Abstract
Objectives. To assess the effect of propofol on the change in airway pressure produced by diaphragmatic contraction.
Design and setting. Prospective, controlled study in patients anaesthetised with propofol in a university hospital.
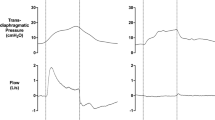
Patients and methods. We stimulated the phrenic nerves before and immediately after induction of anaesthesia in 11 subjects, using a pair of 43-mm mean diameter double magnetic coils and measured the change in airway pressure at the mouth (TwPmo) produced by the resulting diaphragmatic contraction. Supramaximality of stimulation was confirmed with electromyogram and pressure measurements. We recorded the change in Resting End Expiratory Position (REEP) using a spirometer. We applied an approximate correction for the effect of lung volume on the amplitude of twitch pressure produced by diaphragmatic contraction.
Intervention. Following the initial stimulations, the patients were anaesthetised with a propofol infusion. Once stable, repeat measurements were made.
Measurements and results. Following induction, REEP fell by mean 0.3 l standard deviation (SD) 0.2 l. TwPmo fell by mean 14.2% SD 14.0% (P=0.01), mean 22.3% SD 11.7% corrected (P<0.001). Twitch transdiaphragmatic pressure fell by 18.1% and 20.0% (25.8% and 27.7% corrected) in two further subjects studied with oesophageal and gastric balloon catheters.
Conclusion.Propofol does reduce the effectiveness with which diaphragmatic contraction produces changes of pressure in the airway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaw, I., Mills, G. & Turnbull, D. The effect of propofol on airway pressures generated by magnetic stimulation of the phrenic nerves. Intensive Care Med 28, 891–897 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1347-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1347-x