Ch channel activity in lipid bilayers. Am. J. Physiol. 266, 870–875 (1994).
Dalemans, W. et al. Altered chloride ion channel kinetics associated with ΔF508 cystic fibrosis mutation. Nature 354, 526–528 (1991).
Thomas, P.J. & Pedersen, P.L. Effects of the ΔF508 mutation on the structure, function, and folding of the first nucleotide-binding domain of CFTR. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 25, 11–19 (1993).
Pind, S., Riordan, J.R. & Williams, D.B. Participation of the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone calnexin (p88, IP90) in the biogenesis of the cystic f ibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J. biol. Chem. 269, 12784–12788 (1994).
Yang, Y., Janich, S., Cohn, J.A. & Wilson, J.M. The common variant of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is recognized by hsp70 and degraded in a pre-Golgi nonlysosomal compartment. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 9480–9484 (1993).
Cheng, S.H. et al. Functional activation of the cystic fibrosis trafficking mutant ΔF508-CFTR by overexpression. Am. J. Physiol. 268, L615–624 (1995).
Kuehn, M.R., Bradley, A., Robertson, E.J. & Evans, M.J. A potential animal model for Lesch-Nyhan syndrome through introduction of HPRT mutations into mice. Nature 326, 295–298 (1987).
Cuthbert, A.W., Halstead, J., Ratcliff, R., Coiledge, W.H. & Evans, M.J. The genetic advantage hypothesis in cystic fibrosis heterozygotes: a murine study. J. Physiol. 482, 449–454 (1995).
Cuthbert, A.W. et al. Ion-transporting activity in the murine colonic epithelium of normal animals and animals with cystic fibrosis. Pflugers Arch. 428, 508–515 (1994).
Grubb, B.R., Paradiso, A.M. & Boucher, R.C. Anomalies in ion transport in CF mouse tracheal epithelium. Am. J. Physiol. 267, 293–300 (1994).
MacLeod, R.J., Hamilton, J.R., Kopelman, H. & Sweezey, N.B. Developmental differences of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator functional expression in isolated fetal distal airway epithelial cells. Pediatric Res. 35, 45–49 (1993).
Knowles, M.R. et al. Abnormal ion permeation through cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelium. Science 221, 1067–1069 (1983).
Drumm, M.L. et al. Chloride conductance expressed by ΔF508 and other mutant CFTRs in Xenopus oocytes. Science 254, 1797–1799 (1991).
Johnson, L.G. et al. Efficiency of gene transfer for restoration of normal airway epithelial function in cystic fibrosis. Nature Genet. 2, 21–25 (1992).
Chu, C.S., Trapnell, B.C., Curristin, S.M., Cutting, G.R. & Crystal, R.G. Extensive post-transcriptional deletion of the coding sequences for part of nucleotide-binding fold 1 in respiratory epithelial mRNA transcripts of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene is not associated with the clinical manifestations of cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest. 90, 785–790 (1992).
Dorin, J.R. et al. Long-term survival of the exon 10 insertional cystic fibrosis mutant mouse is a consequence of low level residual wild-type cftr gene expression Mamm. Genome 5, 465–472 (1994).
Reid, L.A., Gregg, R.G., Smithies, O. & Koller, B.H. Regulatory elements in the introns of the human HPRT gene are necessary for its expression in embryonic stem cells. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 4299–4303 (1990).
Kim, H.-S. & Smithies, O. Recombinant fragment assay for gene targeting based on the polymerase chain reaction. Nucl. Acids Res. 15, 8887–8903 (1988).
Chomczynski, P. & Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162, 156–159 (1987).
Delaney, S.J. et al. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator splice variants are not conserved and fail to produce chloride channels. Nature Genet. 4, 426–431 (1993).
Illsley, N.P. & Verkman, A.S. Membrane chloride transport measured using a chloride-sensitive fluorescent indicator. Biochemistry 26, 1215–1219 (1987).
Rich, D.P. et al. Regulation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channel activity by negative charge in the R domain J. biol. Chem. 268, 20259–20267 (1993).
Marshall, J. et al. Stoichiometry of recombinant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in epithelial cells and its functional reconstitution into cells in vitro J. biol. Chem. 269, 29897–2995 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colledge, W., Abella, B., Southern, K. et al. Generation and characterization of a ΔF508 cystic fibrosis mouse model. Nat Genet 10, 445–452 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0895-445
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0895-445
This article is cited by
-
Genetic quality: a complex issue for experimental study reproducibility
Transgenic Research (2022)
-
Serum inflammatory profiles in cystic fibrosis mice with and without Bordetella pseudohinzii infection
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Methodological tools to study species of the genus Burkholderia
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2021)
-
Impact of gene editing on the study of cystic fibrosis
Human Genetics (2016)
-
Animal Models in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2015)