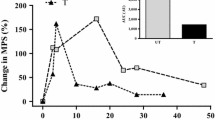
Abstract
The effects of timed ingestion of high-quality protein before and after resistance exercise are not well known. In this study, young men were randomized to protein (n = 11), placebo (n = 10) and control (n = 10) groups. Muscle cross-sectional area by MRI and muscle forces were analyzed before and after 21 weeks of either heavy resistance training (RT) or control period. Muscle biopsies were taken before, and 1 and 48 h after 5 × 10 repetition leg press exercise (RE) as well as 21 weeks after RT. Protein (15 g of whey both before and after exercise) or non-energetic placebo were provided to subjects in the context of both single RE bout (acute responses) as well as each RE workout twice a week throughout the 21-week-RT. Protein intake increased (P ≤ 0.05) RT-induced muscle cross-sectional area enlargement and cell-cycle kinase cdk2 mRNA expression in the vastus lateralis muscle suggesting higher proliferating cell activation response with protein supplementation. Moreover, protein intake seemed to prevent 1 h post-RE decrease in myostatin and myogenin mRNA expression but did not affect activin receptor IIb, p21, FLRG, MAFbx or MyoD expression. In conclusion, protein intake close to resistance exercise workout may alter mRNA expression in a manner advantageous for muscle hypertrophy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams GR, Caiozzo VJ, Haddad F, Baldwin KM (2002) Cellular and molecular responses to increased skeletal muscle loading after irradiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C1182–C1195
Andersen LL, Tufekovic G, Zebis MK, Crameri RM, Verlaan G, Kjaer M, Suetta C, Magnusson P, Aagaard P (2005) The effect of resistance training combined with timed ingestion of protein on muscle fiber size and muscle strength. Metabolism 54:151–156
Berthet C, Aleem E, Coppola V, Tessarollo L, Kaldis P (2003) Cdk2 knockout mice are viable. Curr Biol 13:1775–1785
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK, Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K, Pan ZQ, Valenzuela DM, DeChiara TM, Stitt TN, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (2001) Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294:1704–1708
Boirie Y, Dangin M, Gachon P, Vasson MP, Maubois JL, Beaufrere B (1997) Slow and fast dietary proteins differently modulate postprandial protein accretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:14930–14935
Borsheim E, Tipton KD, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR (2002) Essential amino acids and muscle protein recovery from resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E648–E657
Burke DG, Chilibeck PD, Davidson KS, Candow DG, Farthing J, Smith-Palmer T (2001) The effect of whey protein supplementation with and without creatine monohydrate combined with resistance training on lean tissue mass and muscle strength. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 11:349–364
Candow DG, Burke NC, Smith-Palmer T, Burke DG (2006a) Effect of whey and soy protein supplementation combined with resistance training in young adults. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 16:233–244
Candow DG, Chilibeck PD, Facci M, Abeysekara S, Zello GA (2006b) Protein supplementation before and after resistance training in older men. Eur J Appl Physiol 97:548–556
Charge SB, Rudnicki MA (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 84:209–238
Cribb PJ, Hayes A (2006) Effects of supplement timing and resistance exercise on skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:1918–1925
Cribb PJ, Williams AD, Stathis CG, Carey MF, Hayes A (2007) Effects of whey isolate, creatine, and resistance training on muscle hypertrophy. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:298–307
Durnin JV, Womersley J (1974) Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Br J Nutr 32:77–97
Esmarck B, Andersen JL, Olsen S, Richter EA, Mizuno M, Kjaer M (2001) Timing of postexercise protein intake is important for muscle hypertrophy with resistance training in elderly humans. J Physiol 535:301–311
