Abstract
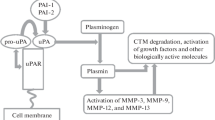
Several molecular interactions between the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and the plasminogen/plasmin (fibrinolytic) system may affect cellular fibrinolysis. MMP-3 (stromelysin-1) specifically hydrolyzes urokinase (u-PA), yielding a 17 kD NH2-terminal fragment containing the functionally intact receptor (u-PAR)-binding sequence and a 32 kD COOH-terminal fragment containing the intact serine proteinase domain. MMP-3 generates an angiostatin like fragment (containing kringles 1-4 with the cellular binding domains) from plasminogen. Treatment with MMP-3 of monocytoid THP-1 cells saturated with bound plasminogen, resulted in a dose-dependent reduction of the amount of u-PA-activatible plasminogen. Treatment with MMP-3 of cell-bound u-PA, in contrast, did not alter cell-associated u-PA activity. These data thus indicate that MMP-3 may downregulate cell-associated plasmin activity by decreasing the amount of activatible plasminogen, with out affecting cell-bound u-PA activity. MMP-3 also specifically interacts with the main inhibitors of the fibrinolytic system. Thus, MMP-3 specifically hydrolyzes human α2-antiplasmin (α2-AP), the main physiological plasmin inhibitor. α2-AP cleaved by MMP-3 no longer forms a stable complex with plasmin and no longer interacts with plasminogen. Cleavage and inactivation of α2-AP by MMP-3 may constitute a mechanism favoring local plasmin-mediated proteolysis. Furthermore, MMP-3 specifically hydrolyzes and inactivates human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). Stable PAI-1 bound to vitronectin is cleaved and inactivated by MMP-3 in a comparable manner as free PAI-1; the cleaved protein, however, does not bind to vitronectin. Cleavage and inactivation of PAI-1 by MMP-3 may thus constitute a mechanism decreasing the antipro teolytic activity of PAI-1 and impairing the potential inhibitory effect of vitronectin-bound PAI-1 on cell adhesion and/or migration. These molecular interactions of MMP-3 with enzymes, substrates and inhibitors of the fibrinolytic system may thus play a role in the regulation of (cellular) fibrinolysis. Furthermore, the temporal and topographic expression pattern of MMP components, as well as studies in gene-deficient mice, suggest a functional role in neointima formation after vascular injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Lijnen, H. R., and Collen, D. (1995) Baillière's Clin. Haematol., 8, 277-290.
Lijnen, H. R., and Collen, D. (1999) Thromb. Haemost., 82, 837-845.
Lijnen, H. R. (2000) Fibrinolysis Proteolysis, 14, 175-181.
Carmeliet, P., Moons, L., Herbert, J.-M., Crawley, J., Lupu, F., Lijnen, H. R., and Collen, D. (1997) Circ. Res., 81, 829-839.
Carmeliet, P., Moons, L., Lijnen, H. R., Baes, M., Lemaitre, V., Tipping, P., Drew, A., Eeckhout, Y., Shapiro, S., Lupu, F., and Collen, D. (1997) Nature Genet., 17, 439-444.
Lijnen, H. R., van Hoef, B., Vanlinthout, I., Verstreken, M., Rio, M. C., and Collen, D. (1999) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 19, 2863-2870.
Nagase, H., and Woessner, J. F., Jr. (1999) J. Biol. Chem., 274, 21491-21494.
Okada, Y., Gonoji, Y., Naka, K., Tomita, K., Nakanishi, I., Iwata, K., Yamashita, K., and Hayakawa, T. (1992) J. Biol. Chem., 267, 21712-21719.
Suzuki, K., Enghild, J. J., Morodomi, T., Salvesen, G., and Nagase, H. (1990) Biochemistry, 29, 10261-10270.
Eeckhout, Y., and Vaes, G. (1977) Biochem. J., 166, 21-31.
He, C. S., Wilhelm, S. M., Pentland, A. P., Marmer, B. L., Grant, G. A., Eisen, A. Z., and Goldberg, G. I. (1989) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 86, 2632-2636.
Baramova, E. N., Bajou, K., Remacle, A., L'Hoir, C., Krell, H. W., Weidle, U. H., Noel, A., and Foidart, J. M. (1997) FEBS Lett., 405, 157-162.
Keski-Oja, J., Lohi, J., Tuuttila, A., Tryggvason, K., and Vartio, T. (1992) Exp. Cell Res., 202, 471-476.
Lijnen, H. R., Silence, J., van Hoef, B., and Collen, D. (1998) Blood, 91, 2045-2053.
Ogata, Y., Enghild, J. J., and Nagase, H. (1992) J. Biol. Chem., 267, 3581-3584.
Brew, K., Dinakarpandian, D., and Nagase, H. (2000) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1477, 267-283.
Lijnen, H. R., Silence, J., Lemmens, G., Frederix, L., and Collen, D. (1998) Thromb. Haemost., 79, 1171-1176.
Hajjar, K. A., Hamel, N. M., Harpel, P. C., and Nachman, R. L. (1987) J. Clin. Invest., 80, 1712-1719.
