Summary
The present study provides light and electron microscopical evidence of Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide — (VIP) like immunoreactive nerves in human lower respiratory tract. Peroxidase antiperoxidase (PAP) technique was used to localize VIP-like immunoreactivity light microscopically and ultrastructurally.
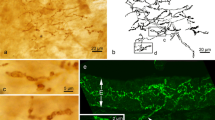
Under light microscopy, VIP-like immunoreactive nerves were observed in the smooth muscle layer of secondary bronchi to small bronchioli, and in bronchial glands. In addition, positive immunoreactive nervous network to VIP was found around nerve cell bodies in small microganglia. The bronchial epithelium of airway tract did not receive any VIP positive nerve fibers. Ultrastructurally VIP-like positive immunoreaction was localized in large granular vesicles ranging from 90 to 210 nm. Usually VIP-like positive immunoreactive nerve profiles contained several immunoreactive large vesicles (100–210). However, nerve profiles containing only a few positive large vesicles (80–150) were also observed. Under electron microscopy VIP-positive nerve profiles corresponded ultrastructurally to nerve profiles containing large granular vesicles observed in conventional electronmicroscopy.
The present study provides new information about the innervation of human lower airway tract and widens the concept of their functional regulation on the anatomical basis reported here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes PJ (1984) The third nervous system in the lung: physiology and clinical perspectives. Thorax 39:561–567
Baumgarten HG, Holstein AF, Owman C (1970) Auerbachs plexus of mammals and man: Electron microscopic identification of three different types of neuronal processes in myenteric ganglia of the large intestine from rhesus monkeys, guinea-pigs and man. J Zellforsch 106:376–397
Costa M, Furness JB, Buffa R, Said SI (1980) Distribution of enteric nerve cell bodies and axons showing immunoreactivity for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the guinea-pig intestine. Neuroscience 5:587–596
Dey RD, Shannon Jr, WA, Said S (1981) Localization of VIP-immunoreactive nerves in airways and pulmonary vessels of dogs, cats, and human subjects. Cell Tissue Res 220:231–238
Fahrenkrug J, Haglund U, Jodal M, Lundgren O, Olbe L, de Muckadell OB (1978) Nervous release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the gastrointestinal tract of cats: a possible physiological implications. J Physiol (Lond) 284:291–305
Fuxe K, Hökfelt T, Said SI, Mutt V (1977) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and the nervous system: Immunohistochemical evidence for localization in central and peripheral neurons, particularly intracortical neurons of the cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 5:241–246
Gibbins IL (1982) Lack of correlation between ultrastructural and pharmacological types of non-adrenergic autonomic nerves. Cell Tissue Res 221:551–581
Hökfelt T, Elfvin L-G, Schultzberg M, Fuxe K, Said SI, Mutt V, Goldstein M (1977) Immunohistochemical evidence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing neurons and nerve fibers in sympathetic ganglia. Neuroscience 2:885–896
Johansson O, Lundberg JM (1981) Ultrastructural localization of VIP-like immunoreactivity in large dense-core vesicles or “cholinergic-type” nerve terminals in rat exocrine glands. Neuroscience 6(5):847–862
Laitinen A, Partanen M, Hervonen A, Laitinen LA (1985) Electron microscopic study on the innervation of human lower respiratory tract. Evidence of adrenergic nerves. Eur J Respir Dis (in press)
Larsson L-I (1977) Ultrastructural localization of a new neuronal peptide (VIP). Histochemistry 54:173–176
Larsson L-I, Fahrenkrug J, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O, Sundler I, Håkanson R, Rehfeld JF (1976) Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to central and peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:3197–3200
Lorén I, Emson PC, Fahrenkurg J, Björklund A, Alumets J, Håkanson R, Sendler F (1979) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat and mouse brain. Neuroscience 4:1953–1976
Lundberg JM, Hökfelt T, Kewenter J, Petersson G, Ahlman H, Towin R, Dahlström A, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Uvnäs-Wallensten K, Said SI (1979) Substance P-, VIP-, and enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the human vagus nerve. Gastroenterology 77:468–471
Matsuzaki Y, Hamasaki Y, Said SI (1980) Vasoactive intestinal peptide: A possible transmitter of nonadrenergic relaxation of guinea pig airways. Science 210:1252–1253
Partanen M, Laitinen A, Hervonen A, Toivanen M, Laitinen LA (1982) Catecholamine- and acetylcholinesterase-containing nerves in human lower respiratory tract. Histochemistry 76:175–188
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electronmicroscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Richardson JB (1979) Nerve supply to the lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis 119:785–802
Richardson J, Béland J (1976) Nonadrenergic inhibitory nervous system in human airways. J Appl Physiol 41:764–771
Said SI, Rosenberg RN (1976) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: Abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science 192:907–908
Said SL, Giachetti A, Nicosia S (1980) Possible functions of VIP as a neural peptide. In: Costa E, Trabucchi M (eds) Neural peptides and neuronal communications. Raven Press, New York, pp 75–82
Said SI, Kitamura S, Yoshida T, Preskitt J, Holden LD (1974) Humoral control of airways. Ann NY Acad Sci 221:103–114
Simonsson BG, Svedmyr M, Skoogh BE, Andersson R, Bergh NP (1972) In vivo and in vitro studies on alpha-receptors in human airway. Potentiation with bacterial endotoxine. Scand J Respir Dis 53:227–236
Sternberger LA (1974) Immunocytochemistry. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Uddman R, Aluments J, Densert O, Håkanson R, Sundler F (1978) Occurrence and distribution of VIP nerves in the nasal mucosa and tracheobronchial male. Acta Oto-Laryngol 86:443–448
Uddman R, Sundler F (1979) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide nerves in human upper respiratory tract. Acta Oto-Laryngol 41:221–226
Vaalasti A, Linnoila I, Hervonen A (1980) Immunohistochemical demonstration of VIP, |Met−5| — and |Leu5| — enkepahlin immunoreactive nerve fibers in the human prostate and seminal vesicles. Histochemistry 66:89–98
Wharton I, Polar JM, Probert L, DeMey J, McGregor GP, Bryant MG, Bloom SK (1981) Peptide containing nerves in the ureter of the guinea-pig and CAT. Neuroscience 6(15):969–982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laitinen, A., Partanen, M., Hervonen, A. et al. VIP like immunoreactive nerves in human respiratory tract. Histochemistry 82, 313–319 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00494059
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00494059