Gibala MJ, MacDougall JD, Tarnopolsky MA, Stauber WT, Elorriaga A (1995) Changes in human skeletal muscle ultrastructure and force production after acute resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol 78:702–708
Guernec A, Chevalier B, Duclos MJ (2004) Nutrient supply enhances both IGF-I and MSTN mRNA levels in chicken skeletal muscle. Domest Anim Endocrinol 26:143–154
Ha E, Zemel MB (2003) Functional properties of whey, whey components, and essential amino acids: mechanisms underlying health benefits for active people (review). J Nutr Biochem 14:251–258
Halevy O, Nadel Y, Barak M, Rozenboim I, Sklan D (2003) Early posthatch feeding stimulates satellite cell proliferation and skeletal muscle growth in turkey poults. J Nutr 133:1376–1382
Han B, Tong J, Zhu MJ, Ma C, Du M (2008) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and leucine activate pig myogenic satellite cells through mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Mol Reprod Dev 75:810–817
Hartman JW, Tang JE, Wilkinson SB, Tarnopolsky MA, Lawrence RL, Fullerton AV, Phillips SM (2007) Consumption of fat-free fluid milk after resistance exercise promotes greater lean mass accretion than does consumption of soy or carbohydrate in young, novice, male weightlifters. Am J Clin Nutr 86:373–381
Hlaing M, Shen X, Dazin P, Bernstein HS (2002) The hypertrophic response in C2C12 myoblasts recruits the G1 cell cycle machinery. J Biol Chem 277:23794–23799
Hulmi JJ, Ahtiainen JP, Kaasalainen T, Pollanen E, Häkkinen K, Alen M, Selanne H, Kovanen V, Mero AA (2007) Postexercise myostatin and activin IIb mRNA levels: effects of strength training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:289–297
Hulmi JJ, Kovanen V, Lisko I, Selanne H, Mero AA (2008) The effects of whey protein on myostatin and cell cycle-related gene expression responses to a single heavy resistance exercise bout in trained older men. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:205–213
Häkkinen K, Pakarinen A, Newton RU, Kraemer WJ (1998) Acute hormone responses to heavy resistance lower and upper extremity exercise in young versus old men. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 77:312–319
Häkkinen K, Pakarinen A, Kraemer WJ, Häkkinen A, Valkeinen H, Alen M (2001) Selective muscle hypertrophy, changes in EMG and force, and serum hormones during strength training in older women. J Appl Physiol 91:569–580
Jeanplong F, Bass JJ, Smith HK, Kirk SP, Kambadur R, Sharma M, Oldham JM (2003) Prolonged underfeeding of sheep increases myostatin and myogenic regulatory factor myf-5 in skeletal muscle while IGF-I and myogenin are repressed. J Endocrinol 176:425–437
Kerksick CM, Rasmussen CJ, Lancaster SL, Magu B, Smith P, Melton C, Greenwood M, Almada AL, Earnest CP, Kreider RB (2006) The effects of protein and amino acid supplementation on performance and training adaptations during ten weeks of resistance training. J Strength Cond Res 20:643–653
Kim JS, Petrella JK, Cross JM, Bamman MM (2007) Load-mediated downregulation of myostatin mRNA is not sufficient to promote myofiber hypertrophy in humans: a cluster analysis. J Appl Physiol 103:1488–1495
Kraemer WJ, Adams K, Cafarelli E, Dudley GA, Dooly C, Feigenbaum MS, Fleck SJ, Franklin B, Fry AC, Hoffman JR, Newton RU, Potteiger J, Stone MH, Ratamess NA, Triplett-McBride T, American College of Sports Medicine (2002) American college of sports medicine position stand. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:364–380
Kuang S, Charge SB, Seale P, Huh M, Rudnicki MA (2006) Distinct roles for Pax7 and Pax3 in adult regenerative myogenesis. J Cell Biol 172:103–113
Lee SJ, McPherron AC (2001) Regulation of myostatin activity and muscle growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9306–9311
Liu W, Saint DA (2002) Validation of a quantitative method for real time PCR kinetics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294:347–353
Malumbres M, Ortega S, Barbacid M (2000) Genetic analysis of mammalian cyclin-dependent kinases and their inhibitors. Biol Chem 381:827–838
Mascher H, Tannerstedt J, Brink-Elfegoun T, Ekblom B, Gustafsson T, Blomstrand E (2008) Repeated resistance exercise training induces different changes in mRNA expression of MAFbx and MuRF-1 in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 294:E43–E51