Hajjar, K. A., Harpel, P. C., Jaffe, E. A., and Nachman, R. L. (1986) J. Biol. Chem., 261, 11656-11662.
Miles, L. A., and Plow, E. F. (1985) J. Biol. Chem., 260, 4303-4311.
Stephens, R. W., Pöllänen, J., Tapiovaara, H., Leung, K. C., Sim, P. S., Salonen, E. M., Ronne, E., Behrendt, N., Dano, K., and Vaheri, A. (1989) J. Cell Biol., 108, 1987-1995.
Miles, L. A., and Plow, E. F. (1988) Fibrinolysis, 2, 61-71.
Plow, E. F., Freaney, D. E., Plescia, J., and Miles, L. A. (1986) J. Cell Biol., 103, 2411-2420.
Miles, L. A., Dahlberg, C. M., Levin, E. G., and Plow, E. F. (1989) Biochemistry, 28, 9337-9343.
Miles, L. A., Dahlberg, C. M., Plescia, J., Felez, J., Kato, K., and Plow, E. F. (1991) Biochemistry, 30, 1682-1691.
Hajjar, K. A., and Nachman, R. L. (1988) J. Clin. Invest., 82, 1769-1778.
Félez, J., Miles, L. A., Fàbregas, P., Jardi, M., Plow, E. F., and Lijnen, H. R. (1996) Thromb. Haemost., 76, 577-584.
Barnathan, E. S., Kuo, A., van der Keyl, H., McCrae, K. R., Larsen, G. R., and Cines, D. B. (1988) J. Biol. Chem., 263, 7792-7799.
Hajjar, K. A., Jacovina, A. T., and Chacko, J. (1994) J. Biol. Chem., 269, 21191-21197.
Ellis, V., Behrendt, N., and Danø, K. (1991) J. Biol. Chem., 266, 12752-12758.
Ellis, V., Scully, M. F., and Kakkar, V. V. (1989) J. Biol. Chem., 264, 2185-2188.
Ellis, V., Wun, T. C., Behrendt, N., Ronne, E., and Dano, K. (1990) J. Biol. Chem., 265, 9904-9908.
Lee, S. W., Ellis, V., and Dichek, D. A. (1994) J. Biol. Chem., 269, 2411-2418.
Ellis, V., Whawell, S. A., Werner, F., and Deadman, J. J. (1999) Biochemistry, 38, 651-659.
Chavakis, T., Kanse, S. M., Yutzy, B., Lijnen, H. R., and Preissner, K. T. (1998) Blood, 91, 2305-2312.
May, A. E., Kanse, S. M., Chavakis, T., and Preissner, K. T. (1998) Fibrinolysis Proteolysis, 12, 205-210.
Ugwu, F., van Hoef, B., Bini, A., Collen, D., and Lijnen, H. R. (1998) Biochemistry, 37, 7231-7236.
Lijnen, H. R., Ugwu, F., Bini, A., and Collen, D. (1998) Biochemistry, 37, 4699-4702.
Ugwu, F., Lemmens, G., Collen, D., and Lijnen, H. R. (1999) Thromb. Haemost., 82, 1127-1131.
Ugwu, F., Lemmens, G., Collen, D., and Lijnen, H. R. (2001) Thromb. Res., 102, 61-69.
Lijnen, H. R., van Hoef, B., and Collen, D. (2001) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1547, 206-213.
Lijnen, H. R., Arza, B., van Hoef, B., Collen, D., and Declerck, P. J. (2000) J. Biol. Chem., 275, 37645-37650.
Carmeliet, P., and Collen, D. (1988) Thromb. Res., 91, 255-285.
Dollery, C. M., McEwan, J. R., and Henney, A. M. (1995) Circ. Res., 77, 863-868.
Celentano, D. C., and Frishman, W. H. (1997) J. Clin. Pharmacol., 150, 761-776.
Carmeliet, P., Moons, L., Ploplis, V., Plow, E., and Collen, D. (1997) J. Clin. Invest., 99, 200-208.
Carmeliet, P., Moons, L., Herbert, J.-M., Crawley, J., Lupu, F., Lijnen, R., and Collen, D. (1997) Circ. Res., 81, 829-839.
Lijnen, H. R., van Hoef, B., Dewerchin, M., and Collen, D. (2000) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 20, 1488-1492.
Lijnen, H. R., Lupu, F., Moons, L., Carmeliet, P., Goulding, D., and Collen, D. (1999) Thromb. Haemost., 81, 799-807.
Lijnen, H. R., van Hoef, B., Soloway, P., and Collen, D. (1999) Circ. Res., 85, 1186-1191.
Lovdahl, C., Thyberg, J., Cercek, B., Blomgren, K., Dimayuga, P., Kallin, B., and Hultgardh-Nilsson, A. (1999) Histol. Histopathol., 14, 1101-1112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lijnen, H.R. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Cellular Fibrinolytic Activity. Biochemistry (Moscow) 67, 92–98 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013908332232
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013908332232