McCroskery S, Thomas M, Maxwell L, Sharma M, Kambadur R (2003) Myostatin negatively regulates satellite cell activation and self-renewal. J Cell Biol 162:1135–1147
McPherron AC, Lawler AM, Lee SJ (1997) Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-beta superfamily member. Nature 387:83–90
Nagasawa T, Hirano J, Yoshizawa F, Nishizawa N (1998) Myofibrillar protein catabolism is rapidly suppressed following protein feeding. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1932–1937
Nakazato K, Hirose T, Song H (2006) Increased myostatin synthesis in rat gastrocnemius muscles under high-protein diet. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 16:153–165
Ohkubo Y, Kishimoto T, Nakata T, Yasuda H, Endo T (1994) SV40 large T antigen reinduces the cell cycle in terminally differentiated myotubes through inducing Cdk2, Cdc2, and their partner cyclins. Exp Cell Res 214:270–278
Olsen S, Aagaard P, Kadi F, Tufekovic G, Verney J, Olesen JL, Suetta C, Kjaer M (2006) Creatine supplementation augments the increase in satellite cell and myonuclei number in human skeletal muscle induced by strength training. J Physiol 573:525–534
Paddon-Jones D, Sheffield-Moore M, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR, Ferrando AA (2005) Exogenous amino acids stimulate human muscle anabolism without interfering with the response to mixed meal ingestion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288:E761–E767
Reeves ND, Maganaris CN, Narici MV (2004) Ultrasonographic assessment of human skeletal muscle size. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:116–118
Rios R, Carneiro I, Arce VM, Devesa J (2002) Myostatin is an inhibitor of myogenic differentiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C993–C999
Sedliak M, Finni T, Cheng S, Haikarainen T, Häkkinen K (2007) Diurnal variation in maximal and submaximal strength, power and neural activation of leg extensors in men: multiple sampling across two consecutive days. Int J Sports Med 29(3):217–224
Thalacker-Mercer AE, Fleet JC, Craig BA, Carnell NS, Campbell WW (2007) Inadequate protein intake affects skeletal muscle transcript profiles in older humans. Am J Clin Nutr 85:1344–1352
Tipton KD, Wolfe RR (2001) Exercise, protein metabolism, and muscle growth. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 11:109–132
Tipton KD, Elliott TA, Cree MG, Aarsland AA, Sanford AP, Wolfe RR (2007) Stimulation of net muscle protein synthesis by whey protein ingestion before and after exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E71–E76
Vissing K, Andersen JL, Schjerling P (2005) Are exercise-induced genes induced by exercise? FASEB J 19:94–96
Wagner KR (2005) Muscle regeneration through myostatin inhibition. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17:720–724
Wernbom M, Augustsson J, Thomee R (2007) The influence of frequency, intensity, volume and mode of strength training on whole muscle cross-sectional area in humans. Sports Med 37:225–264
Wilkinson SB, Tarnopolsky MA, Macdonald MJ, Macdonald JR, Armstrong D, Phillips SM (2007) Consumption of fluid skim milk promotes greater muscle protein accretion after resistance exercise than does consumption of an isonitrogenous and isoenergetic soy-protein beverage. Am J Clin Nutr 85:1031–1040
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Hanna Salmijärvi, Marja Katajavuori, Liisa Kiviluoto, Marko Haverinen, Mikko Pietikäinen, Hermanni Oksanen, Tuomas Kaasalainen, Tuovi Nykänen, Risto Puurtinen, and Aila Ollikainen for their help in data collection and analysis. We also thank the very dedicated group of subjects who made this project possible. The Finnish Ministry of Education and the Ellen and Artturi Nyyssönen Foundation (Juha Hulmi personal grant) supported this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hulmi, J.J., Kovanen, V., Selänne, H. et al. Acute and long-term effects of resistance exercise with or without protein ingestion on muscle hypertrophy and gene expression. Amino Acids 37, 297–308 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0150-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0150-6